1. Learning the Basics: A Whistle-Stop Tour of React
The journey of a thousand miles begins with one step.
Lao Tzu
Before you embark on your React Native journey, you must know a little bit about React(also known as ReactJS or React.js). In this chapter, you will quickly look at the core concepts of React, which will help you to work on React Native. React is different from most popular web technologies, and you will learn why as you move forward in this chapter. Its core concepts will really open up your mind to a new way of thinking if you have spent a considerable amount of time with traditional frameworks; this new way of thinking is sometimes called the React way of thinking . You may have heard the phrase write once, run everywhere but dismissed it as nearly impossible due to the proliferation of form factors (web, mobile, tablets). React has a different guiding principle: learn once, write anywhere. Wow, that seems quite different, and liberating. So youll begin this first chapter with a quick tour of React, which will help you get ready for React Native. If you have an elementary knowledge of React, you may skip this chapter and move on to .
React is a JavaScript library for creating user interfaces. It was built in a combined effort by Facebook and Instagram teams. React was first introduced to the world in 2013, and has taken it by storm, with community-wide acceptance and the benefit of being the technology at the heart of Facebook. According to official documentation, some consider React Native as the V in MVC because React Native makes no assumptions about rest of the technology stack used. You may use whatever technology you wish and you can create a single section of your app with React Native; you may also conveniently make changes in an already created application.
Why React?
But do we need another JavaScript library in a world full of js libraries and frameworks? There is hardly a month that goes by without a new js framework introduced.
React came into existence because its creators were faced with a significant problem: how to build large applications where data changes frequently. This problem occurs in almost any real-world application and React was created from the ground up to solve it. As you know, many popular frameworks are MVC or MV* but heres a point to be noted and re-iterated: React is not an MV* framework. Its a just a library for building composable user interfaces for UI components whose data changes over time. Unlike popular js frameworks, React does not use templates or HTML directives. React builds user interfaces by breaking the UI into many components. Thats itnothing else. This means that React uses the full features of programming languages to build and render views.
The following are some of the advantages of choosing React for your next project:
React uses JavaScript extensively : Traditionally the views in HTML are separated from the functionality in JavaScript. With React, components are created and there is one monolithic section where JavaScript has intimate knowledge of your HTML.
Extendable and maintainable : Components are formed by a unified markup with its view logic, which actually makes the UI easy to extend and maintain.
Virtual DOM : React applications are blazing fast. The credit for this goes to the virtual DOM and its diffing algorithm.
One-way data flow : Two-way data binding is a great idea, but in real-world applications it produces more pain than benefits. One of the common drawbacks with two-way data binding is that you have no idea how your data gets updated. With one-way data flow, things are simple: you know exactly where data is mutating, which makes it easier to maintain and test your app.
In order to have a strong foundation of a new technology, its necessary to understand its core concepts. In the next section, you will explore a few unique concepts of React, which will takes you one step closer to understanding this amazing technology.
Virtual DOM
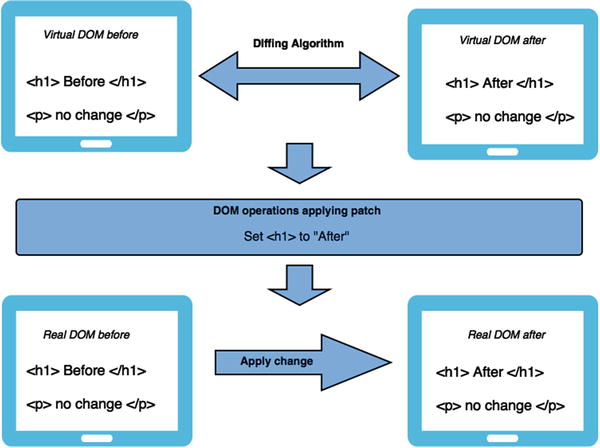
In all web applications one of the most expensive operations from which an app suffers is mutating the DOM. To solve this problem, React maintains a virtual representation of the DOM (as shown in Figure ), which is called Virtual DOM or VDOM. Along with a diffing algorithm, React Native is able to compute the delta against the actual DOM and only update the part of the DOM that is changed. The amount of change is therefore less, which leads to a blazing fast application. In the beginning of your application you might not see it, but as your project balloons to insane complexity (which usually happens in real-world apps) you will begin to see the benefits of a snappy experience for users.
Figure 1-1.
Virtual DOM and diffing algorithm operations
Manual DOM manipulation is messy, and keeping track of the previous state of the DOM is very hard. As shown in Figure , React solves this problem by keeping two copies of a virtual DOM. Next, a diffing algorithm is applied on these two virtual DOMs, which essentially checks for the changes that occurred and returns a stream of DOM operations. These DOM operations are then applied to the actual browser DOM.
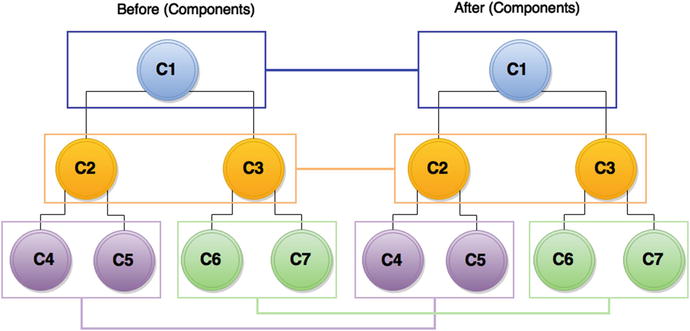
Lets now understand in terms of components how a virtual DOM works. In React, every component has a state; this state is likely observable. Whenever there is a change in state, React essentially knows that this change requires a re-render. So when the application state changes, it generates a new VTree; once again the diff algorithm shared the DOM paths for required changes, as shown in Figure . This results in keeping manual DOM manipulation to the minimum.
Figure 1-2.
Components with virtual DOM
This feature of virtual DOM is not just important but a killer feature of React. DOM access is super slow, and humbly speaking, the world has made it worse by hitting the DOM again and again in most of the applications. To make your application fast, you should touch the DOM as little as possible, and this is beautifully handled by the implementation of virtual DOM. You wont notice this with a small and trivial application, but once your app grows to having thousands of DOM elements all trying to get updated, React will not let your performance feel the impact.
One-Way Data Flow
React is primarily the V in a MVC pattern but before you dive into the idea of one-way data flow in React, you must understand the challenges of MVC frameworks. One of the biggest challenges of a MVC framework is managing the view. As you know, the view component of the MVC framework is mainly the DOM representation. It is simple when you write code that interacts with the DOM, but it is very complicated for the framework to handle various DOM manipulations.
Traditional MVC views generally encompass a lot of heavy UI, and as the data changes even for a tiny element, it eventually re-renders the app again, and the cycle continues. The reason for this is that typically most of these MVC frameworks follow two-way data binding (see Figure ).







![Mateusz Grzesiukiewicz [Mateusz Grzesiukiewicz] - Hands-On Design Patterns with React Native](/uploads/posts/book/119470/thumbs/mateusz-grzesiukiewicz-mateusz-grzesiukiewicz.jpg)
![Sagar Ganatra [Sagar Ganatra] - React Router Quick Start Guide: Routing in React Applications Made Easy](/uploads/posts/book/119450/thumbs/sagar-ganatra-sagar-ganatra-react-router-quick.jpg)