Tools and Treasures of
Ancient
Rome
Matt Doeden
What
Can We
Learn from Early
Civilizations?
Tools and Treasures of
Ancient
Rome
Matt Doeden
Lerner Publications Company
Minneapolis
Copyright 2014 by Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
All rights reserved. International copyright secured. No part of this book may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means
electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwisewithout the prior written
permission of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc., except for the inclusion of brief quotations in
an acknowledged review.
Lerner Publications Company
A division of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
241 First Avenue North
Minneapolis, MN 55401 U.S.A.
For reading levels and more information, look up this title at www.lernerbooks.com.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Doeden, Matt.
Tools and treasures of ancient Rome / by Matt Doeden.
pages cm. (Searchlight booksWhat can we learn from early
civilizations?)
Includes index.
ISBN 9781467714334 (lib. bdg. : alk. paper)
ISBN 9781467725088 (eBook)
1. RomeCivilizationJuvenile literature. I. Title.
DG77.D64 2014
937.63dc23
2013022290
Manufactured in the United States of America
1 PC 12/31/13
Contents
THE ANCIENT
ROMANS
THE CULTURE OF
ANCIENT ROME
Chapter
THE ANCIENT
ROMANS
Almost three thousand years
ago, a small village formed in
present- day Italy. At first, Rome
was like any other village in the area.
But it soon became the center of one
of Europes greatest civilizations. Rome
changed the world in many ways. Its people
left behind amazing tools and treasures.
Rome was not
always a huge,
crowded city.
What was it like
in its early years?
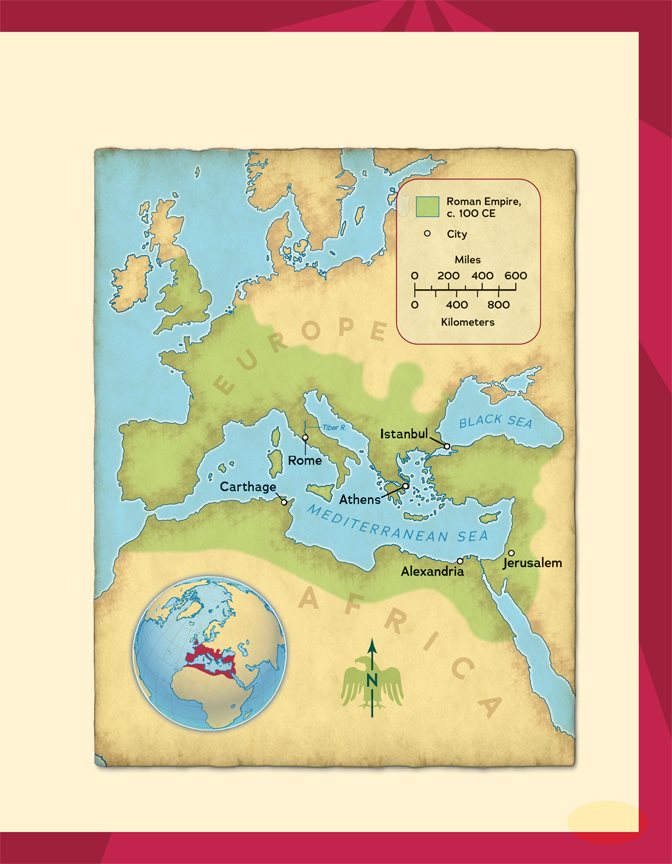
The Rise of Rome
Rome started as a simple farming village. It sat near the
Tiber River at a spot that was easy to cross. Travelers
and traders often stopped there. Soon, Rome grew into a
busy city.
The Tiber River runs through
the heart of modern Rome.
Around BCE, Rome formed a government called
a republic. Landowners chose some men to make laws.
These men were called senators.
Rome began taking over other lands. Soon the
Romans controlled most of present -day Italy.
This marble
statue from
CE shows
Roman senators.
