Picture Window Books
A Capstone Imprint
1710 Roe Crest Drive
North Mankato, MN 56003
www.mycapstone.com
Copyright 2007 by Picture Window Books
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be
reproduced without written permission from the
publisher. The publisher takes no responsibility
for the use of any of the materials or methods
described in this book, nor for the products thereof.
Library of Congress Cataloging- in- Publication Data
Dixon, Dougal.
Coelophysis and other dinosaurs of the South /
by Dougal Dixon ; illustrated by Steve Weston &
James Field.
p. cm. ( Dinosaur find)
Includes bibliographical references and index.
ISBN: 978- 1- 4048- 2747- ( library binding)
ISBN: 978-1-5158-5610-8 (eBook) Coelophysis Juvenile literature. Dinosaurs
South Atlantic States Juvenile literature. I. Weston,
Steve, ill. II. Field, James, 1959 ill. III. Title. IV. Series:
Dixon, Dougal. Dinosaur find.
QE862. S3D593 2007
567.912 dc22 2006012132
Acknowledgments
This book was produced for Picture Window Books by
Bender Richardson White, U. K.
Illustrations by James Field ( cover and pages 5, 7,
11, 15, 17) and Steve Weston ( pages 9, 13, 19, 21).
Diagrams by Stefan Chabluk.
Photographs:
EyeWire Inc: , Bruce
MacQueen, ;
Shutterstock: Valerie Johnson, .
Consultant:
John Stidworthy, Scientific Fellow of
the Zoological Society, London, and former
Lecturer in the Education Department, Natural History
Museum, London.
Reading Adviser: Susan Kesselring, M. A., Literacy
Educator, Rosemount Apple Valley Eagan
( Minnesota) School District
Chicken
feet ( centimeters) tall
pounds ( 2.7 kilograms)
Adult person
feet ( 1.8 meters) tall
pounds ( 76.5 kg)
Elephant
feet ( m) tall
12,000 pounds
( 5,400 kg)
Types of dinosaurs
In this book, a red shape at the
top of a left- hand page shows
the animal was a meat- eater.
A green shape shows it was
a plant- eater.
Just how big or small
were they?
Dinosaurs were many different
sizes. We have compared their
sizes to one of the following:

T ABLE OF C ONTENTS
W HATS I NSIDE ?
Dinosaurs! These dinosaurs lived in
what is now southern North America
Find out how they survived millions
of years ago and what they have in
common with todays animals

