Appendix Illustrated Glossary of Photographic and Digital Terms
If you've turned to this portion of the book, there's probably a technical term you don't fully understand, or, perhaps, you'd like to see how related photographic concepts or techniques fit together. So, I've stuffed it with all the most common words you're likely to encounter when working with your digital camera and the photographs you create. This glossary includes most of the jargon included in this book, and some that is not within these pages, but which you'll frequently come across as you work. Most of the terms relate to digital cameras or photography, but I've sprinkled in a little information about image editing and photo reproduction.
16-bit images
So-called "48-bit" High Dynamic Range image files that contain 16 bits of information (65, 535 different tones) per channel, rather than the 8 bits per channel found in ordinary, 24-bit 16.8 million color images. Photoshop CS 2.0 has new HDR features that let you combine several images taken at different exposures to produce one extended-range image.
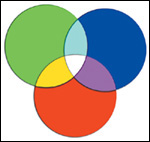
additive primary colors
The red, green, and blue hues which are used alone or in combinations to create all other colors you capture with a digital camera, view on a computer monitor, or work within an image-editing program like Photoshop. See also .
AE/AF lock
A control that lets you lock the current autoexposure and/or autofocus settings prior to taking a picture, freeing you from having to hold the shutter release partially depressed.
Figure A.1. The additive primary colors, red, green, and blue combine to make other colors, plus white.
airbrush
Originally developed as an artist's tool that sprays a fine mist of paint, the computer version of an airbrush is used both for illustration and retouching in most imageediting programs.
ambient lighting
Diffuse nondirectional lighting that doesn't appear to come from a specific source but, rather, bounces off walls, ceilings, and other objects in the scene when a picture is taken.
analog/digital converter
In digital imaging, the electronics built into a camera or scanner that convert the analog information captured by the sensor into digital bits that can be stored as an image bitmap. See also .
angle-of-view
The area of a scene that a lens can capture, determined by the focal length of the lens. Lenses with a shorter focal length have a wider angle-of-view than lenses with a longer focal length.
anti-alias
A process in image editing that smoothes the rough edges in images (called jaggies or staircasing) by creating partially transparent pixels along the boundaries that are merged into a smoother line by our eyes.
aperture-preferred
A camera setting that allows you to specify the lens opening or f-stop that you want to use, with the camera selecting the required shutter speed automatically based on its light-meter reading. See also .
aperture ring
A control on the barrel of many SLR lenses that allows setting the f-stop manually. Some lenses have the aperture set by the camera only, and lack this ring.
artifact
A type of noise in an image, or an unintentional image component produced in error by a digital camera or scanner during processing.
aspect ratio
The proportions of an image as printed, displayed on a monitor, or captured by a digital camera. An 8 x 10-inch or 16 x 20-inch photo each have a 4:5 aspect ratio. Your monitor set to 800 x 600, 1024 x 768, or 1600 x 1200 pixels has a 4:3 aspect ratio. When you change the aspect ratio of an image, you must crop out part of the image area, or create some blank space at top or sides.
autofocus
A camera setting that allows the camera to choose the correct focus distance for you, usually based on the contrast of an image (the image will be at maximum contrast when in sharp focus) or a mechanism such as an infrared sensor that measures the actual distance to the subject. Cameras can be set for single autofocus (the lens is not focused until the shutter release is partially depressed) or (the lens refocuses constantly as you frame and reframe the image).
Figure A.2. A dramatic view of an amusement park taken at the 70mm zoom setting (top) becomes even more dramatic at the 35mm wide-angle setting.

autofocus assist lamp
A light source built into a digital camera that provides extra illumination that the autofocus system can use to focus dimly lit subjects.
averaging meter
A light-measuring device that calculates exposure based on the overall brightness of the entire image area. Averaging tends to produce the best exposure when a scene is evenly lit or contains equal amounts of bright and dark areas that contain detail. Most digital cameras use much more sophisticated exposure measuring systems based in center-weighting, spot-reading, or calculating exposure from a matrix of many different picture areas. See also .
B (bulb)
A camera setting for making long exposures. Press down the shutter button and the shutter remains open until the shutter button is released. Bulb exposures can also be made using a camera's electronic remote control, or a cable release cord that fits to the camera. See also .
background
In photography, the background is the area behind your main subject of interest.
backlighting
A lighting effect produced when the main light source is located behind the subject. Backlighting can be used to create a silhouette effect, or to illuminate translucent objects. See also . Backlighting is also a technology for illuminating an LCD display from the rear, making it easier to view under high ambient lighting conditions.
balance
An image that has equal elements on all sides.
barrel distortion
A lens defect typically associated with wide-angle focal lengths that causes straight lines at the top or side edges of an image to bow outward into a barrel shape. See also .
beam splitter
A partially silvered mirror or prism that divides incoming light into two portions, usually to send most of the illumination to the viewfinder and part of it to an exposure meter or focusing mechanism.
bilevel image
An image that stores only black-and-white information, with no gray tones.
bit
A binary digit, either a 1 or a 0, used to measure the color depth (number of different colors) in an image. For example, a grayscale 8-bit scan may contain up to 256 different tones (28), while a 24-bit scan can contain 16.8 million different colors (224).
bitmap
A way of representing an image as rows and columns of values, with each picture element stored as one or more numbers that represent its brightness and color. In Photoshop parlance, a bitmap is a bilevel black/white-only image.
black
The color formed by the absence of reflected or transmitted light.
black point
The tonal level of an image where blacks begin to provide important image information, usually measured by using a histogram. When correcting an image with a digital camera that has an on-screen histogram, or within an image editor, you'll usually want to set the histogram's black point at the place where these tones exist.
Figure A.3. Backlighting produces a slight silhouette effect, and also serves to illuminate the translucent petals of this flower.

blend
















