CUPPING THERAPY
FOR BODYWORKERS
A Practical Manual
ILKAY ZIHNI CHIRALI

LONDON AND PHILADELPHIA
Contents
Preface
For centuries, cupping therapy has been traditionally employed as one of the most effective and important tools of the Traditional Chinese Medicine arsenal. As part of folklore medicine, too, many cultures from East to West and from North to South, over many thousands of years, have employed cupping therapy in order to treat a broad range of medical conditions, such as elevated blood pressure, the common cold and joint and musculoskeletal complaints, and to remove pus and infection from the body. Cupping was and still is used today in many Turkish baths (hamams) as a traditional relaxation medium as well as to treat painful and stiff joints and muscles.
Resurrection of cupping therapy
Internationally recognised personalities and celebrities, including Gwyneth Paltrow, David Beckham and, more recently, the swimmer Michael Phelps at the 2016 Rio Olympics, have candidly exhibited dramatic cupping marks on various parts of their body, leading to media frenzy! This has helped to reignite interest in this ancient but highly effective therapy, particularly from athletes, massage therapists and beauty therapists.
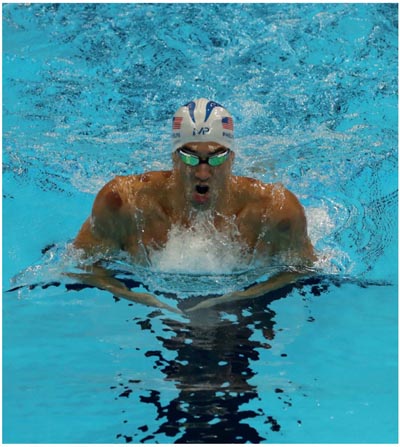

