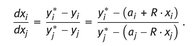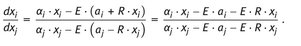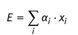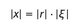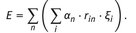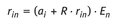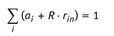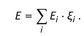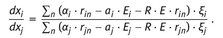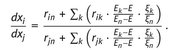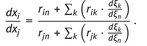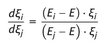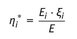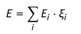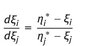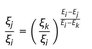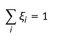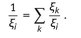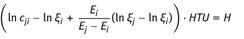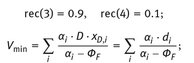A.1 Coordinate transformation
The basic differential equation for the concentration profiles in distillation arrives from and division follows
Insertion of the equilibrium yields
The denominator in
transforms on the basis of the matrix
to
Replacing (see )
and taking into account
yields
Replacing the | x | on the right side of gives
With follows
Differentiation of the yields
A comparison of and (A.8) finally results in
or by defining an equilibrium equation in analogy to
with
results in
with the solution in analogy to
with the constant j determined by the initial conditions of the transformed concentrations ||.
For a polynary mixture of n components there are ( n 1) independent equations of the form (A.14). The concentrations || again (see ) are calculated using the mass balance equation
in the form
The concentration profiles i = f ( H ) follow from
in analogy to .
Application of the matrix finally yields the concentrations | x |.
In the same way as discussed in may be visualized as distillation lines within the distillation space in form of a polyhedron formed by the nodes and the separation lines or separation planes for a ternary or a polynary mixture, respectively.
A.2 Distillation of an ideal five-component mixture (King [17])
A.2.1 Conceptual design
Recovery of the key components: rec i = x D,i / x F ,i D / F = d i / f i ;
The unknown variables d 1 , d 2 , d 5 and V min are determined by solving the four as a function of the Number of Transfer Units.
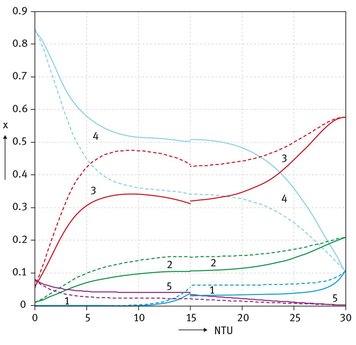
The key components 3 and 4 intersect at the 15th NTU in good agreement with the feed conditions and the feed should be introduced at this position, therefore. Since the method of Shiras indicated that the lowest and the highest boiling component are not distributing, the calculation is extremely sensitive to the chosen concentration of the lowest boiling component in the bottom product and the highest boiling component in the distillate, respectively. The product concentrations applied in are:
. Concentration profiles of the liquid () and the vapour (- -) at limiting flow conditions vs. the number of transfer units ( R = R min = 0.5842)
The dimensions of the column follow from a cost optimisation based on a calculation of the Number of Transfer Un its vs. the reflux ratio. Since the investment costs decrease with an increasing reflux ratio and the energy costs increase with a decreasing reflux ratio, the total costs must show a minimum vs. the reflux ratio [57].
A.2.2 Geometry of the distillation column [17, 57]
Assuming an average height of a transfer unit ( HTU ) = 0.4 m results in a height of the column H = NTU HTU = 12.00 m with the feed introduced at a height of 6 m.
The diameter of the column follows from fluid dynamic and economic considerations based e.g. on the
- physical and chemical properties of the mixture,
- kind of internals like stages or packings,
- maximum permissible vapour and liquid load of the column,
- ease of operation in case of flow fluctuations,
- economic optimisation.
The final design of the column should be based on specific information given by the supplier of the internals.
Author
Professor
Dr.-Ing. Alfons Vogelpohl
Clausthal University of Technology
Institute for Separation and Process Technology
Leibnizstr. 15
38678 Clausthal-Zellerfeld
Germany
References
Forbes, R. J.: Of the Art of Distillation from the Beginnings up to the Death of Cellier Blumenthal , Copyright 1948 by E. J. Brill, Leiden, Holland
Underwood, A. J. V.: Distillation Art and Science, Chemistry and Industry , June 23 (1963)
Hausbrand, E.: Die Wirkungsweise der Rectificir- und Destillirapparate , Berlin (1893) cited in [1]
Sorel, E.: La rectification de Ialcool , Paris (1894) cited in [1]
Lewis, W. K., Trans. Am. Inst. Chem. Engrs. , 44 (1922) 329
Lord Rayleigh, Philos. Magazine , 4 (1902) 521