Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2016
Coen de Graaf and Ria Broer Magnetic Interactions in Molecules and Solids Theoretical Chemistry and Computational Modelling 10.1007/978-3-319-22951-5_1
1. Basic Concepts
Abstract
In this chapter we examine some basic concepts of quantum chemistry to give a solid foundation for the other chapters. We do not pretend to review all the basics of quantum mechanics but rather focus on some specific topics that are central in the theoretical description of magnetic phenomena in molecules and extended systems. First, we will shortly review the SlaterCondon rules for the matrix elements between Slater determinants, then we will extensively discuss the generation of spin functions. Perturbation theory and effective Hamiltonians are fundamental tools for understanding and to capture the complex physics of open shell systems in simpler concepts. Therefore, the last three sections of this introductory chapter are dedicated to standard RayleighSchrdinger perturbation theory, quasi-degenerate perturbation theory and the construction of effective Hamiltonians.
1.1 Slater Determinants and SlaterCondon Rules
The Slater determinant is the central entity in molecular orbital theory. The exact N -electron wave function of a stationary molecule in the Born-Oppenheimer approximation is a 4 N -dimensional object that depends on the three spatial coordinates and a spin coordinate of the N electrons in the system. This object is of course too complicated for any practical application and is, in first approximation, replaced by a product of N orthonormal 4-dimensional functions that each depend on the coordinates of only one of the electrons in the system.
These one-electron functions are commonly referred to as spin orbitals and the product is known as the Hartree product
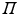
. Obviously, the product suffers from important deficiencies with respect to the foundations of Quantum Mechanics. The wave function is not antisymmetric with respect to the permutation of any two electrons, and hence, does not fulfill the Pauli principle. However, by replacing the product by a determinant
this requirement is automatically fulfilled. Shorthand notations for this Slater determinant are
where only the diagonal elements of the determinant are shown, the four coordinates are compacted in one index, and the normalization factor is implicit. The one-electron functions are ordered by columns (from left to right) and the electrons by rows (from top to bottom) . An alternative, more explicit way of writing the wave function is obtained by defining an operator that antisymmetrizes the Hartree product
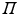
with
where
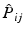
permutes the electron labels i and j in the Hartree product,
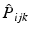
replaces the electron labels
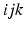
by jki and
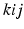
.
1.1
Write out explicitly the wave function
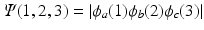
and show that
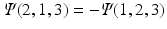
. What happens to the wave function when two electrons are described by the same one-electron function?
A serious deficiency is that neither a Hartree product nor a Slater determinant can be an eigenfunction of the N -electron Hamilton operator. Therefore
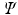
cannot be a solution of the time-independent electronic Schrdinger equation. The reason is that the N -electron Hamiltonian cannot be written as a sum of N one-electron Hamiltonians, due to the repulsive Coulomb interactions between the electrons. Nevertheless, in practice it turns out that we can work rather well with an approximate wave function consisting of only one Slater determinant if we choose that particular Slater determinant
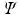
that yields the lowest energy expectation value
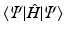
. In other words, we must vary the spin orbitals in
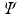
until we have reached the lowest value of
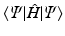
. The variation theorem tells us that this lowest value is still above the exact ground state energy E .
This variational procedure leads to a set of equations
called the HartreeFock equations, which determine the spin orbitals in
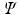
. The set of equations ( are eigenfunctions of
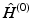
, with eigenvalues
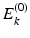
equal to the sum of the orbital energies of the spin orbitals used in
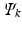
.
The calculation of the energy of a Slater determinant and the interaction between two different Slater determinants may seem a rather complicated task given the large number of terms ( N !) when the determinant is written in its explicit form. However, the SlaterCondon rules given in Table establish a few simple relations to calculate matrix elements between two Slater determinants.














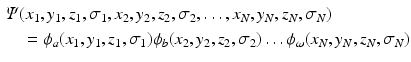
 . Obviously, the product suffers from important deficiencies with respect to the foundations of Quantum Mechanics. The wave function is not antisymmetric with respect to the permutation of any two electrons, and hence, does not fulfill the Pauli principle. However, by replacing the product by a determinant
. Obviously, the product suffers from important deficiencies with respect to the foundations of Quantum Mechanics. The wave function is not antisymmetric with respect to the permutation of any two electrons, and hence, does not fulfill the Pauli principle. However, by replacing the product by a determinant 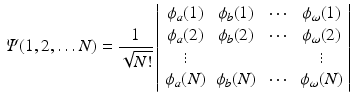
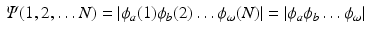
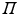
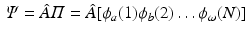
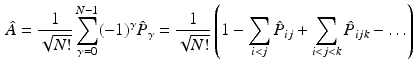
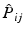 permutes the electron labels i and j in the Hartree product,
permutes the electron labels i and j in the Hartree product, 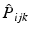 replaces the electron labels
replaces the electron labels 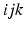 by jki and
by jki and 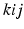 .
.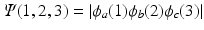 and show that
and show that 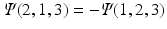 . What happens to the wave function when two electrons are described by the same one-electron function?
. What happens to the wave function when two electrons are described by the same one-electron function?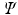 cannot be a solution of the time-independent electronic Schrdinger equation. The reason is that the N -electron Hamiltonian cannot be written as a sum of N one-electron Hamiltonians, due to the repulsive Coulomb interactions between the electrons. Nevertheless, in practice it turns out that we can work rather well with an approximate wave function consisting of only one Slater determinant if we choose that particular Slater determinant
cannot be a solution of the time-independent electronic Schrdinger equation. The reason is that the N -electron Hamiltonian cannot be written as a sum of N one-electron Hamiltonians, due to the repulsive Coulomb interactions between the electrons. Nevertheless, in practice it turns out that we can work rather well with an approximate wave function consisting of only one Slater determinant if we choose that particular Slater determinant 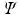 that yields the lowest energy expectation value
that yields the lowest energy expectation value 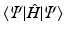 . In other words, we must vary the spin orbitals in
. In other words, we must vary the spin orbitals in 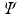 until we have reached the lowest value of
until we have reached the lowest value of 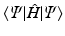 . The variation theorem tells us that this lowest value is still above the exact ground state energy E .
. The variation theorem tells us that this lowest value is still above the exact ground state energy E .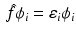
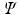 . The set of equations ( are eigenfunctions of
. The set of equations ( are eigenfunctions of 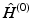 , with eigenvalues
, with eigenvalues 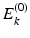 equal to the sum of the orbital energies of the spin orbitals used in
equal to the sum of the orbital energies of the spin orbitals used in 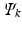 .
.