Appendix
Rhythm Summary
SINUS RHYTHMS
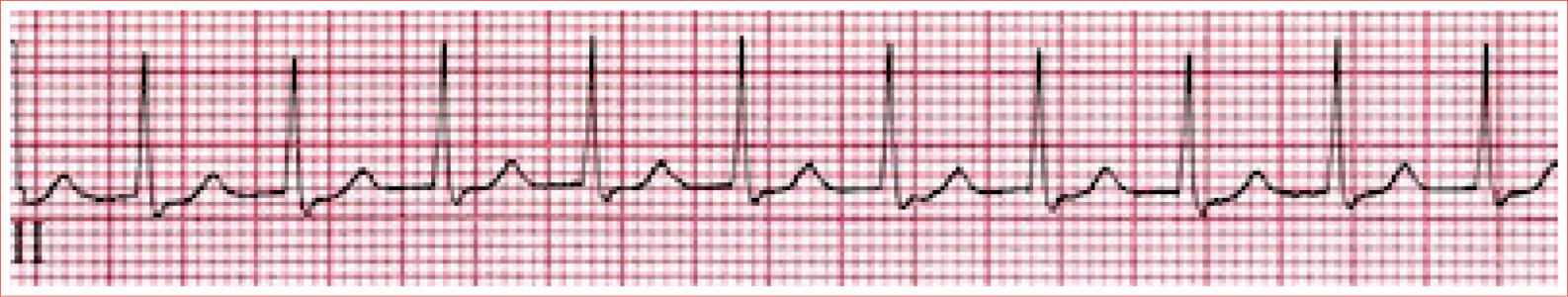
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Regular rhythm
Rate of 60 to 100 beats/minute
QRS complexes are typically less than 100 ms duration
P waves are present and ALWAYS upright in leads I and II and inverted in aVR
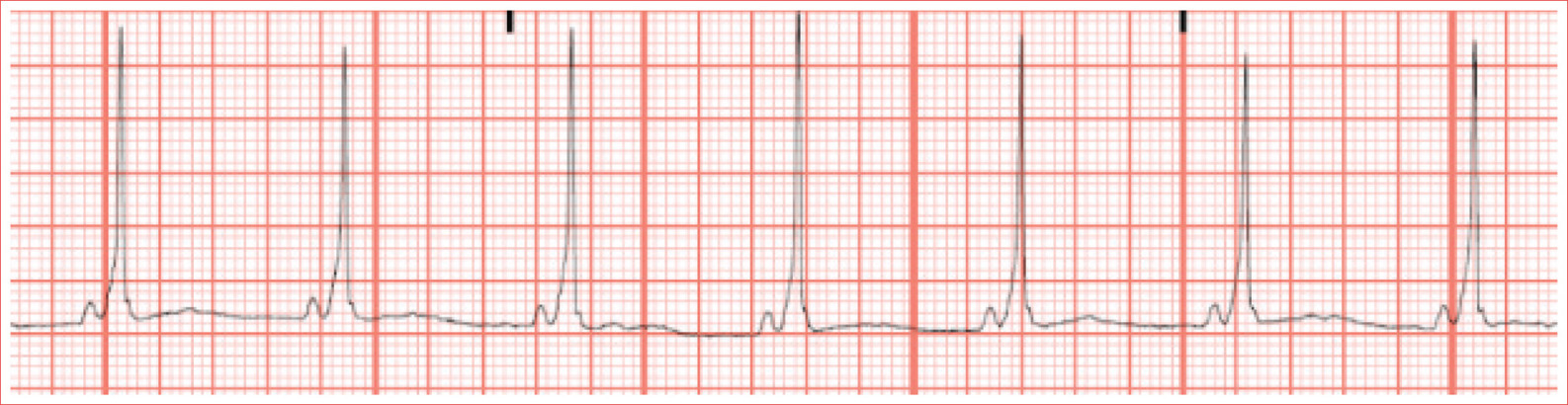
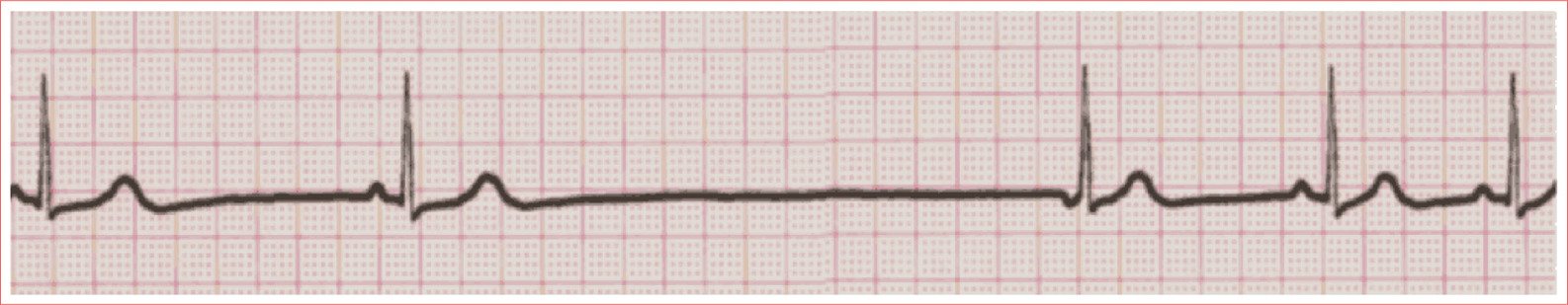
Sinus Bradycardia
Regular rhythm