L IFE IN THE S OUTH
Dinosaurs lived between million
and million years ago. The world
did not look the same then. In most
parts of the world, the land and
seas were not in the same places.
At times, there were all over
southern North America, while at
other times, there were rivers and
heavily wooded forests.
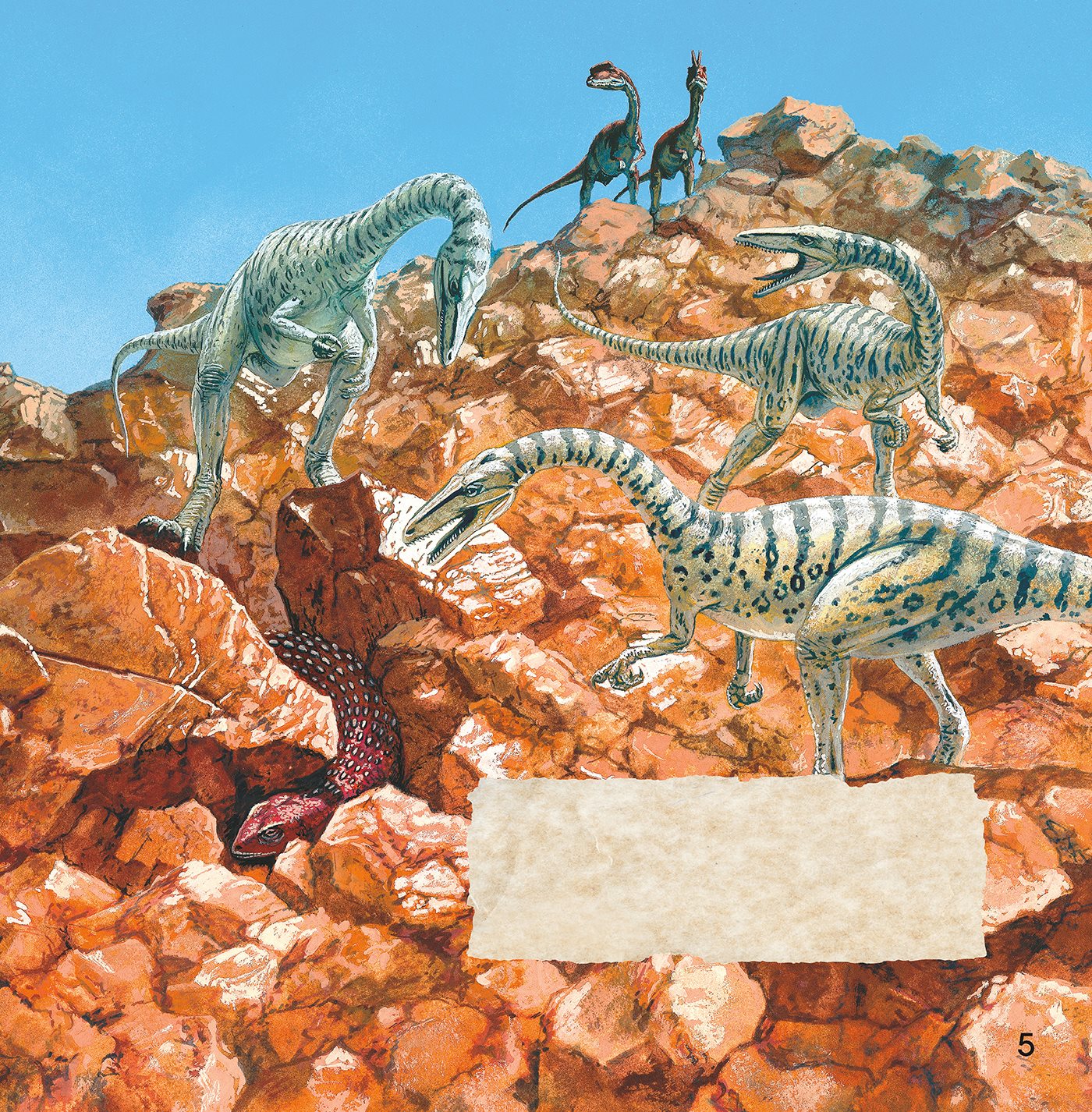

In the deserts of North America lived
Scutellosaurus and such
fierce, meat- eating dinosaurs as
Coelophysis and Dilophosaurus.

C OELOPHYSIS
Pronunciation:
SEE- lo- FY- sis
Coelophysis was one of the first
meat- eating dinosaurs. It traveled
around in , hunting other
animals. Its jaws were long, and
its teeth were like steak knives.
Coelophysis could easily tear the
flesh off other dinosaurs.
Hunting animals today
About the same size as
Coelophysis, the coyote
also has long jaws and
sharp teeth.
Size Comparison

