History of the Powered Parachute
As early as the 12th century, the Chinese used an umbrella-shape parachute design for recreation. About 300 years later, Leonardo da Vinci blueprinted a pyramid-shaped parachute. In the late 18th century, man jumped from towers and balloons with a parachute. The first parachute jump from an airplane occurred in 1912.
After World War II, sport jumping became a recreational activity. The sport started with round parachutes, ranging in size from 20 to 30 feet in diameter. Parachutes evolved into a steerable, gliding wing smaller than todays rectangular ram-air powered parachute (PPC) wing which is approximately 38 feet wide.
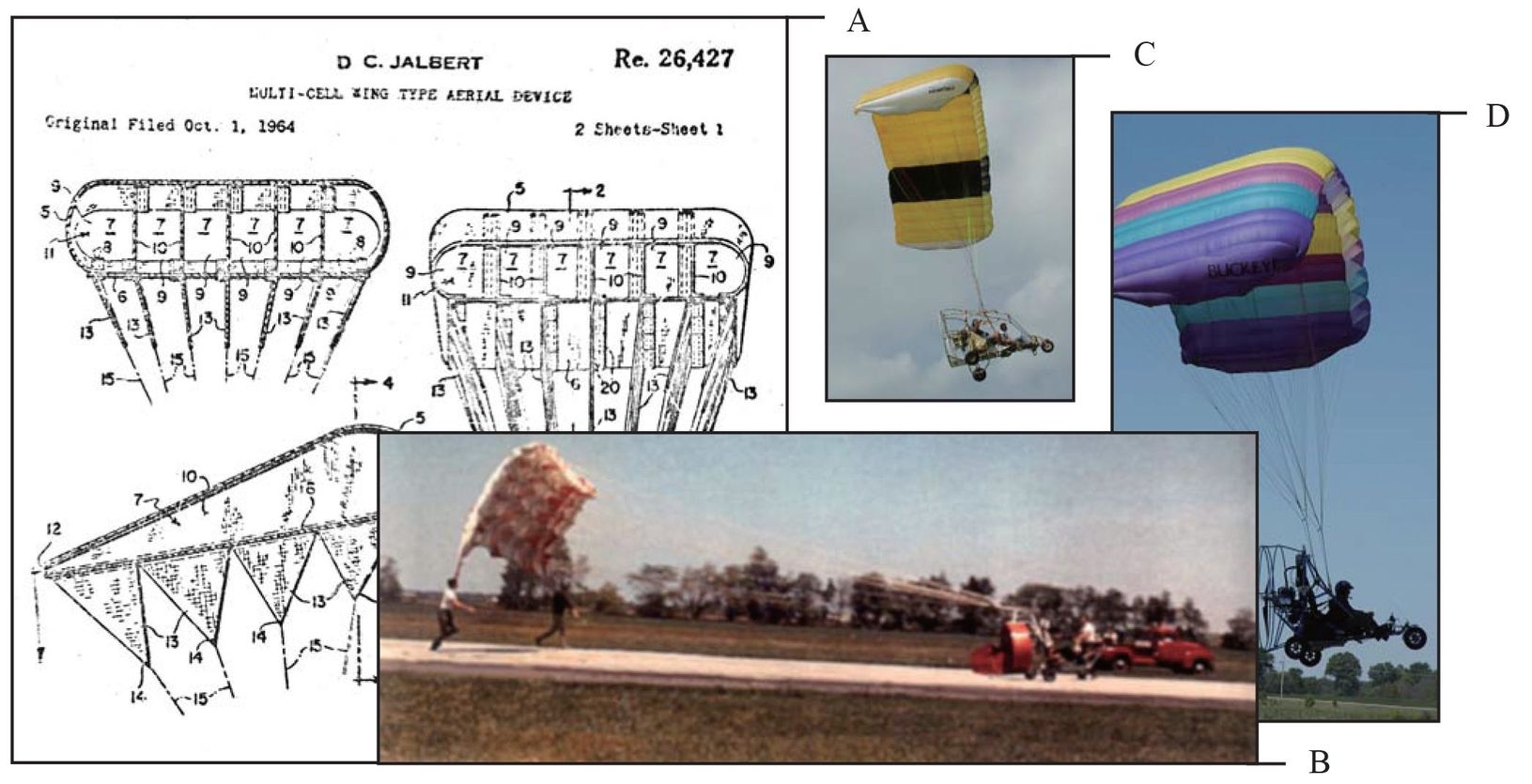
On October 1, 1964, Domina C. Jalbert applied for a patent for his Multi-Cell Wing named Parafoil (also known as a ram-air wing), which was a new parachute design. His ideas were registered as a U.S. patent on November 15,1966. [ B] Farrand was the first person to put an engine on a ram-air inflated parachute wing, starting the evolution of the powered parachute with the Irish Flyer. This wing evolved into todays modern powered parachute canopies, which include rectangular, elliptical, semi-elliptical, and hybrid wings.
