Contents
Guide

Publisher: Mike Sanders
Associate Publisher: Billy Fields
Senior Acquisitions Editor: Brook Farling
Development Editor: Christopher Stolle
Cover and Book Designer: Becky Batchelor
Photographer: Kimberly Davis
Illustrator: Becky Batchelor
Prepress Technician: Brian Massey
Proofreader: Laura Caddell
Indexer: Celia McCoy
PRODUCTION, LONDON
Digital Producer: Alex Valizadeh
Senior Digital Producer: Miguel Cunha
DIGITAL OPERATIONS, DELHI
Head of Digital Operations: Manjari Hooda
Producer: Rahul Kumar
Editor: Etika Kapil
Operations Coordinator: Tauhid Nasir
First American Edition, 2017
Published in the United States by DK Publishing
6081 E. 82nd Street, Indianapolis, Indiana 46250
Copyright 2017 Dorling Kindersley Limited
A Penguin Random House Company
16 17 18 19 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
001296238March/2017
All rights reserved.
Without limiting the rights under the copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise), without the prior written permission of the copyright owner.
Published in the United States by Dorling Kindersley Limited.
eISBN: 9781465458193
Library of Congress Catalog Card Number: 2016950733
Note: This publication contains the opinions and ideas of its authors. It is intended to provide helpful and informative material on the subject matter covered. It is sold with the understanding that the authors and publisher are not engaged in rendering professional services in the book. If the reader requires personal assistance or advice, a competent professional should be consulted. The authors and publisher specifically disclaim any responsibility for any liability, loss, or risk, personal or otherwise, which is incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and application of any of the contents of this book.
Trademarks: All terms mentioned in this book that are known to be or are suspected of being trademarks or service marks have been appropriately capitalized. Alpha Books, DK, and Penguin Random House LLC cannot attest to the accuracy of this information. Use of a term in this book should not be regarded as affecting the validity of any trademark or service mark.
DK books are available at special discounts when purchased in bulk for sales promotions, premiums, fund-raising, or educational use. For details, contact: DK Publishing Special Markets, 345 Hudson Street, New York, New York 10014 or .
www.dk.com
BEEKEEPING
BEGINNING
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO MAKE YOUR HIVE THRIVE!
Tanya Phillips
Introduction
Welcome to the amazing world of honeybees!
Until I became a beekeeper, I had no idea just how fascinating and intelligent honeybees were. Theyve survived for centuries using their keen senses of vision, taste, and smell to thrive and multiply throughout most areas of the world. Theyre one of the few living creatures that cause no harm in order to live their day-to-day lives. In fact, when they take what they need to eat for survival, they actually benefit others through their pollination of plants, in the creation of beeswax, and in the making of excess honey that we get to harvest and eat.
This book is designed to give you all the information youll need to get started with keeping bees and some of the best techniques to use for hive management as your colony grows from season to season and for years to come. Bees are truly remarkable and resilient creatures that I hope youll come to respect and admire as much as I do.
Every beekeeper has their own story as to why they started keeping bees. I read about a class on top-bar hives that was advertised in a Craigslist ad and thought it looked interesting to me. I thought it might be a fun hobby to try with my husband, so we signed up for the class. Once I committed to ordering bees and got my husband working on hive construction, I started researching beekeeping and joined a local county bee club to learn more. I learned bees were having trouble survivingand dying from something called CCDand suddenly, it wasnt about having a hobby anymore. I was on a mission to save the honeybee.
We began our ventures into beekeeping by rescuing bee swarms, and our apiary quickly grew to 20 colonies our first year. Weve easily doubled our numbers each year with swarms and splits. What started as a little hobby quickly became my full-time business.
How will your bee story begin?
