This edition published in 2014 by:
The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc.
29 East 21st Street
New York, NY 10010
Additional end matter copyright 2014 by The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form without permission in writing from the publisher, except by a reviewer.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Wanjie, Anne.
The basics of ecology/Anne Wanjie.1st ed.New York: Rosen, 2014
p. cm.(Core concepts)
Includes bibliographical references and index.
ISBN: 978-1-4777-0551-3 (Library Binding)
1. EcologyJuvenile literature. 2. Habitat (EcologyJuvenile literature. I. Title.
QH541.14 .W36 2014
Manufactured in the United States of America
CPSIA Compliance Information: Batch #S13YA: For further information, contact Rosen Publishing, New York, New York, at 1-800-237-9932.
2004 Brown Bear Books Ltd.
CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1: THE BASICS OF ECOLOGY
CHAPTER 2: NATURES CYCLES
CHAPTER 3: THE EARTHS CLIMATE
CHAPTER 4: WHAT ARE ECOSYSTEMS?
CHAPTER 5: WATER ECOSYSTEMS
CHAPTER 6: THE IMPACT OF HUMANS
CHAPTER 7: THE EFFECTS OF CONSERVATION
CHAPTER 8: BIOGRAPHY: ALEXANDER VON HUMBOLDT
GLOSSARY
FOR MORE INFORMATION
FOR FURTHER READING
INDEX
CHAPTER ONE
THE BASICS OF ECOLOGY
Ecology is about the pattern of natureit is the study of the interactions among living organisms and their environment.
E very living thing depends on other things for its survival. House sparrows living in a park have to find seeds to eat. The seeds come from plants that must find places to grow. Sparrows feed on insects, too, and the insects need plants to eat. Sparrows also need air to breathe, water to drink, and places to lay eggs. So each sparrow is at the center of a web of relationships involving other living things and its surroundings, or environment. Ecology is the science that studies these types of relationships. Instead of concentrating only on a sparrow, ecologists study how it interacts with other organisms and its environment.
A gypsy moth caterpillar. Many caterpillars eat leaves, and many birds then eat the caterpillars. This link between leaf, caterpillar, and bird forms a food chain.
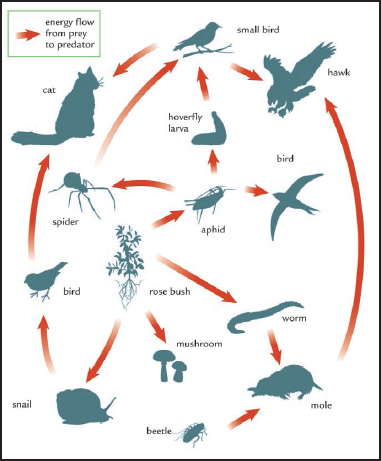
A FOOD WEB DIAGRAM
This diagram shows a food web based on the plants and trees in a small forest. A food web is much more complicated than a simple food chain, in which each plant or animal provides food for just one other animal. The plants provide food for many insects, worms, and other small animals, which in turn provide food for larger animals, such as cats, moles, and many different types of birds.
WHAT ARE FOOD CHAINS AND WEBS?
One of the most basic ideas in ecology is the food chain. Green plants make food from water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide (in the air) by a process called photosynthesis. Animals cannot do this, so they must eat other living organisms to get their food.
Caterpillars eat leaves and turn them into caterpillar flesh. In a simple food chain other animals, such as small birds, eat the caterpillars, and the birds themselves may be eaten by cats. However, the caterpillars are also eaten by other insects. Thus most food chains are not so simple. Several linked chains make up a food web.
HABITATS AND NICHES
All animals, plants, and other living organisms struggle to survive. Many organisms die, and only the best adapted live long enough to reproduce. This process is called natural selection, the basis of evolution. What does fittest mean? That depends on the environment. A goldfish can survive very well in a pond, but it would die in a desert. A lizard can live in a desert, but it would freeze in the Arctic. Even if an animal or plant survives, it may not do as well as its neighbors. So over time it is crowded out. Every living organism has characteristics, or adaptations, that make it suited to its environment. The place in which an animal or plant lives is called its habitat.
A habitat could be a rocky seashore or a tropical forest. Such places offer all kinds of ways in which animals and plants can live. Every species of living organism has its own special way of surviving in its habitat, and that is called its niche. For example, some birds specialize in eating large fruits, while others feed on small insects. The two types of birds occupy different niches.
STUDY A FOOD WEB
Make a list of all the animals that live in your backyard or in a local park. Remember to include insects and other mini-beasts, and all the animals with fur, feathers, or scales. Check out the animals in a book to see what they eat. Then try to arrange them in a food web like the one shown on page 7. It might get complicated!
EFFECTS ON PLANTS AND ANIMALS
By figuring out the relationships between plants and animals and their environment, an ecologist can try to predict what will happen if one part of the pattern is taken away. So if there is a plan to drain a mosquito-infested swamp, an ecologist can find out what other animals live in the swamp and how they might be affected. It may turn out that draining the swamp could destroy some rare and beautiful waterbirds.
Alligators living in a swamp could be affected if other animals or plants were removed from their habitat. Every organism plays an important role in an ecosystem.
MAKING A COMMUNITY
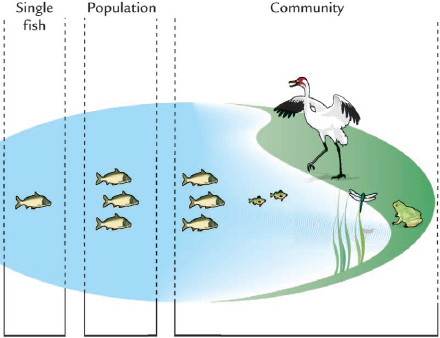
A niche can be occupied by just one species. A small lake may have only enough food for one big predatory fish, such as a pike, but a large lake contains enough food for several pike, and they form a population. All the animals in a population are of the same species and occupy the same ecological niche. They share their lives with other populations of different animals and plants, and together these interacting populations form a community. So the fish, insects, birds, and plants in a lake make up a community.
POPULATIONS AND COMMUNITIES
MAKE YOUR OWN ECOSYSTEM
Create your own mini-ecosystem in a big glass jar by collecting some water from a pond in summer. Tell an adult before you go, and take care not to fall in! Fill your jar about three-quarters full. Then add some mud taken from the bottom of the pond.
A layer one to two fingers thick should be enough. Add some water plants to produce oxygen. You can get them from the pond or at pet stores. Put your jar in a cool window, and wait for a while. The water will clear, and you may be surprised at what you can see. The plants and animals will keep each other healthy for a period of time.
WHAT ARE ECOSYSTEMS?
An ecological community can contain plants, animals, fungi, and micro-organisms, such as bacteria. These living organisms share an environment that has nonliving elements, such as the climate (the typical weather experienced over a year), the soil, and the location, which might be an exposed, rocky headland or a sheltered, sandy beach. A river might be slow and muddy or swift and sparkling. The possibilities are endless.