. The evolution of powered parachutes.
The United States (U.S.) government had a number of test programs that used the square parachute as a means to glide spacecraft back to earth or glide payloads dropped out of airplanes to a specific location.
Two-place powered parachutes have years of testing, development, and evolution. Training exemptions to Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations (14 CFR) part 103, Ultralight Vehicles, permitted individuals to give instruction in two-place ultralight vehicles, instead of being restricted to vehicles intended for single occupants. [ D]
Powered Parachute Terms
Different terms have been used throughout the powered parachute community. [] The terms standardized throughout this book are as follows:
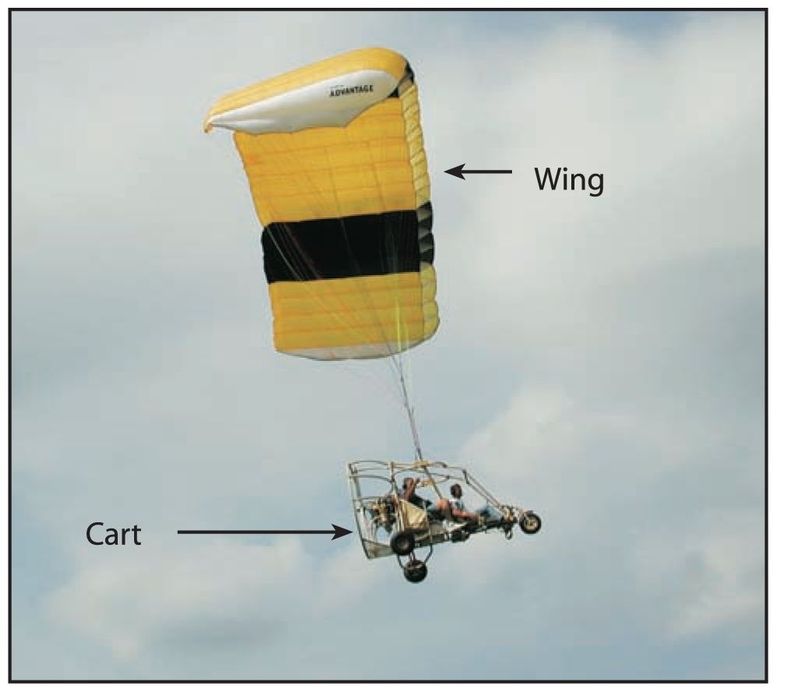
- Powered Parachute The complete aircraft.
- Cart The engine and seats, attached by a structure to wheels; may also be referred to as the fuselage, cockpit, chaise, or airframe.
- Wing Typically a ram-air inflated and pressurized wing including lines that attach to the cart. The wing is not in position to fly until the aircraft is in motion; when not inflated, referred to as a parachute or chute.
. Two-place powered parachute aircraft.
Introduction to the Powered Parachute
The powered parachute is a category of aircraft that flies in a manner unique among light-sport aircraft. Three significant differences separate the PPC from other types of light sport aircraft (LSA): []
- The wing must be inflated and pressurized by ram air prior to each takeoff.
- The aircraft uses a pendulum configuration, where the cart hangs about 20 feet below the wing, connected via flexible suspension lines.
- The wing is at a relatively fixed angle with the suspension lines and flies at a relatively constant speed. Other aircraft categories allow pilots to change the speed of the aircraft, but the powered parachute airspeed remains within a very small range.
