After the second edition of the book "Theory, laboratories and exercises for Mikrotik RouterOS" (actually only in italian language) some readers asked to extend the work to other key topics of Mikrotik's RouterOS system. This booklet was born starting from this request and sorting out my notes on advanced routing, it wants to deepen the main themes of routing through the lens of the RouterOS system exploration used in Mikrotik products. At the same time, this book aims to be a concrete preparation for the Mikrotik Certified Routing Engineer (MTCRE) exam even through the analysis of real cases in which advanced routing is a fundamental and decisive tool. If you want you can tweet tagging @vittore. Due to the complexity of the topics I had to left out some guidelines that had helped me in the first book: in almost all the laboratories of this book more than one router is needed and the laboratories are not located at the end of each chapter but have been moved in useful points to reinforce the knowledge just acquired.
This text is a work-in-progress. All suggestions are welcome. If you have directions, write to vittore@zen.pn.it . A special thanks goes to my colleagues who have sacrificed themselves in trying all the exercises.
Basic routing
Second star to the right, ...and straight on till morning! Edoardo Bennato
Routing is the basis of the network functionality implemented by level 3 entities (OSI) and allows two nodes A and B, not directly connected, to communicate each other through the collaboration of other nodes placed on a path in the network that connects A and B.
The task of the network layer is therefore the transmission of packets between two arbitrary hosts, which in general are not directly connected, that is they do not have a direct connection between them. In the ISO / OSI model, the network layer software is present in all the nodes of the network, while that of the higher levels is present only in the terminal nodes. In detail, the functions of the network layer are:
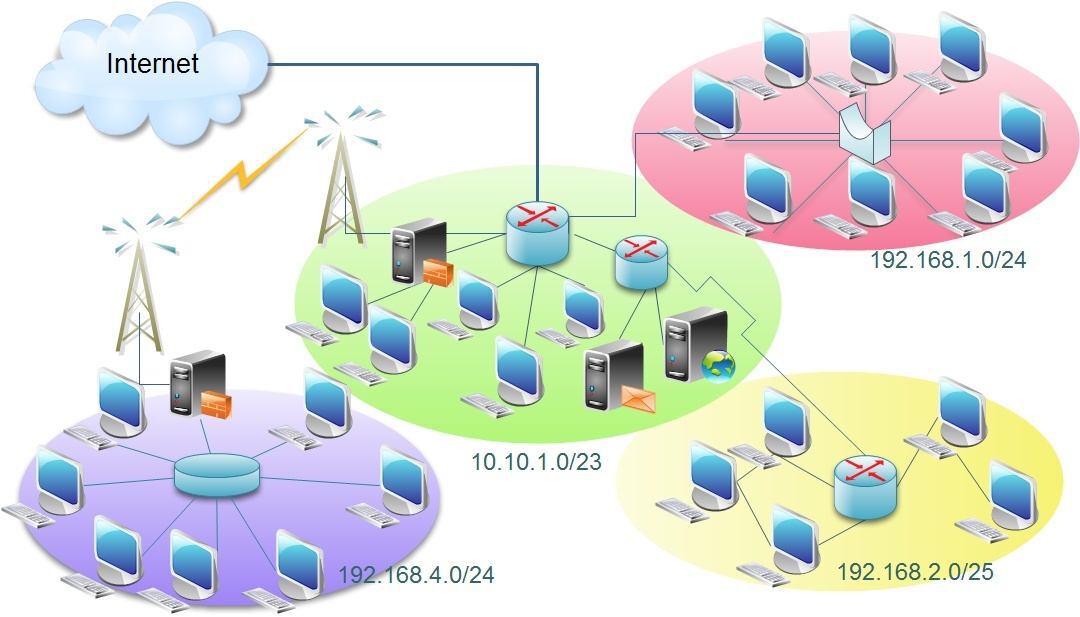
Purpose of routing: connecting networks.
Routing is necessary when the network starts to become complex; If we want:
- to be able to monitor and better manage the network;
- make the network more secure as firewall filters become simpler and more complete;
- to improve performance by concentrating broadcast traffic only in each subnet / network;
- to connect together public IP networks;
- to connect different Wide Area Netwok (company, provider, ...).
