Page List

Published in 2016 by Rosen Publishing
29 East 21st Street, New York, NY 10010
Copyright 2016 Alix Wood Books
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form without permission in writing from the publisher, except by a reviewer.
Editor: Eloise Macgregor
Designer: Alix Wood
Consultant: Kevin E. Yates, Fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society
Photo Credits: Cover, 1, 16, 24 Shutterstock; 4, 5, 6-7, 8, 22 Dollar Photo Club; 7 inset, 10, 11, 12, 13, 17, 18, 20, 21, 23 NASA; 12 Gregory H. Revera; 14 Alana Sise; 19 European Southern Observatory; 23 Eduemoni; 26 Jonathan Zdziarski; 27 iStock
Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Wood, Alix.
Why do we have night and day? / by Alix Wood.
p. cm. (The galaxy guides)
Includes index.
ISBN 978-1-4994-0850-8 (pbk.)
ISBN 978-1-4994-0849-2 (6 pack)
ISBN 978-1-4994-0848-5 (library binding)
1. Day Juvenile literature. 2. Night Juvenile literature. 3. Earth (Planet) Rotation Juvenile literature. 4. Sun Juvenile literature. 5. Moon Juvenile literature. I. Wood, Alix. II. Title.
QB633.W66 2016
525.35d23
Manufactured in the United States of America
CPSIA Compliance Information: Batch #: WS15PK
For Further Information contact Rosen Publishing, New York, New York at 1-800-237-9932
Contents
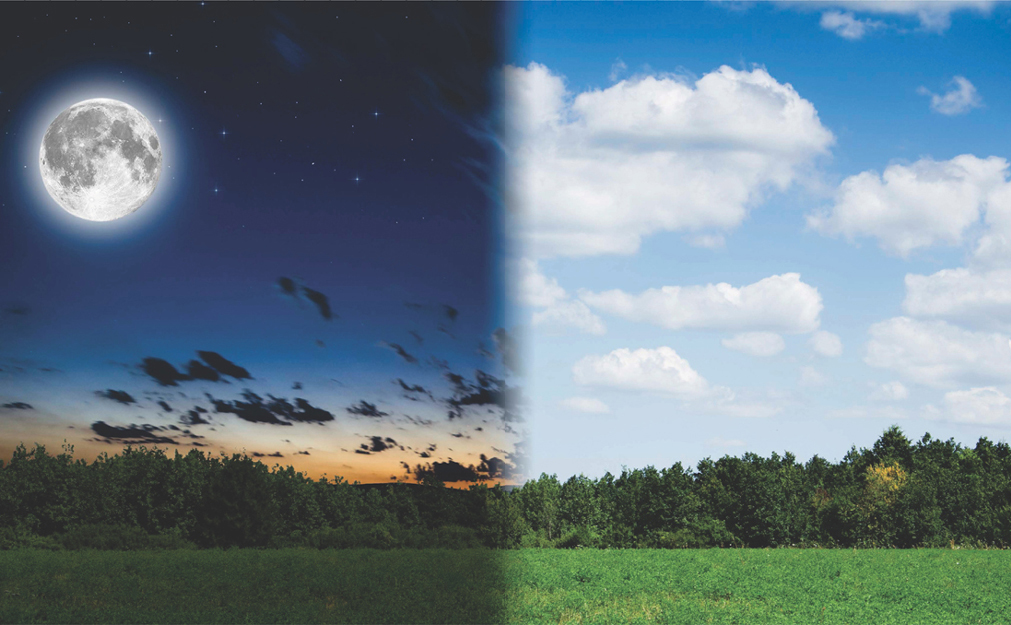
H ave you ever wondered why Earth has nights and days? When you look up at the sky at night it is very different from the sky during the day. The main difference is that it is dark. Why?
The sky is dark because the Sun is no longer visible. We can see the Moon and the stars on a clear night. They light up the dark a little. The Sun is a star too. It is much closer to Earth than other stars. Because it is closer it lights up our sky.
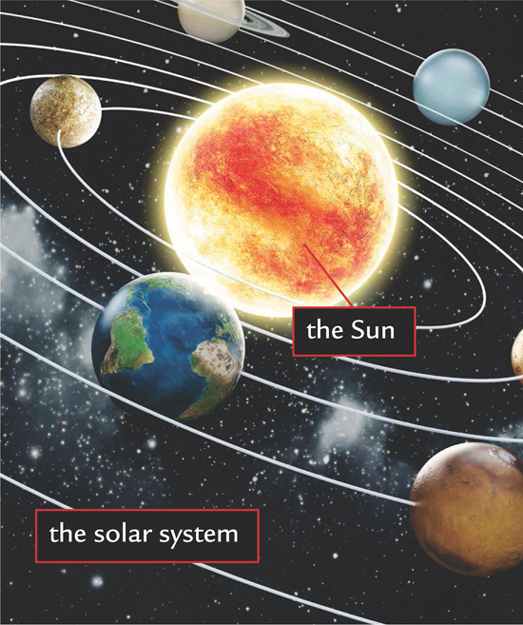
Sol is the Latin name for the Sun. We get the name solar system from the word. The Sun is not just important because it gives us light. The Sun is the center of our solar system.