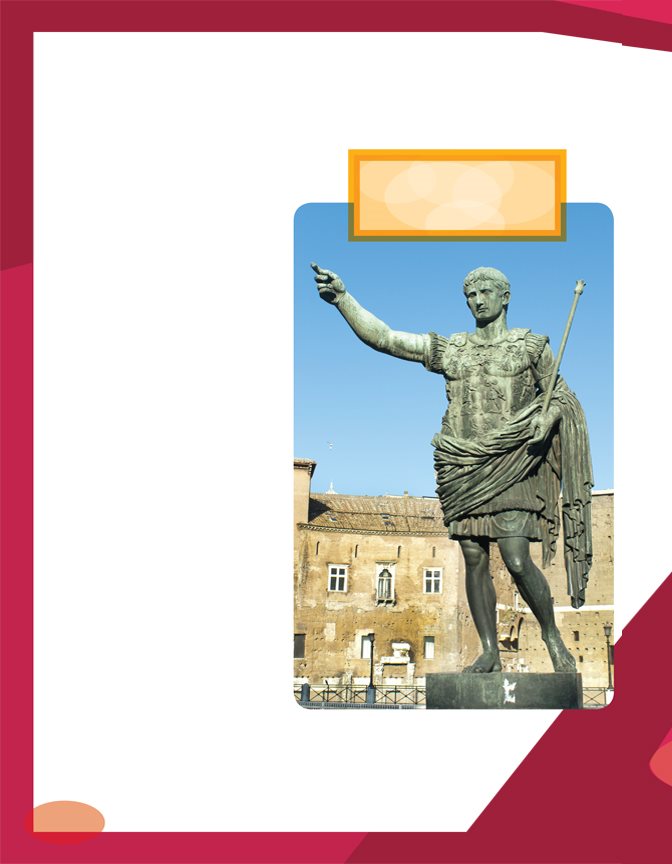
Ancient Rome
In BCE,
Augustus became
Romes first
emperor. He ruled
all the lands Rome
had conquered.
These lands were
called the Roman
Empire. During
Augustuss rule,
the empire grew
even stronger. It
spread to Europe,
Africa, and Asia.
Rome was the most
powerful civilization
in the world.
Emporer Augustus
ruled Rome for more
than forty years.
Chapter
DAILY LIFE
The Romans were proud
of their civilization.
They believed they
were better than any
other people. They
worked hard to support
the empire.
Classes
Each person in the Roman Empire
had a specific role. Landowners
made up the highest class of people.
They were wealthier than most Romans.
Some landowners even became
senators. They made laws to govern
the empire.
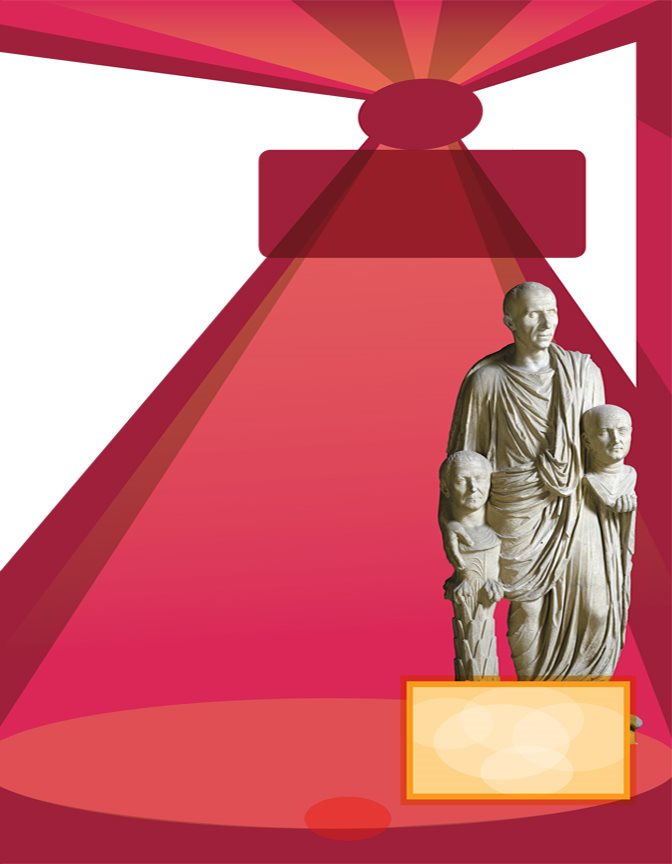
This Roman landowner
holds busts of two
relatives. How were
landowners different
from other Romans?
Most Romans
were commoners.
They worked as
farmers, builders,
and craftsmen.
Their lives
were centered
on family.
Aunts, uncles,
grandparents, and
other relatives
often lived
together in one
home. The
oldest father
was in charge.
THIS URN SHOWS A ROMAN
FAMILY EATING A MEAL.
Women had to obey their
fathers and husbands. But
Roman women had more
rights than women in many
other ancient cultures.
Roman women could own
property. They could
divorce their husbands.
Some Roman women even
gave men advice about how
to run the government.