Tanya Phillips
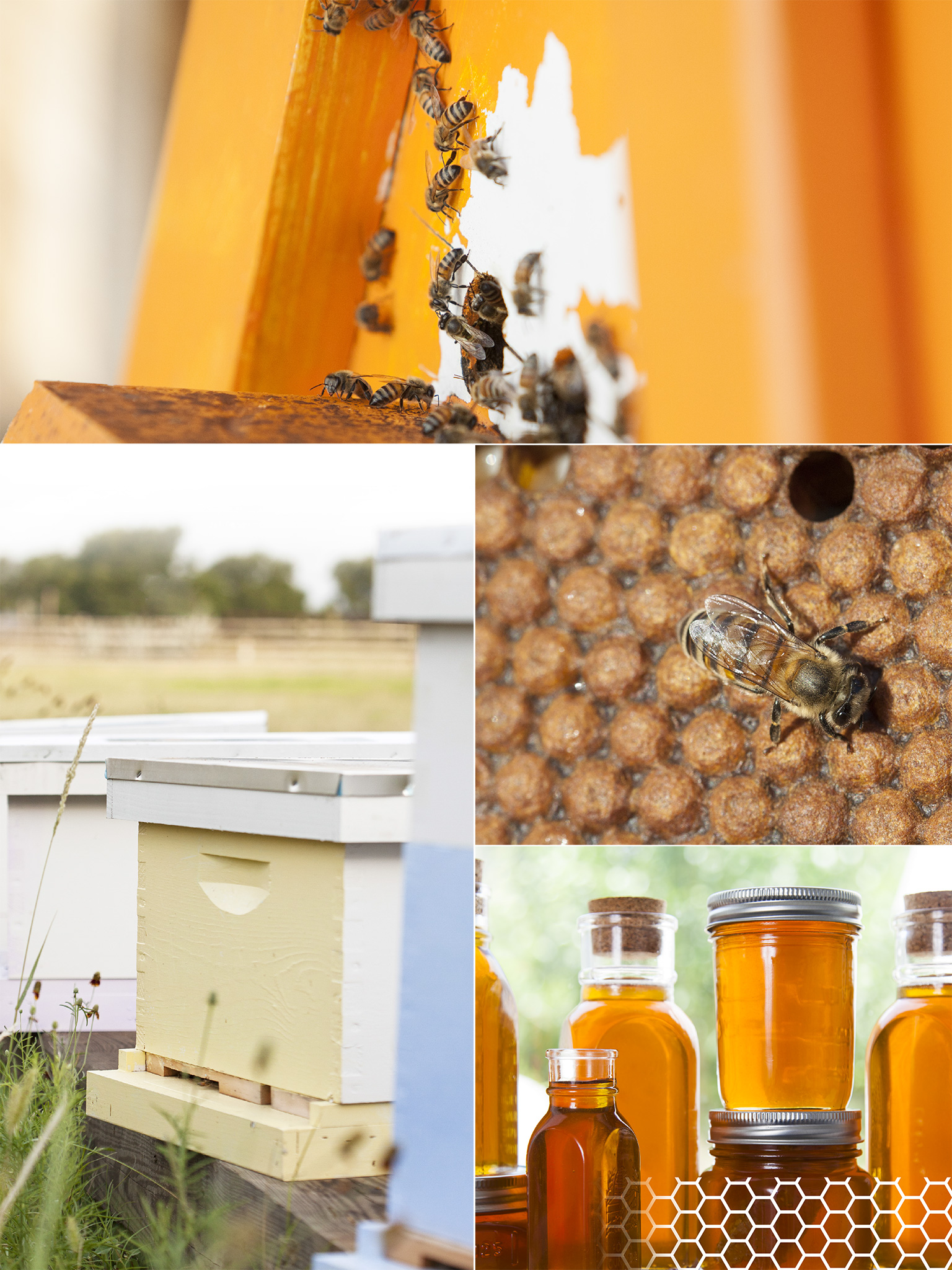

All About Honeybees
One of the best ways to become a good beekeeper is to better understand the creatures youre dealing with. Bees have become more and more important to humans in recent decades, and because their survival is constantly at risk, knowing more about the vital role they play in our lives will help beekeepers everywhere ensure they continue to flourish.
In this chapter, youll learn about the physiological changes that occur in honeybees based on breed, gender, and caste. Youll also learn about the importance of bees for human survival as well as how the colony functions as a whole. Its amazing how 40,000 bees can work together on common goalsall with the best interest of the entire colony at heart.
Why We Need Honeybees
Despite their name, honeybees do more than make delicious honey. Theyre also responsible for one third of the worlds food supply as well as the survival of plants and trees. And they might just be the best superorganism role models for Earths creaturesincluding humans.
They Pollinate Crops
Honeybees pollinate more than $15 billion worth of crops in the United States each year. In fact, beekeepers rent out more than 2.5 million colonies each year for the pollination of about 90 different US crops, especially almonds, apples, alfalfa seed, and vegetables. These crops grow on approximately 3.5 million acres, and they translate to one third of our daily dietand honeybees make sure those foods remain in abundant supply. Bees are typically active no matter what season it is, meaning humans can rest assured knowing well have food year-round. But like any organism, honeybees also need food to surviveand that all begins with pollination.
