Every day, the Earth rotates around its axis, which is like an invisible pole. This rotation is what causes day and night. The places on the surface of the Earth where the ends of this invisible pole are found are called the Earths poles the North Pole and the South Pole.
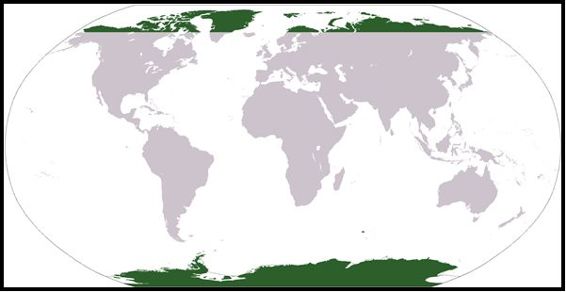
The North Pole is the northernmost part of the Earth. It is located in the middle of the Arctic Ocean, where the waters are almost permanently covered in blocks of sea ice. The area around the North Pole is called the Arctic Circle.
The South Pole is the southernmost part of the Earth. It is located on the continent of Antarctica, of which about ninety-eight percent is covered in ice at least a mile (1.6 kilometers) thick. The area around the South Pole is called the Antarctic Circle.
Antarctica is considered the worlds largest cold desert, receiving only 8 inches (20.3 centimeters) of rainfall at most each year. It is also the windiest, coldest and driest continent.
Life in the Polar Regions
The North and South Poles are the parts of the Earth that receive the least amount of heat from the Sun. Because of this, they are the coldest places on Earth. At the North Pole, temperatures range from 41 degrees Fahrenheit (5 Celsius) to as much as 45 degrees Fahrenheit (43 Celsius) below zero while at the South Pole, it is even colder, the temperature dipping to as low as negative 128 degrees Fahrenheit (-89 Celsius)! These extremely cold temperatures are responsible for the formation of huge amounts of ice.
At both the North and South Poles, the sun is never high up in the sky, but hovers just above the horizon.
At the North Pole, there are four seasons winter, spring, summer and fall, with winter and summer being the longer seasons. In winter from November to February there are days when the Sun does not rise at all. In summer the Sun does not set and it is constantly daytime.
During summer, some of the sea ice in the North Pole melts while some stays frozen all year long. Due to global warming, studies show that more and more of the sea ice melts every summer, making scientists believe that Arctic summers may eventually be completely free of ice.

Broken Glaciers of North Pole by Pranav
At the South Pole, there are only two seasons winter and summer, each lasting six months. In winter from March to September there is no sunlight and sometimes it is completely dark except for the faint moonlight. In summer, the Sun is constantly above the horizon.
Snow falls on both the North and South Poles but falls more heavily and more frequently at the South Pole. Sometimes, in Antarctica, there is so much snow that the ice sheets sink below sea level. In the Arctic, there are only certain places that are covered with snow all year round.
Blizzards occur every year in the Arctic and the Antarctic. These are massive snowstorms with strong winds and large amounts of snow. Ice storms, which have little wind but have freezing rain, also occur.
Some plants do grow in the Arctic tundra but in the Antarctic, only mosses and two species of flowering plants can be found, which only grow for a short time each year.
There are about two million people living in the Arctic Circle, many of whom belong to ethnic groups who have their culture tied to life in the Arctic. In the Antarctic, as few as 4000 people can be found, living in research stations, and more than half of them leave during winter.
Because of these harsh conditions at the North and South Poles, in order to survive, polar animals have to do at least two things keep themselves warm and find food.
Keeping Warm
Polar animals have evolved to withstand freezing temperatures. They have compact bodies, short legs, short ears and short tails. This way, they have an easier time keeping themselves warm.

Polar bear resting but alert by Susanne Miller, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Many polar animals are also large, or larger than their relatives who live in warmer areas. This is because bigger is warmer the larger the animal, the smaller its relative surface area, and the less heat it loses.
Most polar animals have thick fur or feathers, sometimes with as many as three layers, in order to keep themselves warm. Some shed their thick coats in the summer and then grow them again in winter.

Polar bear and cubs by Karilop311
For animals that do not have fur, they have an extra layer under their skin composed entirely of fat, called blubber . This layer of fat not only provides them with heat and but also energy.
Sometimes, however, having a thick coat is not enough, which is why polar animals tend to live in dens or burrows. Although these dwellings are made in the snow, it is still warmer inside them than out in the open air. Also, these dwellings provide protection from strong winds.
Large groups of animals who cannot fit in dens huddle together, sharing their body warmth. Often, in formations like these, the young animals are in the middle where it is warmest, and also where they are most protected.

Polar Bear by Michael Bentley
Some polar animals have the special ability to control their blood flow so that only warm blood flows to their most important organs, such as their brain, heart and lungs.
When it is very cold, some polar animals hibernate, which is a way for them to preserve both body heat and energy. Others who cannot hibernate migrate to warmer areas.