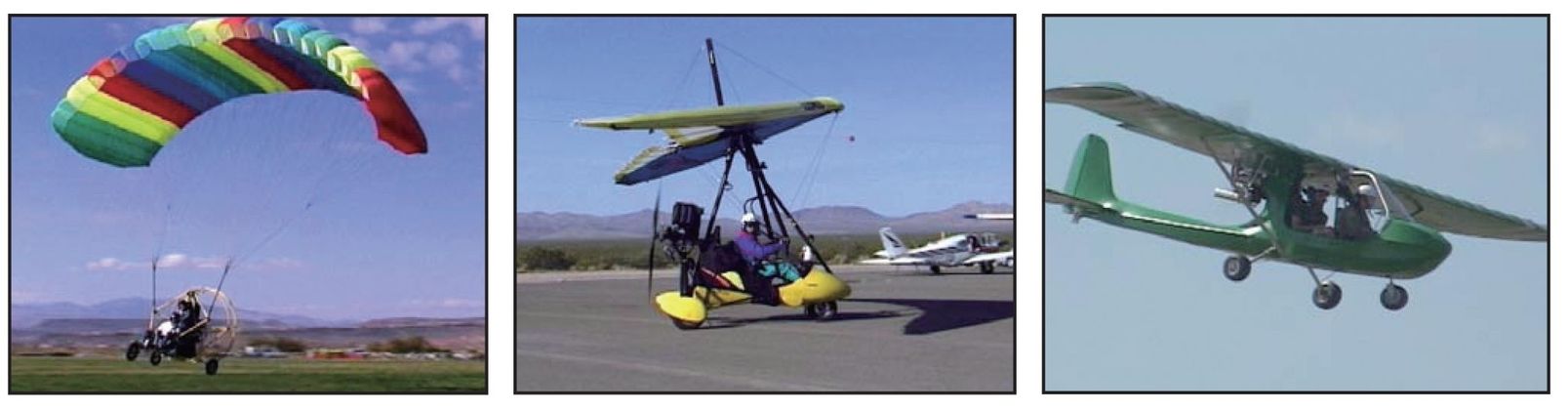
. The powered parachute has some unique operating characteristics as compared to other light-sport aircraft. Left, PPC with inflated wing; middle, weight-shift control aircraft; right, fixed-wing LSA.
A powered parachute can be a single place ultralight flying vehicle, a single place light-sport aircraft, or a multi-place light-sport aircraft. The common acronyms for this vehicle/aircraft are PPC (powered parachute), PPCL (powered parachute land) or PPCS (powered parachute sea).
A light-sport aircraft PPC used for sport and private flying must be registered with an FAA N-number, have an airworthiness certificate, a pilots operating handbook (POH), and/or limitations with a weight and balance document aboard. The aircraft must be maintained properly by the aircraft owner or other qualified personnel and have the aircraft logbooks available for inspection. Dual controls are required in the aircraft for training.
Powered Parachute Pilot Certificate Eligibility Requirements
You may not act as pilot in command (PIC) of a light-sport aircraft powered parachute unless you hold a pilot certificate with a powered parachute rating issued by the FAA. At this time the only pilot certificates with powered parachute ratings are Student, Sport and Private. The FAA is empowered by the U.S. Congress to promote aviation safety by prescribing safety standards for pilots and the other civil aviation programs. The Code of Federal Regulations (CFRs), formerly referred to as Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs), are one of the primary means of conveying these safety standards.
Title 14 CFR, part 61 specifies the requirements to earn a pilot certificate. This regulation also states the pilot applicant must be able to read, speak, write, and understand the English language. The FAA Practical Test Standards (PTS) establish the standards for the knowledge and skills necessary for the issuance of a pilot certificate. [] You should reference both these documents to understand the knowledge, skills and experience required to obtain a pilot certificate to fly a powered parachute.
. The PTS is used to test the knowledge and skill of a pilot applicant.
Pilot applicants must have a valid U.S. drivers license or a current third-class medical certificate issued under 14 CFR part 67. If you use your valid drivers license to exercise the privileges of a Sport Pilot certificate, then you must also adhere to any restrictions on that drivers license. You must hold a current third-class medical certificate to exercise the privileges of a Private Pilot certificate.
The process of learning to fly includes a combination of ground training (to include successful completion of the FAA Knowledge Exam) and flight training to include dual flights with a certified flight instructor (CFI), as well as solo flights under the supervision of your CFI.
To be eligible to fly solo in a PPC, you must be at least 16 years of age and demonstrate satisfactory aeronautical knowledge on a test developed by your instructor. You must have received and logged flight training for the maneuvers and procedures in 14 CFR part 61 for the PPC, as well as demonstrated satisfactory proficiency and safety. Only after all of these requirements are met can your instructor endorse your student pilot certificate and logbook for solo flight.
Once you obtain the required aeronautical knowledge and experience required by 14 CFR part 61, your flight instructor will endorse you to take a practical test (often called a checkride) with a sport pilot examiner (SPE) or an FAA inspector. After youve demonstrated satisfactory aeronautical knowledge and skill in the Areas of Operation and Tasks outlined in the PTS, this examiner or inspector will issue your temporary (paper) pilot certificate. You will receive a plastic certificate in the mail once the results of the practical test are received by the FAA Registration branch.