This document describes the procedure for preparation and quality control (QC) testing of blood culture bottles (adult and pediatric) for medical use.

Figure 3 Blood culture bottle metal cap crimping device.
Quality control
Internal Quality Control (IQC)
Sterility control . Depending on the batch size, follow the sampling plan as outlined in .
Growth promotion testing
Strains used as positive control
- Disinfect the bottle septum with 70% ethanol.
- Use a fresh overnight subculture of the two strains.
- Prepare a 0.5McFarland solution for each strain by using the reference tube for 0.5McFarland.
Table 1 Sampling plan for sterility control of blood culture bottles from Australian Guidelines ()
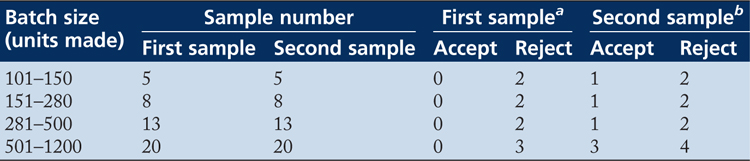
Interpretation: For a batch of 520 bottles, the quality control sample would be 20 bottles.
a First Sample: Accept the batch if none of the bottles are contaminated. If 3 bottles are contaminated, reject the batch. If 1 or 2 bottles are contaminated, collect another sample of 20 bottles as second sample. WARNING!! Total the number of contaminated bottles between the first and second samples!
b Second Sample: Accept the batch if the number of contaminated bottles (sample 1 plus sample 2) is equal to or less than 3 bottles. If the cumulative number of bottles is equal to or greater than 4, reject the batch.
- Perform a 10 -5 dilution.
- Inoculate one bottle from each batch with:
- 100 ml of 10 -5 dilution of each organism
- 5 ml of sheep blood
- Label the bottle with the date, operator name, and organism name.
- Incubate both bottles at 35C for a maximum of 3 days.
- When bottle appears turbid, subculture:
- S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619 on BAP
- H. influenzae ATCC 49247 on chocolate agar
- Incubate 24 h in a candle jar.
- Check for growth.
- Record the data on QC form for: Preparation of Blood Culture Bottles .
Independent External Quality Control (EQC)
Performed at Sihanouk Hospital Center of Hope microbiology laboratory using SOP UHS-05, Enumeration of Microorganisms.
Safety and security
- BHI powder: use a N95 mask.
- ATCC strains: use a biosafety cabinet.
References
Brain Heart Infusion M210-5kg, HiMedia Laboratories datasheet http://www.theasm.org.au/assets/ASM-Society/Guidelines-for-the-Quality-Assurance-of-Medical-Microbiological-culture-media-2nd-edition-July-2012.pdf
Sodium polyanethol sulfonate (S.P.S.) datasheet FD786-25G HiMedia Laboratories.
Microbiology of Food, Animal Feed and Water Preparation, Production, Storage and Performance Testing of Culture Media. ISO 11133:2014.
Guidelines for the Quality Assurance of Medical Microbiological Culture Media, Australian Society of Microbiology (17).
Batch Life Process for Blood Culture bottles, prepared by Integrated Quality Laboratory Services.
APPENDIX B STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD CULTURE
Test summary
Blood culture processing assists in the diagnosis of bacteremia and sepsis. Pathogens include Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae , and other Enterobacteriaceae, Streptococcus pneumoniae , and Haemophilus influenzae . Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi, other Salmonella , and Burkholderia pseudomallei are important blood culture isolates seen in Cambodia.
Principle
Blood is a sterile fluid. Inoculation of blood in prepared media bottles and incubation may detect the presence of organisms in the blood. Growth of an organism allows us to perform identification and susceptibility testing.
Specimen Handling and Preparation
- Blood samples are inoculated into blood culture media bottles.
- It is encouraged to collect two separate venipuncture collections per patient.
- Ten milliliters of blood for each adult collection (20 ml total in two bottles) and 2 to 5 ml in one bottle for a pediatric collection).
- It is important to use aseptic technique when collecting blood for blood culture so that skin flora or environmental organisms are not introduced into the bottles.
- Refer to blood culture collection procedures. DMDP document code: 084 and training material video blood culture collection procedure.
Quality Control
Appropriate QC testing should be performed for all media used, biochemical testing, Gram stain, and antimicrobial susceptibility test (AST) performed according to the laboratory QC procedures.
Reagents, materials, and equipment
- Adult and pediatric blood culture bottles
- Venting needles
- Media for subculture of blood from blood culture bottles:













