Getting Started
This chapter will be about getting started with Git. We will begin at the beginning by explaining some background on version control tools, then move on to how to get Git running on your system and finally how to get it setup to start working with. At the end of this chapter you should understand why Git is around, why you should use it and you should be all setup to do so.
About Version Control
What is version control, and why should you care? Version control is a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later. For the examples in this book you will use software source code as the files being version controlled, though in reality you can do this with nearly any type of file on a computer.
If you are a graphic or web designer and want to keep every version of an image or layout (which you would most certainly want to), a Version Control System (VCS) is a very wise thing to use. It allows you to revert files back to a previous state, revert the entire project back to a previous state, compare changes over time, see who last modified something that might be causing a problem, who introduced an issue and when, and more. Using a VCS also generally means that if you screw things up or lose files, you can easily recover. In addition, you get all this for very little overhead.
Local Version Control Systems
Many people's version-control method of choice is to copy files into another directory (perhaps a time-stamped directory, if they're clever). This approach is very common because it is so simple, but it is also incredibly error prone. It is easy to forget which directory you're in and accidentally write to the wrong file or copy over files you don't mean to.
To deal with this issue, programmers long ago developed local VCSs that had a simple database that kept all the changes to files under revision control (see Figure 1-1).
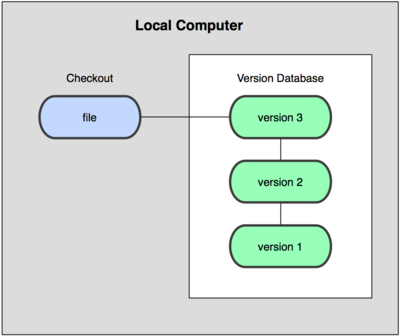
One of the more popular VCS tools was a system called rcs, which is still distributed with many computers today. Even the popular Mac OS X operating system includes the rcs command when you install the Developer Tools. This tool basically works by keeping patch sets (that is, the differences between files) from one change to another in a special format on disk; it can then re-create what any file looked like at any point in time by adding up all the patches.
Centralized Version Control Systems
The next major issue that people encounter is that they need to collaborate with developers on other systems. To deal with this problem, Centralized Version Control Systems (CVCSs) were developed. These systems, such as CVS, Subversion, and Perforce, have a single server that contains all the versioned files, and a number of clients that check out files from that central place. For many years, this has been the standard for version control (see Figure 1-2).
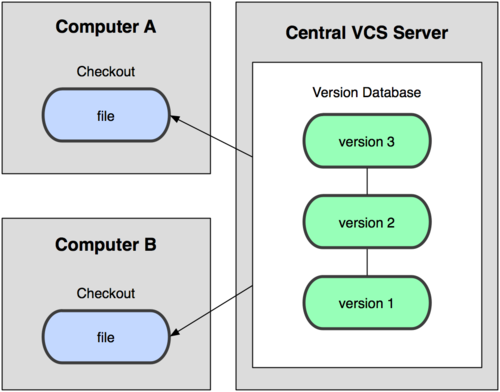
This setup offers many advantages, especially over local VCSs. For example, everyone knows to a certain degree what everyone else on the project is doing. Administrators have fine-grained control over who can do what; and it's far easier to administer a CVCS than it is to deal with local databases on every client.
However, this setup also has some serious downsides. The most obvious is the single point of failure that the centralized server represents. If that server goes down for an hour, then during that hour nobody can collaborate at all or save versioned changes to anything they're working on. If the hard disk the central database is on becomes corrupted, and proper backups haven't been kept, you lose absolutely everything-the entire history of the project except whatever single snapshots people happen to have on their local machines. Local VCS systems suffer from this same problem-whenever you have the entire history of the project in a single place, you risk losing everything.
Distributed Version Control Systems
This is where Distributed Version Control Systems (DVCSs) step in. In a DVCS (such as Git, Mercurial, Bazaar or Darcs), clients don't just check out the latest snapshot of the files: they fully mirror the repository. Thus if any server dies, and these systems were collaborating via it, any of the client repositories can be copied back up to the server to restore it. Every checkout is really a full backup of all the data (see Figure 1-3).
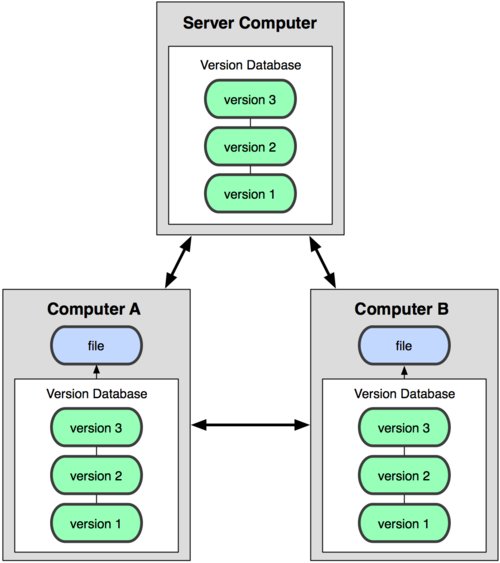
Furthermore, many of these systems deal pretty well with having several remote repositories they can work with, so you can collaborate with different groups of people in different ways simultaneously within the same project. This allows you to set up several types of workflows that aren't possible in centralized systems, such as hierarchical models.
A Short History of Git
As with many great things in life, Git began with a bit of creative destruction and fiery controversy. The Linux kernel is an open source software project of fairly large scope. For most of the lifetime of the Linux kernel maintenance (1991-2002), changes to the software were passed around as patches and archived files. In 2002, the Linux kernel project began using a proprietary DVCS system called BitKeeper.
In 2005, the relationship between the community that developed the Linux kernel and the commercial company that developed BitKeeper broke down, and the tool's free-of-charge status was revoked. This prompted the Linux development community (and in particular Linus Torvalds, the creator of Linux) to develop their own tool based on some of the lessons they learned while using BitKeeper. Some of the goals of the new system were as follows:
- Speed
- Simple design
- Strong support for non-linear development (thousands of parallel branches)
- Fully distributed
- Able to handle large projects like the Linux kernel efficiently (speed and data size)
Since its birth in 2005, Git has evolved and matured to be easy to use and yet retain these initial qualities. It's incredibly fast, it's very efficient with large projects, and it has an incredible branching system for non-linear development (See Chapter 3).
Git Basics
So, what is Git in a nutshell? This is an important section to absorb, because if you understand what Git is and the fundamentals of how it works, then using Git effectively will probably be much easier for you. As you learn Git, try to clear your mind of the things you may know about other VCSs, such as Subversion and Perforce; doing so will help you avoid subtle confusion when using the tool. Git stores and thinks about information much differently than these other systems, even though the user interface is fairly similar; understanding those differences will help prevent you from becoming confused while using it.
Snapshots, Not Differences
The major difference between Git and any other VCS (Subversion and friends included) is the way Git thinks about its data. Conceptually, most other systems store information as a list of file-based changes. These systems (CVS, Subversion, Perforce, Bazaar, and so on) think of the information they keep as a set of files and the changes made to each file over time, as illustrated in Figure 1-4.