Ana Fred Maria Marsico - PATTERN RECOGNITION APPLICATIONS AND METHODS: 5th international conference, icpram
Here you can read online Ana Fred Maria Marsico - PATTERN RECOGNITION APPLICATIONS AND METHODS: 5th international conference, icpram full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. City: Cham, year: 2017, publisher: Springer International Publishing, genre: Home and family. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:PATTERN RECOGNITION APPLICATIONS AND METHODS: 5th international conference, icpram
- Author:
- Publisher:Springer International Publishing
- Genre:
- Year:2017
- City:Cham
- Rating:3 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
PATTERN RECOGNITION APPLICATIONS AND METHODS: 5th international conference, icpram: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "PATTERN RECOGNITION APPLICATIONS AND METHODS: 5th international conference, icpram" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Ana Fred Maria Marsico: author's other books
Who wrote PATTERN RECOGNITION APPLICATIONS AND METHODS: 5th international conference, icpram? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.














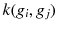 more quickly than RWK. NHK uses logical operations such as the exclusive OR on the label set of adjacent vertices, while WLSK uses a concatenation of label strings of the adjacent vertices to compute
more quickly than RWK. NHK uses logical operations such as the exclusive OR on the label set of adjacent vertices, while WLSK uses a concatenation of label strings of the adjacent vertices to compute 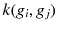 . The labels updated by repeating the hash or concatenation propagate the label information over the graph and uniquely represent the higher-order structures around the vertices beyond the vertex or edge level. An SVM with two graph kernels works well with benchmark data consisting of graphs.
. The labels updated by repeating the hash or concatenation propagate the label information over the graph and uniquely represent the higher-order structures around the vertices beyond the vertex or edge level. An SVM with two graph kernels works well with benchmark data consisting of graphs.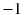 are equivalent in each column of the Hadamard matrix except for the first column, labels assigned by our graph kernel follow a binomial distribution with zero mean under a certain assumption. Therefore, the expected value of the label is zero, and for such labels, a large memory space is not required. This characteristic is used to compress vertex labels in graphs, allowing the proposed graph kernel to be computed quickly.
are equivalent in each column of the Hadamard matrix except for the first column, labels assigned by our graph kernel follow a binomial distribution with zero mean under a certain assumption. Therefore, the expected value of the label is zero, and for such labels, a large memory space is not required. This characteristic is used to compress vertex labels in graphs, allowing the proposed graph kernel to be computed quickly.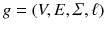 , where V is a set of vertices,
, where V is a set of vertices, 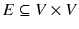 is a set of edges,
is a set of edges, 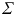 is a set of vertex labels, and
is a set of vertex labels, and 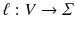 is a function that assigns a label to each vertex in the graph. Additionally, the set of vertices in graph g is denoted by V ( g ). Although we assume that only the vertices in the graphs have labels in this paper, the methods used in this paper can be applied to graphs where both the vertices and edges have labels. The vertices adjacent to vertex v are represented as
is a function that assigns a label to each vertex in the graph. Additionally, the set of vertices in graph g is denoted by V ( g ). Although we assume that only the vertices in the graphs have labels in this paper, the methods used in this paper can be applied to graphs where both the vertices and edges have labels. The vertices adjacent to vertex v are represented as 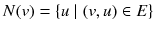 . A sequence of vertices from v to u is called a path, and its step refers to the number of edges on that path. A path is described as being simple if and only if the path does not have repeating vertices. Paths in this paper are not always simple.
. A sequence of vertices from v to u is called a path, and its step refers to the number of edges on that path. A path is described as being simple if and only if the path does not have repeating vertices. Paths in this paper are not always simple.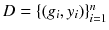 , where each example is a pair consisting of a labeled graph
, where each example is a pair consisting of a labeled graph 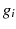 and the class
and the class