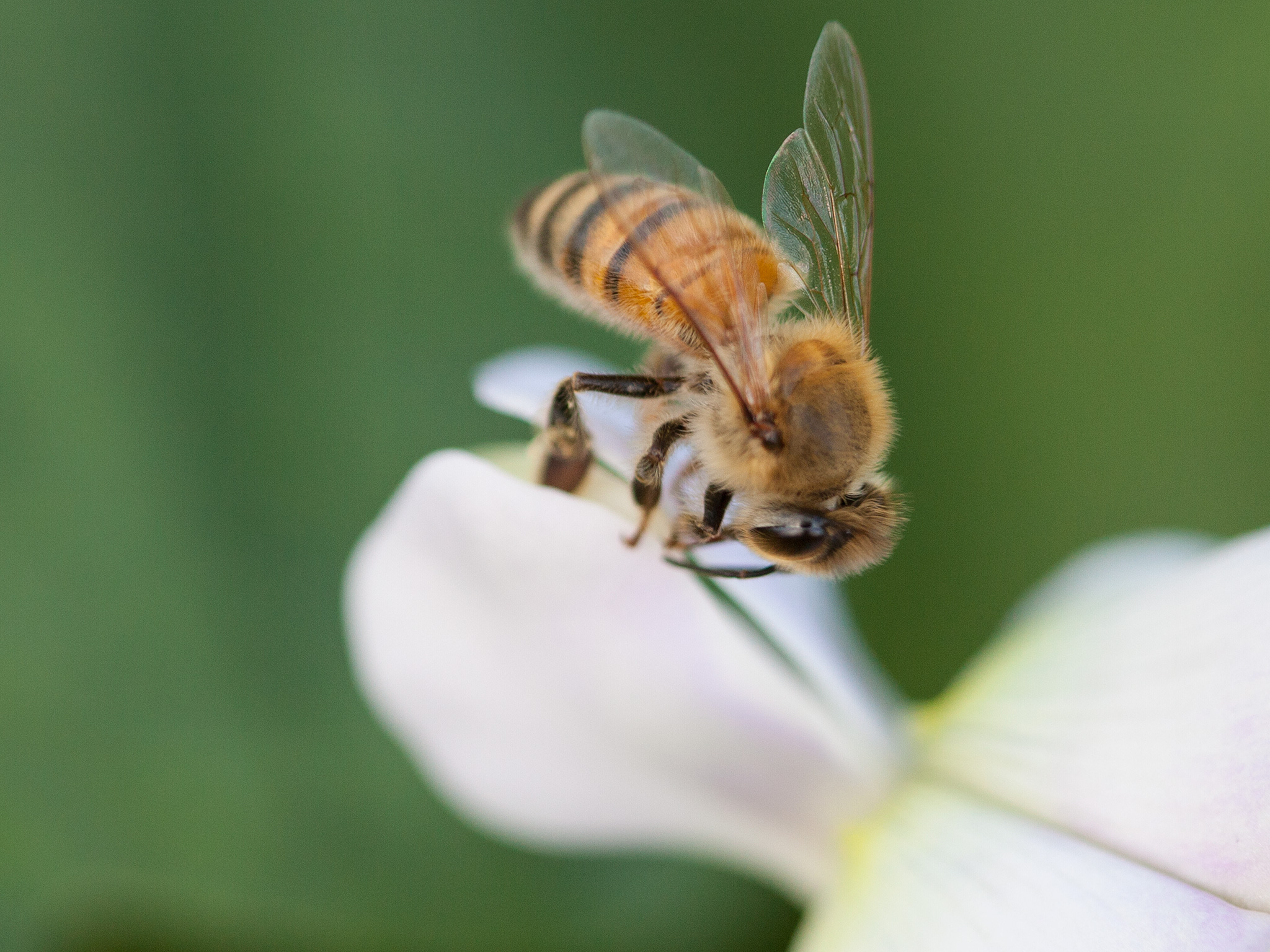
They Pollinate Flowers
Bees pollinate flowers more than any other insect and more than any other plant. Surprisingly, bee pollination is actually an accidental process that occurs during the course of their natural foraging behaviors. As a worker bee moves from flower to flower, drinking nectar, she brushes up against anthers full of pollen, which transfer to the hairs covering her body. As she flies along, she begins combing the pollen with her legs and transferring it to the pollen baskets ( corbicula ) on her hind legs. During that process, she inadvertently drops some of the pollen back onto other flowers, causing pollination.