Tools and Treasures of
Ancient
Mesopotamia
Matt Doeden
What
Can We
Learn from Early
Civilizations?
Tools and Treasures of
Ancient
Mesopotamia
Matt Doeden
Lerner Publications Company
Minneapolis
Copyright 2014 by Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
All rights reserved. International copyright secured. No part of this book may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means
electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwisewithout the prior written
permission of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc., except for the inclusion of brief quotations in
an acknowledged review.
Lerner Publications Company
A division of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
241 First Avenue North
Minneapolis, MN 55401 U.S.A.
For reading levels and more information, look up this title at www.lernerbooks.com.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Doeden, Matt.
Tools and treasures of ancient Mesopotamia / by Matt Doeden.
pages cm. (Searchlight books : what can we learn from early civilizations?)
Includes index.
ISBN 9781467714327 (lib. bdg. : alk. paper)
ISBN 9781467725071 (eBook)
1. IraqCivilizationTo 634Juvenile literature. I. Title.
DS69.5.D64 2014
935dc23
2013018664
Manufactured in the United States of America
1 PC 12/31/13
Contents
ANCIENT
MESOPOTAMIA
THE CULTURE OF
ANCIENT MESOPOTAMIA
Chapter
ANCIENT
MESOPOTAMIA
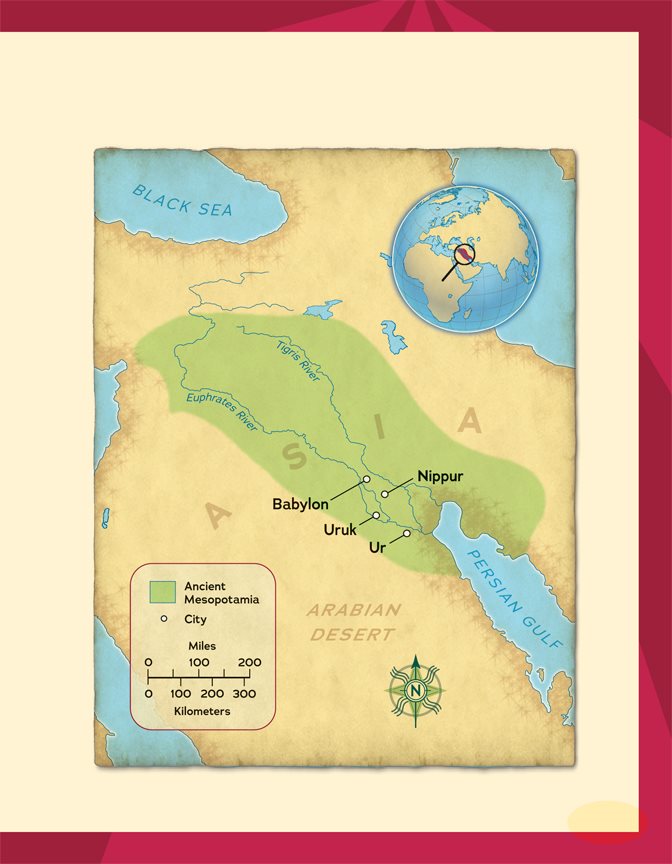
Six thousand years ago,
human beings lived mostly
as hunters and gatherers. They
moved from place to place in search
of food. But in one small area, life was
about to change forever. Between the
Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in modern-
day Iraq, civilization was beginning.
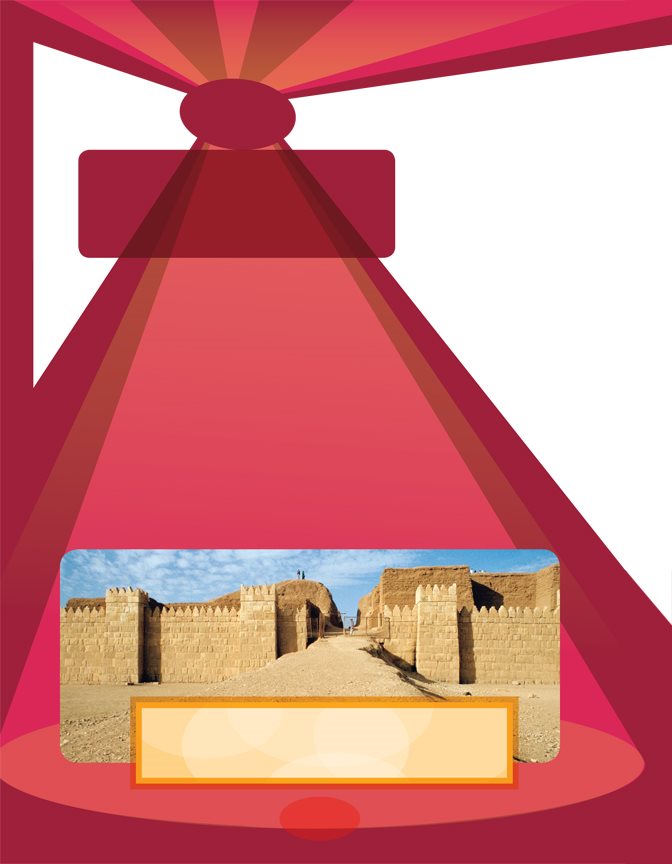
These ruins
are in modern-
day Iraq. How
long ago did
civilization
begin here?
