Part I
Location Services
- Chapter 1: Introducing the Android Location Service
- Chapter 2: Determining a Device's Current Location
- Chapter 3: Tracking Device Movement
- Chapter 4: Proximity Alerts
Chapter 1
Introducing the Android Location Service
What's in this chapter?
Providing overview of how location information is provided in Android
Presenting an overview of GPS
Discussing why A-GPS is used in Android
Providing an overview of the network location provider
Location information is becoming increasingly important in the world of mobile development. Apps that were once location agnostic now make use of location information to provide a richer user experience. Being able to combine a simple web search engine with up-to-the-minute location information allows Android devices to provide a level of functionality that was previously not possible. The capability to easily retrieve and provide location data to apps is becoming a major feature of today's mobile platforms. Android provides this functionality with its location service.
Android's location service provides access to facilities that can be used to determine a device's current location. This information can be used for a wide variety of functions and can allow a device and the software that runs on it to have a better understanding of its surroundings.
Methods Used to Determine Location
Android makes use of different methods to provide location information to an app. In Android, these facilities are called location providers, and each has its own unique set of strengths and weaknesses. In addition, because location providers have such unique characteristics, they each lend themselves to be used differently in different situations.
The following sections give some high-level explanations as to how the different location acquisition methods work. Although an app has little control over how the providers work, it can decide which location provider to use. Understanding how each provider works goes a long way in understanding its limitations and characteristics.
GPS Provider
The Global Positioning System (GPS) uses a system of satellites orbiting the planet to help a receiver (an Android handset in this case) determine its current location. The term GPS refers to the entire GPS system, which consists of satellites, receivers, and the control stations that monitor and adjust it. The receiver that is located in the phone is useless without the rest of the system.
How It Works
In general, a GPS receiver uses information from the GPS satellites orbiting the earth to calculate its current location. The GPS system contains 27 satellites that continually orbit the earth, transmitting information to would-be receivers. Each satellite follows a defined path, ensuring that at least four satellites are visible from any point on earth at any given time. Being able to have a line of sight to at least four satellites is necessary to determine location using GPS. shows a depiction of the GPS satellite constellation.
GPS satellite constellation
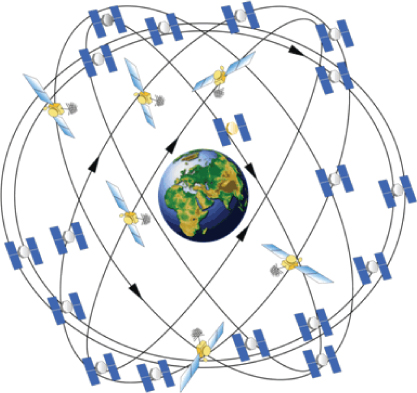
Each GPS satellite in the constellation continuously transmits its current position (ephemeris data) and almanac data. The almanac data includes data about each satellite in the constellation, including orbiting data as well as information about the overall state of the system as a whole. To say it another way, ephemeris data is information about a single satellite, and almanac data is information about every satellite. Every satellite transmits both. Though both the ephemeris data and almanac data provide location data for a given satellite, the ephemeris data provides accuracy for location calculation.
To calculate its location, a GPS receiver must be able to determine its distance from multiple satellites. It does this using the ephemeris data. Included in the data that is transmitted from the satellite, along with the position data, is the time at which the transmission started. Each GPS satellite contains a highly accurate timekeeping mechanism that allows the satellite to keep its time in sync with the rest of the satellites. To produce an accurate location calculation, the GPS satellites and GPS receivers must have their clocks highly synchronized. Even the slightest difference in time can cause large errors when computing location.
Using the transmission start time, the GPS receiver can calculate the time it took for the transmission to be received (the receiver knows when the transmission ended). This calculation is made with the assumption that the radio waves that transmit the data travel at the speed of light in a vacuum (which is not always the case). Using the start time, end time, and a constant for the speed of light, a GPS receiver can calculate the distance of the satellite from the receiver.
Using the distance from multiple satellites, the GPS receiver can triangulate its current location. Essentially, the point at which all the spheres intersect is the location of the receiver. A minimum of three satellites is needed to determine a two-dimensional location (latitude and longitude). Communications from additional satellites allow a GPS receiver to determine additional positional information such as altitude. A GPS receiver will not limit itself to only four satellites. In general as the number of satellites from which the receiver can receive data increases, so does the accuracy of the location (there is an upper limit, however).
GPS is useful for determining current location, but it does have some drawbacks (especially for mobile platforms), one of which is the time it can take to calculate the current position. Before the location can be calculated, multiple satellites must be found. Many satellites are orbiting the earth, but only a handful can be seen at any given time because most will be below the horizon and blocked by the earth (remember, a line of sight is needed). The almanac used by the GPS system can provide assistance in determining which satellites should be used for a given location at a given time. However, if the GPS does not have a relatively current almanac, it will need to have the almanac data transmitted by a GPS satellite. This can be a slow process.
GPS Improvements
Although standard GPS can provide accurate location data, the limitations it imposes make it difficult for mobile devices to use it. To help circumvent some the limitations of standard GPS, modern mobile devices make use of assisted GPS (A-GPS) and possibly simultaneous GPS (S-GPS).
A-GPS
A-GPS uses the mobile network to transmit the GPS almanac along with other pieces of information to a mobile device. This use of the mobile network allows for faster transmission of the almanac, which may lead to faster determination of the device's current location. In addition, because the almanac contains information about all of the GPS satellites, the device will know the approximate location of the GPS satellites in its line of sight. This will also improve the time it takes to acquire a GPS location.
Examination of the GPS configuration file provides some insight into where the A-GPS data comes from. shows an example of a GPS configuration file that is used in Android for a device located in North America.
: An example of a GPS configuration file located in /system/etc/gps.conf
NTP_SERVER=north-america.pool.ntp.orgXTRA_SERVER_1=http://xtra1.gpsonextra.net/xtra.binXTRA_SERVER_2=http://xtra2.gpsonextra.net/xtra.binXTRA_SERVER_3=http://xtra3.gpsonextra.net/xtra.bin