Rate less than 60 beats/minute
QRS complexes are typically less than 100 ms duration
P waves upright in leads I and II and inverted in aVR
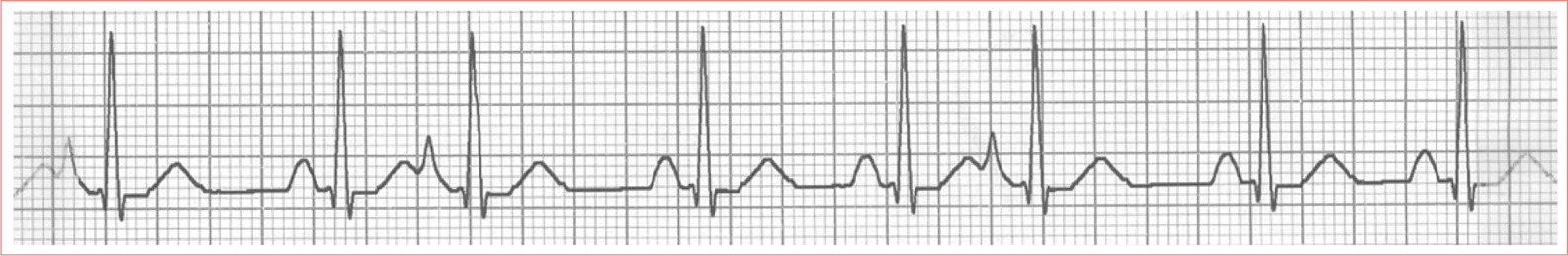
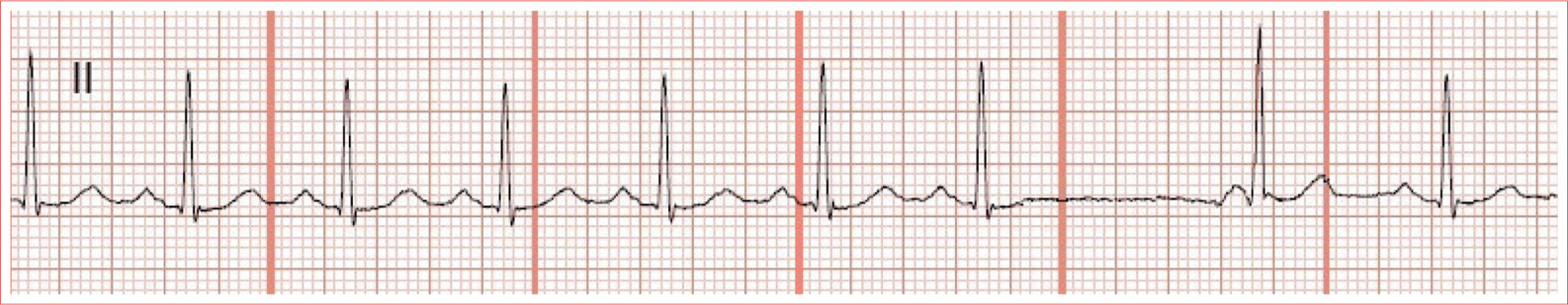
Sinus Tachycardia
Regular rhythm
Rate greater than 100 beats/minute
QRS complexes are typically less than 100 ms duration
P waves are upright in leads I and II and inverted in aVR