Life was hard in the deserts of
early dinosaur times. Scientists
have found of Coelophysis
gathered around a dry water hole,
where the dinosaurs died of thirst.
S EISMOSAURUS
Pronunciation:
SIZE- mo- SAW- rus
Seismosaurus lived about halfway
through the Age of Dinosaurs. It was
the longest dinosaur that ever lived
about the length of three school
buses! Its little mouth could not chew
food properly, so Seismosaurus had
to swallow stones to grind up food in
its stomach.
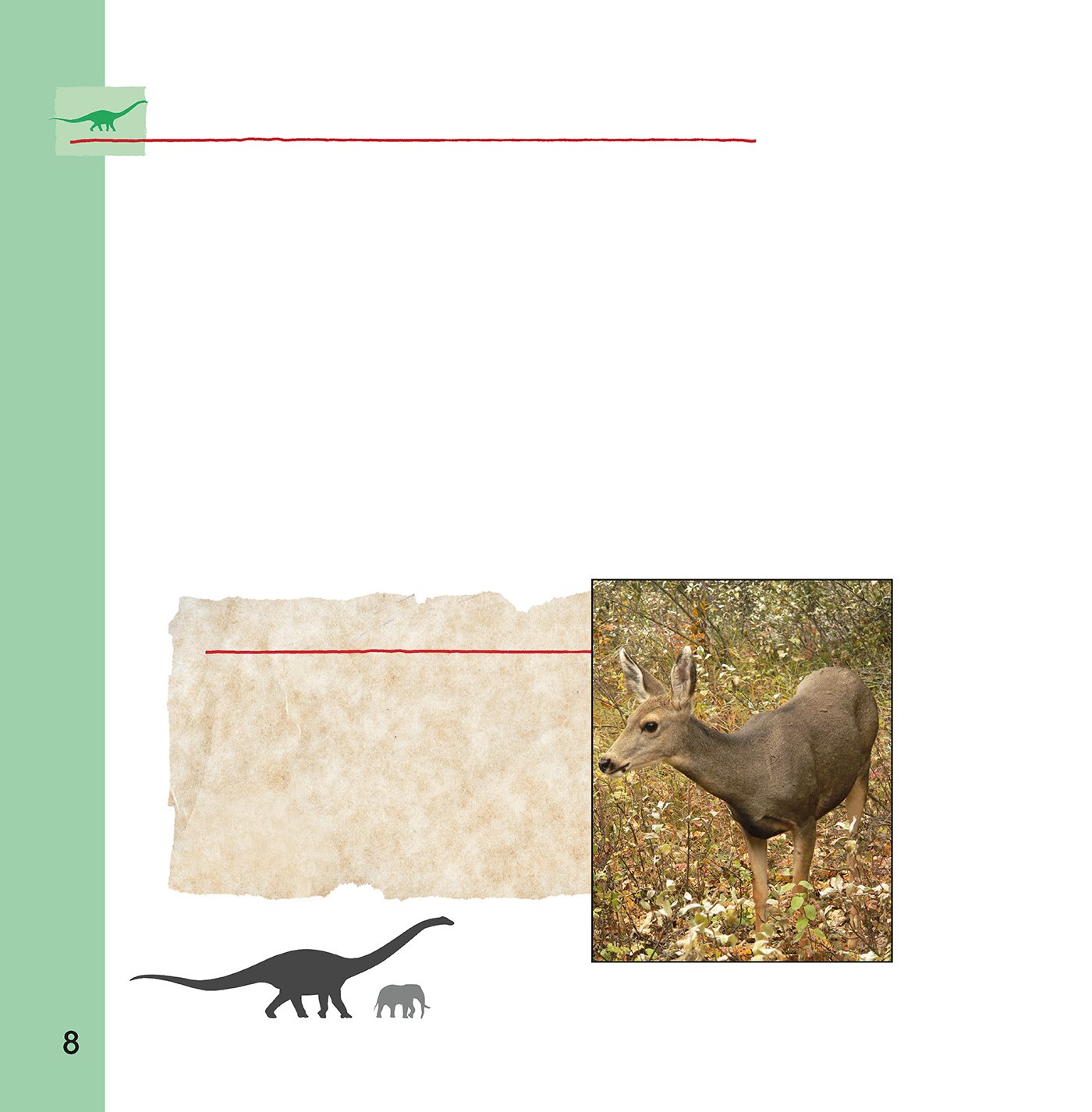
Big animals today
The mule deer is one of
the biggest animals living
in southern North America
today. But it is very small
in size compared to
Seismosaurus.
Size Comparison
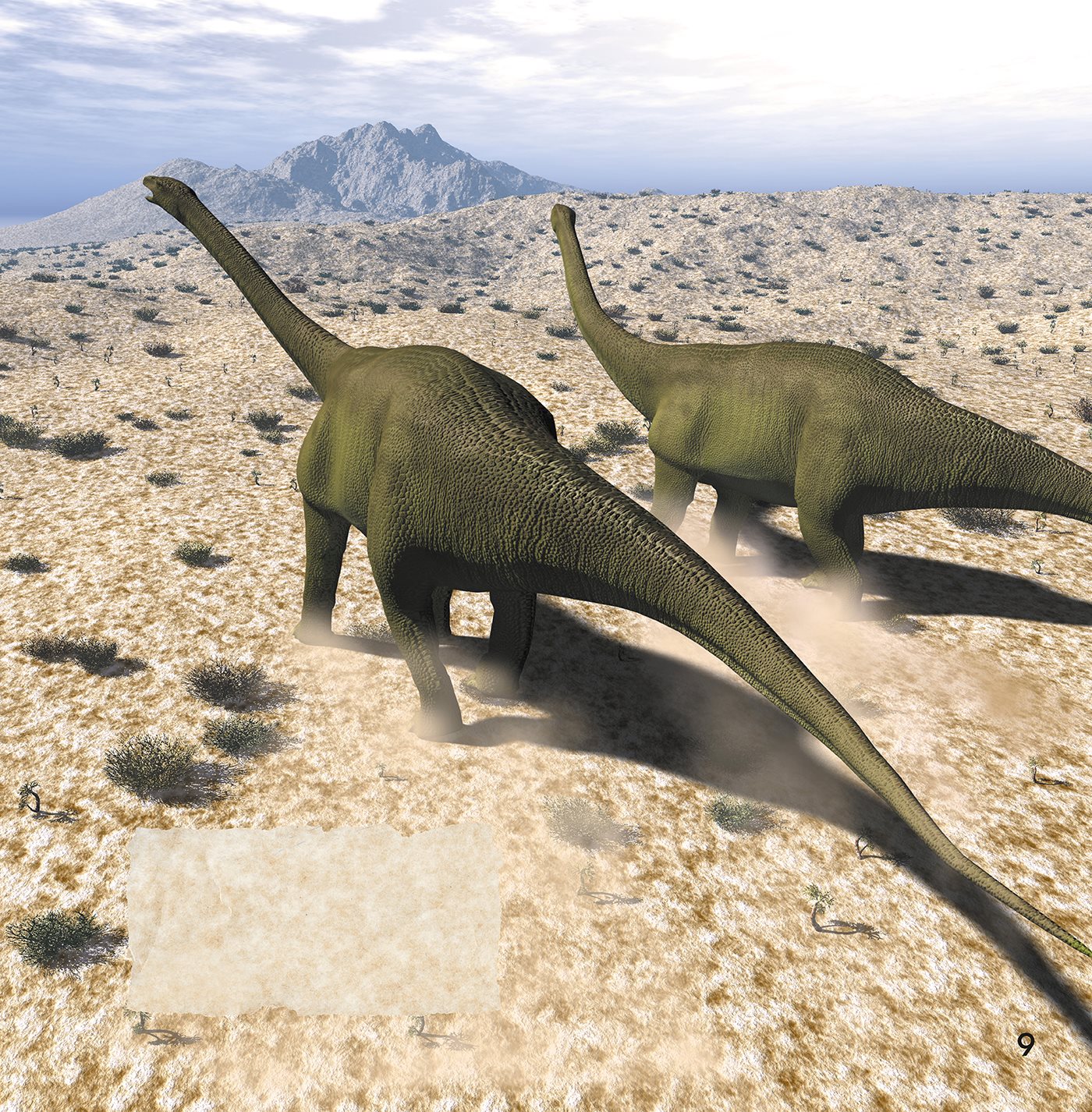