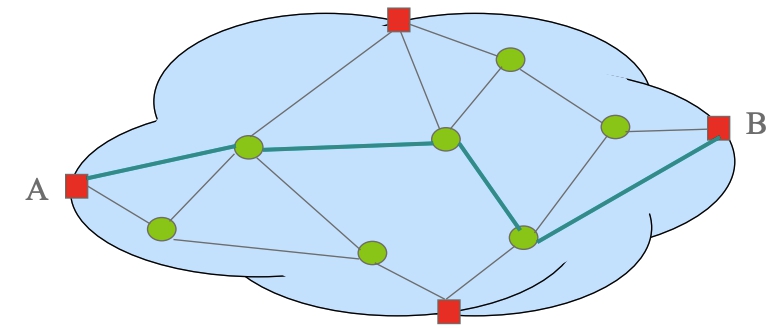
The principle on which IP routing is based is very simple: send packets on the shortest path to the destination. The calculation is performed in a distributed way by the routers through an exchange of information among them; in the table of each router possesses and it is indicated the direction the packet must take, only the next router on the path (next hop) is indicated, not the entire path. This approach exploits the property of graphs according to which even the sub-paths of a minimum path are minimal.
Routing classification
Routing, ie the process for forwarding packets from a network to other networks can be done using:
- Static routing - In this case the administrators perform the routing manually defining each network and its destination gateway and repeating this operation for each router present in all the connected networks.
- Dynamic routing - In this case the administrators make only a simple configuration in which the dynamic routing function is enabled on each router and the routers automatically search for the routes and the best gateway from all the connected networks.
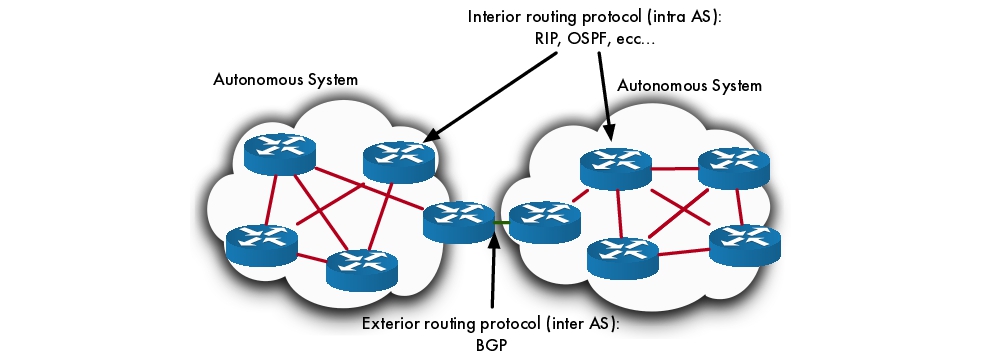
Classification of dynamic routing protocols
routing-protocols
RouterOS routing components
The router keeps the routing information in two separate spaces:
- RIB (Routing Information Base) - is the routing table
- FIB (Forwarding Information Base) - is the forwarding table
Router Information Base (RIB)
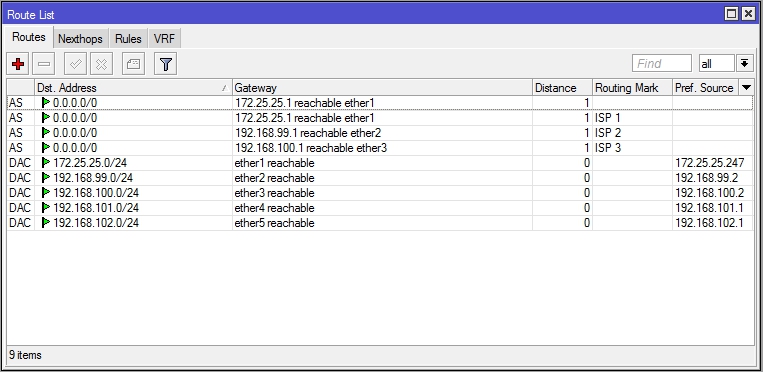
rib The routing table is a table of data that in a specific router lists all the known routes to certain networks. For each route the metric that represents the cost that is spent along this route is indicated. The routing table consists of:
- all routes collected by dynamic routing protocols;
- all paths for the connected networks, that is for the interfaces directly connected to the router;
- each additional route manually added (static routes).
In RouterOS the routing table can be displayed using menu IP > Route > List .
The routing table is used:
- to filter the routing information of all routing protocol types;
- to calculate and choose the best route for a certain network;
- to create and update the forwarding table (see section );
- to distribute routing information using dynamic routing protocols.
For each entry in the routing table there are letters indicating the route status according to the abbreviations shown in the table :
Property | Label | Description |
disabled | X | The route is disabled ie it is not used. |
active | A | The route is used to forward packets. |
dynamic | D | The route was created by the software automatically. |
It will not be exported and cannot be modified directly. |
connected | C | Connected route. |
statica | S | Static Route. |
rip | r | Created through the RIP protocol. |
bgp | b | Created through the BGP protocol. |
ospf | o | Created through the OSPF protocol. |