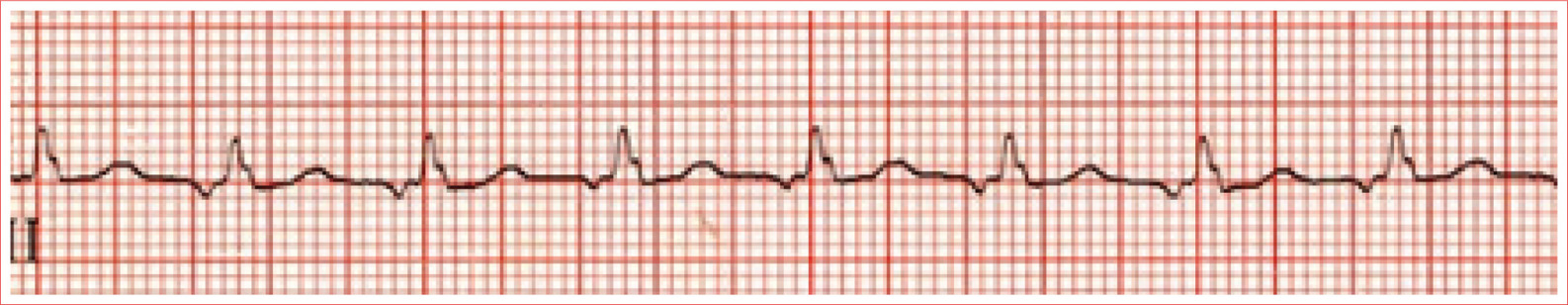
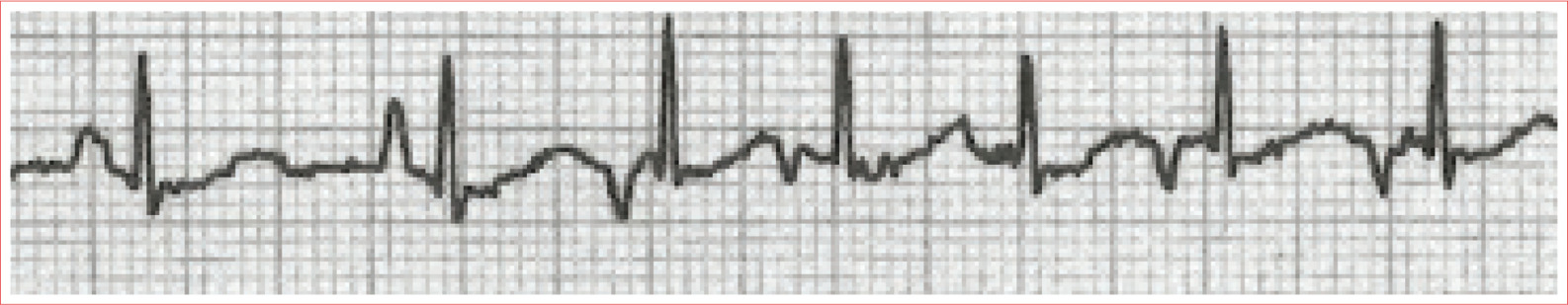
Sinus Arrhythmia
Irregular rhythm, P-P varies by more than 0.16 second
QRS complexes are typically less than 100 ms duration
P waves are upright in leads I and II and inverted in aVR
SUPRAVENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS
Premature Atrial Complex
The P wave occurs before the next P wave was due
The P wave has a different appearance than the P wave
