Tools and Treasures of
Ancient
Egypt
Matt Doeden
What
Can We
Learn from Early
Civilizations?
Tools and Treasures of
Ancient
Egypt
Matt Doeden
Lerner Publications Company
Minneapolis
Copyright 2014 by Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
All rights reserved. International copyright secured. No part of this book may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means
electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwisewithout the prior written
permission of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc., except for the inclusion of brief quotations in
an acknowledged review.
Lerner Publications Company
A division of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
241 First Avenue North
Minneapolis, MN 55401 U.S.A.
For reading levels and more information, look up this title at www.lernerbooks.com.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Doeden, Matt.
Tools and treasures of ancient Egypt / by Matt Doeden.
pages cm. (Searchlight bookswhat can we learn from early
civilizations?)
Includes index.
ISBN 9781467714297 (lib. bdg. : alk. paper)
ISBN 9781467725057 (eBook)
1. EgyptCivilizationJuvenile literature. 2. EgyptSocial life and customs
Juvenile literature. 3. EgyptAntiquitiesJuvenile literature. I. Title.
DT61.D64 2014
932.01dc23
2013015642
Manufactured in the United States of America
1 PC 12/31/13
Contents
THE ANCIENT
EGYPTIANS
THE CULTURE OF
ANCIENT EGYPT
Chapter
THE ANCIENT
EGYPTIANS
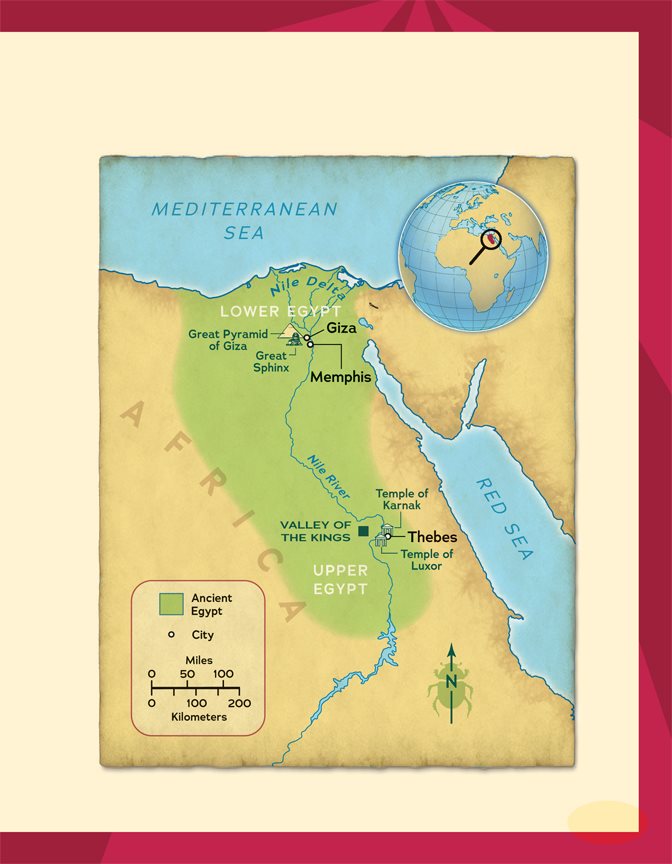
About five thousand years
ago, the great civilization of
ancient Egypt was growing. The
lands of Upper Egypt and Lower
Egypt joined to form one of the longest-
lasting civilizations in history. This society
flourished along the Nile River in northeastern
Africa for thousands of years.
These Egyptian pyramids are more
than four thousand years old. What
else did the ancient Egyptians build?
The ancient Egyptians were skilled farmers and
builders. They enjoyed art, music, and writing. They
built pyramids and monuments. The bodies of many
wealthy Egyptians were preserved by mummification.
Mummies thousands of years old remain in good
condition to this day!
Egyptian artwork often
told stories of day- to-
day life. This painting
shows people fishing.
Civilization in the Desert
Egypt has a harsh desert climate. Its hot. Little rain falls
there. Thats why the Egyptians settled along the Nile.
The river provided them with almost everything they
needed. It flooded every year.
The Nile River flowed through
ancient Egypt. People depended
on the Nile for water and food.
The floods covered the rivers banks with rich soil.
The Egyptians grew crops such as wheat and barley in
this soil. They used the Niles water to irrigate the crops.
They caught fish from its waters.
The Egyptians believed that Hapi,
the god of the Nile (ABOVE), gave
them water for a good harvest.
The desert that surrounded Egypt also shaped the
civilization. It left Egypt isolated from the rest of the
world. Few invading armies dared to cross it. Egypt had
little contact with other societies. That allowed Egypt to
develop a culture like no other.
The Egyptians called this vast desert
the red land. The fertile soil around
the Nile was called black land.
Ancient Egypt
Chapter
DAILY LIFE
Egyptians worked hard
to keep their society
strong. They farmed.
They built tombs and temples.
Each person had a role.
Egyptian bricklayers built tombs,
temples, and homes from stone and
bricks made of mud. What kind of
work did other Egyptians do?
Classes
Daily life depended on ones class. Slaves lived the
harshest lives. They did the worst jobs. Their owners
could beat them or even kill them. But not all slaves
lived badly. Some families treated their slaves like family.
Some even adopted slave children as their own.
Some Egyptian slaves
became skilled in making
pots, vases, or clothing.
Farmers and craftsmen worked hard too. Farmers
planted crops. Plows and other tools were used to
harvest grains. Craftsmen made pots, clothing, and other
goods. These people usually lived in small homes made
from mud bricks.
Mud was formed into bricks and
then baked in the sun. Modern
people in hot, dry climates still
build homes out of mud bricks.
Scribes, priests, and nobles led the best lives. They
lived in the biggest homes. Scribes ran the government.
Priests worked in Egypts temples. Nobles were the
highest class. Among them was Egypts king, or pharaoh.
The pharaoh was even considered a god!
Egyptian artists honored
pharaohs by carving
statues of them.
Communication
The people of ancient Egypt spoke Egyptian. The
language no longer exists. But some Egyptian churches