The name Seismosaurus
means earthquake lizard.
The ground must have
shook as the beast walked.

A LAMOSAURUS
Pronunciation:
AL- uh- mo- SAW- rus
Alamosaurus was one of the last
of the long- necked dinosaurs. It
lived at the very end of the Age
of Dinosaurs. It ate from the trees
that covered the hillsides of
southwestern North America.
Tree- eaters today
The white- tailed deer
eats from the trees. It
has the same diet as
Alamosaurus did, but
it does not eat nearly
as much.
Size Comparison

Alamosaurus did not live
just in the South. It lived
on the hills all over North
America at that time.

N OTHRONYCHUS
Pronunciation:
NOTH- ron- EYE- kus
Nothronychus was a strange- looking
dinosaur. It had a tiny head and
very big . It used its claws to
rip bark and leaves from the trees.
Nothronychus was covered in
feathers to keep warm.
Tree- destroyers today
The modern beaver
brings down trees like
Nothronychus did, but
it uses its teeth to do so
instead of claws.
Size Comparison
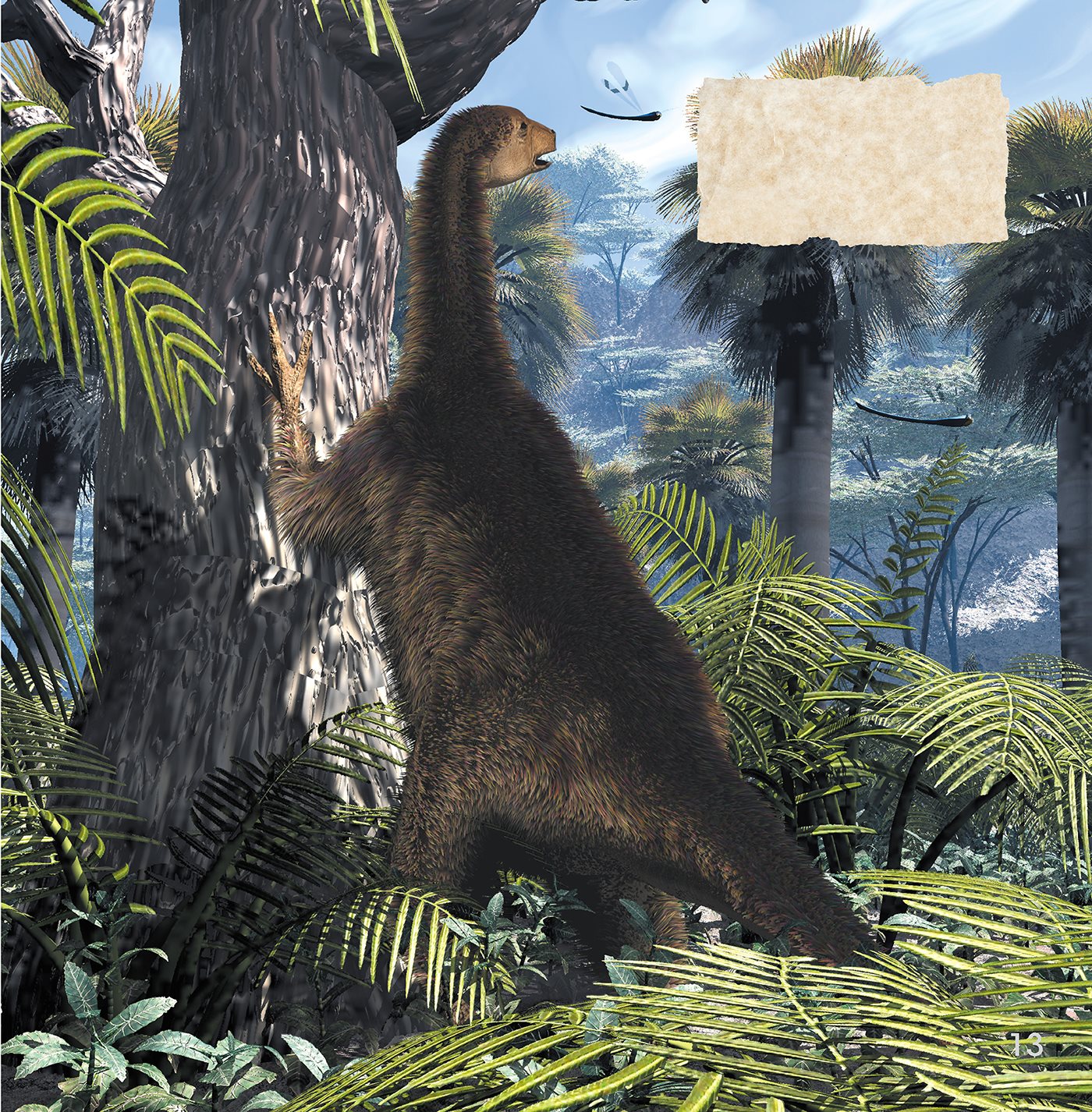

Nothronychus lived
alone in the forests.
There was plenty to
eat from the trees.

D ILOPHOSAURUS Pronunciation:
dye- LO- fuh- SAW- rus
Dilophosaurus was a fast- running,
meat- eating dinosaur.















 In the deserts of North America lived
In the deserts of North America lived
 Life was hard in the deserts of
Life was hard in the deserts of
 The name Seismosaurus
The name Seismosaurus
 Alamosaurus did not live
Alamosaurus did not live
 Nothronychus lived
Nothronychus lived