The First Civilization
People in the area began to farm the land. With farms to
tend to, they could settle in one place. They were leaving
their hunting and gathering lifestyle behind. This group of
people was becoming the worlds first civilization. Later
on, the area where they lived was called Mesopotamia.
The ancient Greeks named the
area between the Tigris and the
Euphrates Mesopotamia. The word
means the land between two rivers.
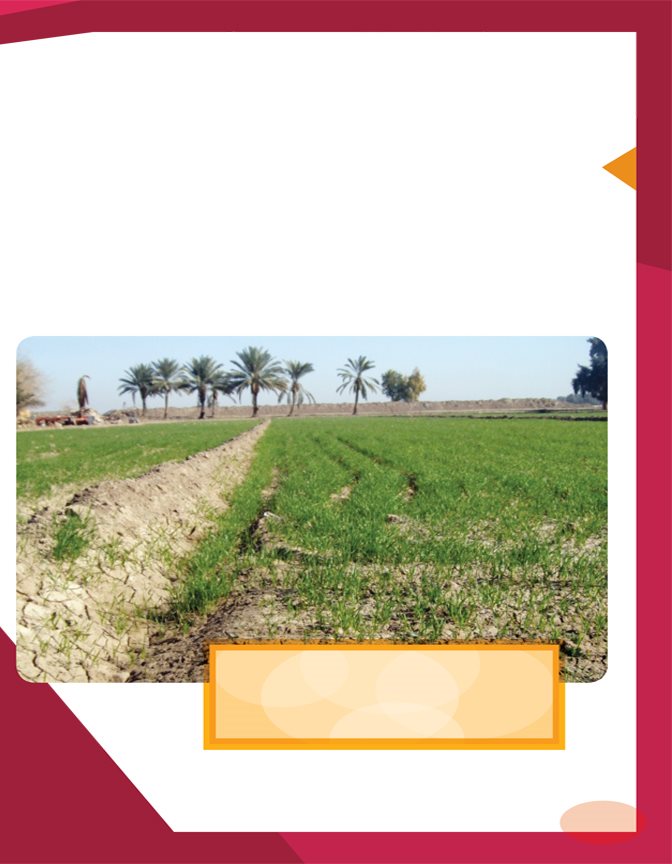
The Tigris and the Euphrates Rivers flooded every
year. Mesopotamians learned to manage these floods.
They built canals to direct floodwaters to the lowlands.
The floods watered the land and brought rich soil.
Modern Iraqis still use
canals to manage the
Tigris and Euphrates Rivers.
This Mesopotamian art
shows someone planting
and tending crops.
People figured out how to plant and grow crops in the
soil. Farming gave them a steady food supply. Villages
formed. Some of them grew into the first cities.
Around 3500 BCE, the culture near the cities of Ur
and Uruk changed suddenly. No one knows exactly why.
But the cities population grew very quickly. The people in
these cities lived and worked together.
A man and a child stand
in the ruins of Uruk.
Ancient Mesopotamia
This society was called Sumer. The people who lived
there were the Sumerians. People in this culture invented
the first system of writing. They produced the first
written history. Soon they wrote the first literature.
Many museums display Sumerian
artifacts. These artifacts come
from Uruk. Uruk is the earliest
city scientists have found.
Empires Rise and Fall
More cities rose in Mesopotamia. Each city and the
lands it controlled was called a city- state. The city- states
often fought with one another. Empires rose and fell.
Around 2000 BCE, a group called the Amorites
invaded. They wiped out the Sumerians. The Amorites
took control of much of Mesopotamia. Another group
called the Assyrians also moved in.
THIS ANCIENT MOSAIC SHOWS
PICTURES OF SUMERIAN WARS.
In the 1700s BCE,
Babylon was the
most powerful city
in Mesopotamia.
Its ruler was
Hammurabi. He
joined all of
Mesopotamia
together. Babylon
ruled the region for
more than a hundred
years. But Babylon
also fell to invaders.
Groups including
the Hittites and the
Assyrians took over
the land.
Hammurabi was one of
the first rulers to write
laws for his people.
Over thousands of years, many empires ruled
Mesopotamia. Each empire borrowed from the one
before it. They copied parts of the previous empires art,
writing, religion, and more. Much of what the Sumerians
established was handed down through the centuries.
Many of their ideas lived on in Mesopotamia long after
they were gone.
Darius III ruled Mesopotamia
in the 300s CE. Greek
ruler Alexander the Great
conquered Mesopotamia
and took power from him.