Introduction
The mechanistic study of the binding characteristics for a number of molecules, such as drugs, activators, inhibitors, etc., to a protein has been a subject of burgeoning interest among researchers for a long time [].
Apart from the bulk studies, single molecular level techniques can also be used to understand such interactions. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) is a powerful single molecular level technique where the temporal fluctuations of the fluorescence intensity from a very small observation volume (~1 fl) are correlated with its mean value []. In the present work, we have utilized the FSC technique to elucidate the binding process in single molecular level.
For the present work, we have chosen HSA as the model protein and coumarin 152 ( C152) as the model ligand. We have taken HSA as the model protein because it is thoroughly studied and well characterized []. However, they have reported a very high binding constant of 28 105 M1 for the binding. This is clear that the measured value of binding constant between C152 and serum albumin differs a lot and this may be due to the strong temperature effect in the binding process. Clearly, a wide temperature variation will provide a better understanding about the temperature-dependent interaction present in the systems. It is also worth to emphasize that in all the previous studies the binding location of C152 was estimated only by the molecular docking study. In the present study, we have used spectroscopic techniques, such as steady-state absorption and emission, Frster resonance energy transfer (FRET), site marker competitive experiment, and theoretical methods, such as molecular docking study and MD simulation, to estimate the binding constant and binding site of C152 with HSA for a wide temperature range from 278 K to 323 K. The temperature-dependent study also helped us to vividly understand the nature of interaction in the binding process. Conformation dynamics of HSA have also been measured for all the temperatures and it was employed to estimate the binding constant at single molecular level and compared with the bulk observations.
Experimental and Methods
Human serum albumin (HSA, essentially fatty acid free, Scheme ]. From the global analysis of the fluorescence correlation function of R6G of varying concentration, the value of has been observed different for the sample on coverslip as well as in the water-circulated sample cell.
Scheme 1
a Structure of human serum albumin (HSA) b Molecular structure of coumarin 152 ( C152)
Atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulations at 293 K and 313 K have been performed for aqueous solution of HSA complexed with C152 under the periodic boundary condition using Amber 9 for 2 ns [].
Results and Discussions
3.1 Binding Study of C152 with HSA at Different Temperatures
Interaction of C152 with serum albumin has already been studied at room temperature through its characteristic fluorescence enhancement upon binding [].
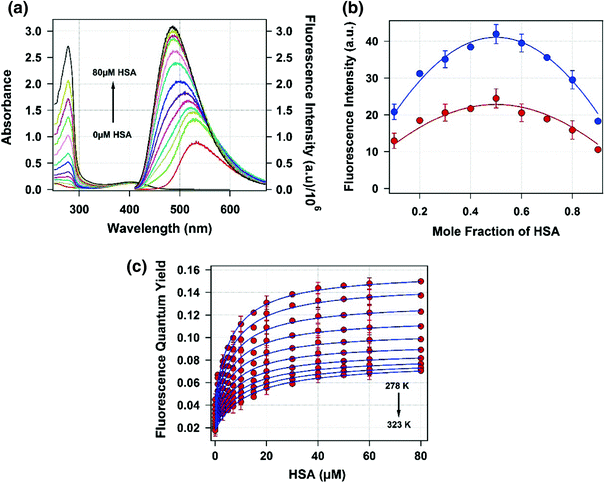
We also have used the fluorescence enhancement method to study the binding process between C152 and HSA at a wide temperature range from 278 K to 323 K. The absorption and emission spectrum of C152 in buffer solution is characterized by its maximum at 404 nm and 532 nm (ex = 400 nm), respectively. The absorption maximum of C152 remains unchanged on addition of HSA, whereas a blue shift of emission maximum was observed with a concomitant increase in the intensity (Fig. b shows the change in fluorescence intensity at 450 nm with mole fraction of HSA at 293 K and 313 K. For both the temperatures, the maximum fluorescence intensity was observed for 0.5 mol fraction of HSA. This clearly indicates that C152 forms a 1:1 complex with HSA in the studied temperature range.
Fig. 1
a Steady-state absorption ( left axis ) and emission ( right axis ) spectra of C152 (5 M) with increasing concentration of HSA at 298 K in pH 7.4 phosphate buffer. b Jobs plot for the complexation of C152 with HSA. Blue - and red - filled circles denote the observed fluorescence intensity of C152HSA complex at 450 nm for 293 K and 313 K. c Plot of observed fluorescence quantum yield ( red solid circles ) with error bars against HSA concentration at different temperatures varying from 298 K to 323 K with an interval of 5 K and solid blue line is the best fit with Eq.
The fluorescence enhancement of C152 upon binding to HSA was used to calculate the binding constant of the process. At 278 K, the fluorescence quantum yield of C152 in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) is found to be 0.045, which monotonically increases on addition of HSA in the system and for 60 M HSA the fluorescence quantum yield of C152 is found to be 0.15. Fluorescence lifetime of C152 also increased in this process. At 278 K, the average lifetime of C152 in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) is 0.75 ns, which increases to 5.1 ns on addition of 60 M HSA. The fluorescence quantum yield and lifetime of C152 and its reliance on binding process are also found to depend on the temperature. At 323 K the fluorescence quantum yield and lifetime of C152 in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) are found to be 0.018 and 0.36 ns, which increases to 0.069 and 3.9 ns on addition of 60 M HSA.
For 1:1 complexation ( P + D PD ), the variation of fluorescence quantum yield of C152 as a function of total protein concentration can be written as