Figure P.1 : Michael Phelps with cupping marks, at the Rio Olympics
While all this new interest in cupping therapy is taking place, many well-qualified people have taken up cupping practice; however, not-so-qualified people have also taken up cupping practices, offering cupping treatment in various locations, even on a kitchen table! As a devout cupping therapy practitioner and teacher, the issue of safe cupping practice is one of my main concerns. In recent years I have been called several times to act for litigation lawyers as a professional cupping therapy witness against cupping therapy malpractice in the UK. I sincerely hope that this book will give cupping therapists a clear and comprehensive guide and help contribute to safe cupping practice.
Chirali, I.Z. (2014) Traditional Chinese Medicine Cupping Therapy , 3rd edition. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
CHAPTER 1
..................................................
A BRIEF HISTORY OF CUPPING
A personal journey
I was born in the village of Lemba (Cirali) near Paphos, Cyprus, where cupping was part of traditional Cypriot folklore medicine, practised by both the Turkish and the Greek population (Turkish s . is . e dus . urmek; Greek ventouses). According to villagers, for the past two to three hundred years the accepted traditional practice was a cupping application for colds and coughs, and hemp tea for all other afflictions!
I experienced cupping on my body from a very young age and continue receiving it to this day. During my Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) studies in Melbourne, Australia, in the 1980s, I was lucky enough to have a teacher who also was a keen cupping therapy practitioner. Most acupuncture sessions at his TCM academy/clinic would conclude with a cupping treatment and Tuina (a TCM massage technique). In a short time, I found myself teaching cupping therapy techniques to new students at the college. I am a devoted cupping therapy practitioner and a teacher, and intend to continue to be so. For more than 35 years in a clinical environment, as well as outside clinical situations, I have witnessed first-hand the truly remarkable benefits of cupping therapy enjoyed by many men and women, old and young, particularly when their suffering was due to the common cold, asthma, pain and countless forms of muscular complaints.
Historical facts
This wonderful healing tool has been used by diverse traditional folklore practitioners for thousands of years. Cupping therapy is a universal practice and cannot be attributed to a single nation or tradition, but rather has spread in a vast geographical spectrum. From the warm Mediterranean villages of Cyprus to freezing towns of Sweden, and from isolated places in South America to modern towns in England, cupping is a familiar but often long-forgotten and out of fashion medical practice. The doctors of ancient Egypt (around 3150 bc ) were keen cupping practitioners, as the carvings of cupping equipment alongside various other medical instruments on the face of a temple in Luxor, Egypt clearly show. In traditional Jewish and Islamic (Hejama) medicine, too, cupping therapy has been extensively studied and practised throughout the ages. Hippocrates of Kos (400 bc ), considered by many to be the founder of modern medicine, was a great advocate of cupping therapy in his teachings. The ancient Greeks and, later, the Ottoman Turks, who practised cupping in the traditional Turkish hamams, were mostly responsible for introducing cupping practices to the continent of Europe. From the 17th to the 19th century, cupping was extensively practised in all European hospitals, including in the UK, and in the USA.
The Chinese Medicine doctors, however, are the true heroes who managed to keep the traditional methods of cupping practices alive and carried forward cupping knowledge as we know it today (). Ancient cupping equipment comprised animal horns, clay cups, bamboo cups (still widely used today in Far Eastern countries) and porcelain cups. Glass cups were first used by the ancient Egyptians as early as 1500 bc . In Far Eastern countries, cupping therapy is still extensively practised, particularly during acupuncture and massage sessions. Throughout the 19th century many sophisticated manual and mechanical cupping machines were invented, particularly by American and European manufacturers.
Contemporary cupping therapy
As I am writing these pages today, in 2018, as far as the clinical practice of cupping therapy is concerned, we have truly come a long way!
Cupping therapy is no longer the exclusive tool of acupuncture practitioners. This ancient but effective treatment method has indeed managed to fascinate a broad range of healing professionals, resulting in much more extensive and sophisticated applications. Cupping Therapy for Bodyworkers is specifically intended for the non-Chinese Medicine practitioners, such as the sports physiotherapist, massage therapist and beauty therapist. It also gives directions on self-cupping application. Its purpose is to share my 50 years of cupping therapy experience and provide a clear, practical and detailed guide demonstrating how to administer cupping safely and effectively , in order to support practitioners in their own specialised field.
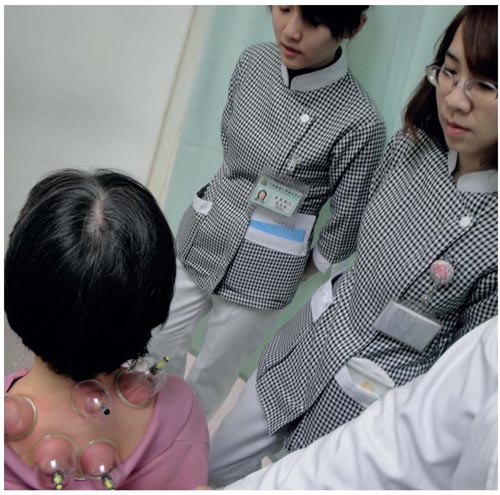

Figure 1.1 : Chinese doctors practising/teaching cupping therapy at China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
Chirali, I.Z. (2014) Traditional Chinese Medicine Cupping Therapy , 3rd edition. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
CHAPTER 2
..................................................
THE MECHANICS OF
CUPPING THERAPY
How does cupping work?
Cupping works through the power of suction, which is created either by introducing a flame into the cup (this is by far the most popular method used in TCM clinics around the world) or by manually extracting the air from the cup (). The aim is to create a controlled vacuum within the cup. As a result, the skin and the fascia, in which the blood vessels, glands, nerves, muscles, ligaments and tendons are wrapped, are lifted and forcefully moved against atmospheric gravity towards the suction cup, resulting in local myofascial decompression. I have italicised the word controlled in order to emphasise the importance of the need to control and manage the degree and intensity of the vacuum during the treatment, in order to avoid damaging the skin. This aspect of cupping therapy will be discussed time and again in the forthcoming chapters. The pulling action on the surface of the skin by the negative pressure inside the cup creates a movement that has a direct effect on both the superficial and the deeper levels of body fascia. This in turn leads to increased blood and fluid circulation, causing cellular, energetic and physical adjustments to take place, such as an increase in the metabolic rate. In my opinion, it is this conflicting gravity trick as well as the unexpected additional increase in microcirculation that sends the self-healing mechanism into action!
Next page