FACT FILE
What Is the Solar System?
Our solar system has the Sun at its center. Planets, moons, comets, and asteroids all move around the Sun. Objects in space attract other objects to them. This attraction is called gravity. Objects with the most mass have the strongest pull. Objects such as Earth are pulled toward the Sun because the Sun has a large mass. Meanwhile, other forces try to pull objects away from the Sun. The forces balance each other out, so Earth forever circles the Sun.
The journey around an object in space is called an orbit. How does an orbit happen? Imagine a large cannon on top of an imaginary giant mountain. If the cannon fires a cannonball using low power (A), the ball will curve down and hit Earth. Increase the power (B) and the ball will go further but still hit Earth. If you fire the ball with just the right force (C), as Earth is round, the ground curves away from the ball, so the ball follows a path around Earth. Earths gravity keeps the ball from going into space.

T he Sun is a star. It looks much larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer to Earth. The Sun is very large. It is over 1 million times bigger than Earth!
The Sun is a ball of burning gases. It is mainly made of a gas called hydrogen. In the center, the temperature is around 27 million degrees Fahrenheit (15 million degrees Celsius)! Even the temperature at its surface is more than 20 times hotter than a household oven at its highest setting.


Hands-On Science
Make a Simple Pinhole Camera
Never look directly at the Sun as it can damage your eyes. Make this pinhole camera to view the Sun safely.
You will need: 2 sheets of stiff white paper, a pin, a sunny day
Using the pin, punch a hole in the center of one piece of paper. Place your second piece of paper on the ground. Stand with the sun behind you and hold the paper with the hole up. Move it until you see the Sun shine through the hole. Move the paper on the floor so that the Sun image lands on it. What you are seeing is not just a dot of light coming through the hole, but an actual image of the Sun!
FACT FILE
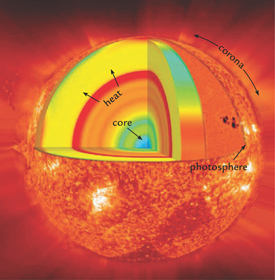
The Suns Layers
The core in the center of the Sun produces the Suns energy. The layers around the center carry energy outward. The outer layer is called the photosphere. Around the outside is the corona, which means crown in Latin. The corona is faint, so you cant usually see it. Energy from the core typically takes 150,000 years to reach the photosphere, so the light you see today was produced in the Stone Age! It takes another eight and a half minutes for the light from the photosphere to reach Earth.
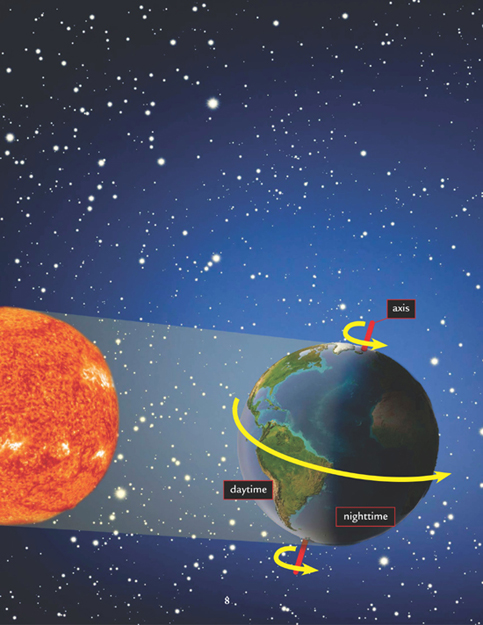
T he Sun doesnt go anywhere, it is always in the same place. Even though you dont feel it, the Earth is spinning all the time. Earth takes 24 hours to completely spin around on its axis. When the part of Earth we live on turns away from the Sun we have nighttime. For people on the other side of the Earth it is daytime.

FACT FILE
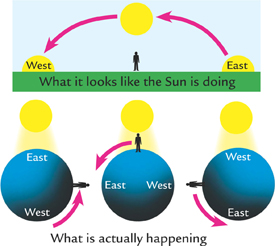
Why Does the Sun Rise in the East and Set in the West?
When viewed from the North Pole the Earth spins counterclockwise. As Earth turns toward the Sun and begins to enter its light, it appears as if the sun rises in the east. In fact the Sun stays still and we spin around to face it. As Earth begins to turn away from the Suns light, the Sun appears to set in the west.

Hands-On Science
Make a Simple Model Sun and Earth
You will need: a ball, a flashlight, and a small sticker
Place the sticker on the ball. The sticker represents where you live on Earth. Turn the flashlight on, place it about seven paces away, shining on the ball. Now, slowly spin the ball so your sticker is lit up by the flashlight. This is you on Earth during the day. Keep spinning the ball until the sticker is not being lit up by the flashlight. This is you on Earth at night. The flashlight hasnt moved, you have spun so you can no longer see the light.