This statue from about
CE shows a young
Roman woman.
Slaves were the
lowest class. Most
slaves came from
outside the Roman
Empire. Romans
bought slaves from
other civilizations.
They also captured
enemies in battle and
brought them home
as slaves.
Slaves had to do
the hardest, most
dangerous jobs. Most
got no pay. But some
slave owners treated
their slaves like family.
They gave their
slaves gifts. Some
paid their slaves or
even set them free.
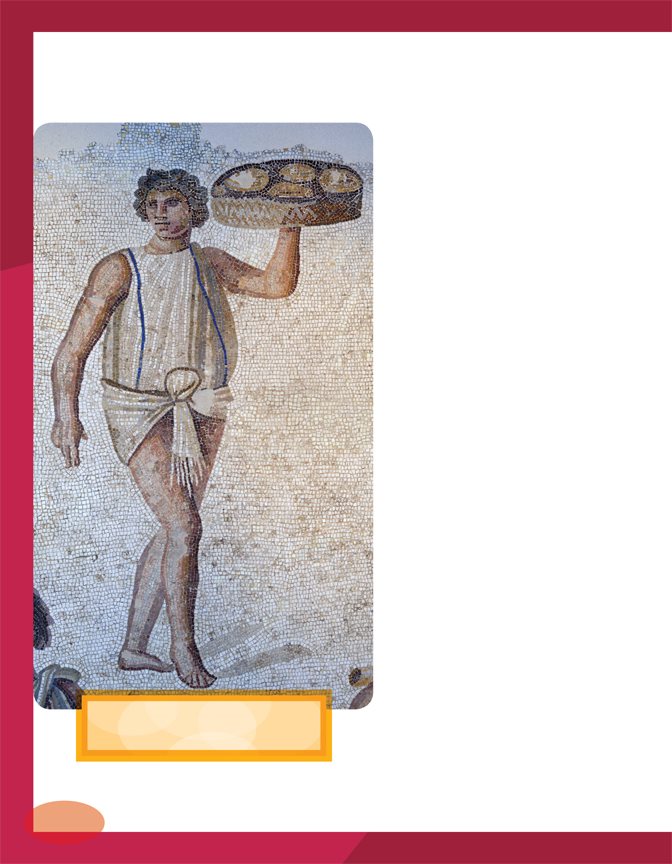
This mosaic from CE
shows a Roman slave.
Freed slaves were called freedmen. They formed their
own class. Most became merchants. They bought and
sold goods in markets. Some freedmen grew very rich.
But they were not allowed to become senators.
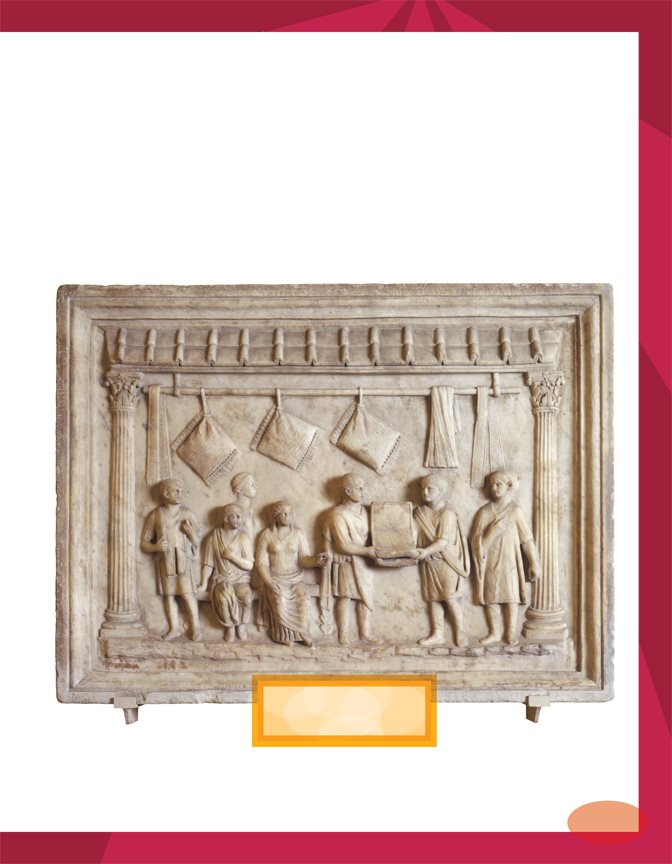
This is a sign for
a pillow merchant.
Work
Rome started as a farming community. So farming was