After the PAC, there is often a small pause before the SA node resumes control
The QRS complex is usually identical to all other QRS complexes
AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT)
Regular rhythm
Rate usually 140 to 220 beats/minute
QRS is typically narrow
P waves are often hidden in the QRS complex
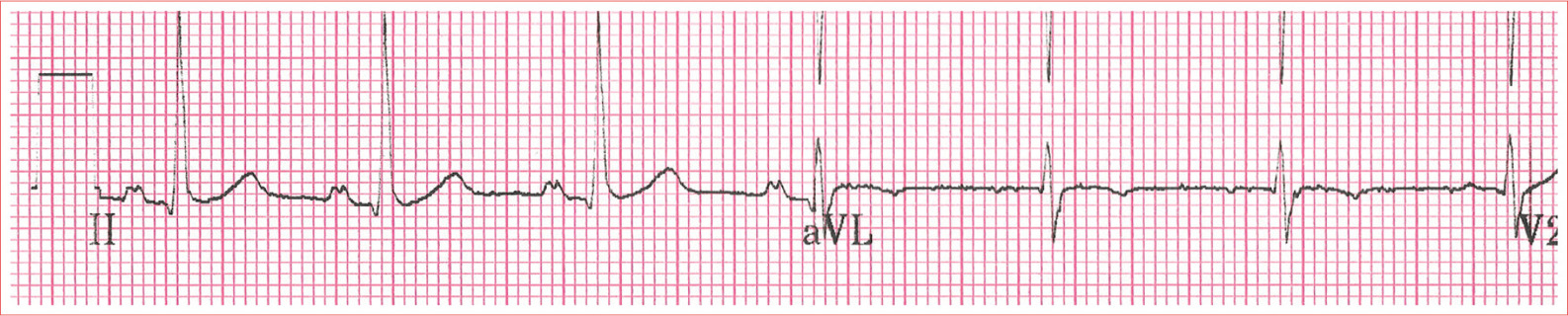
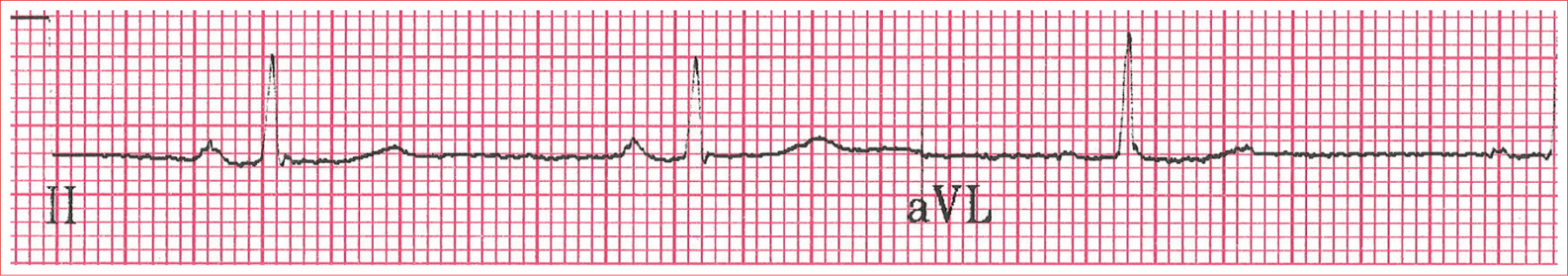
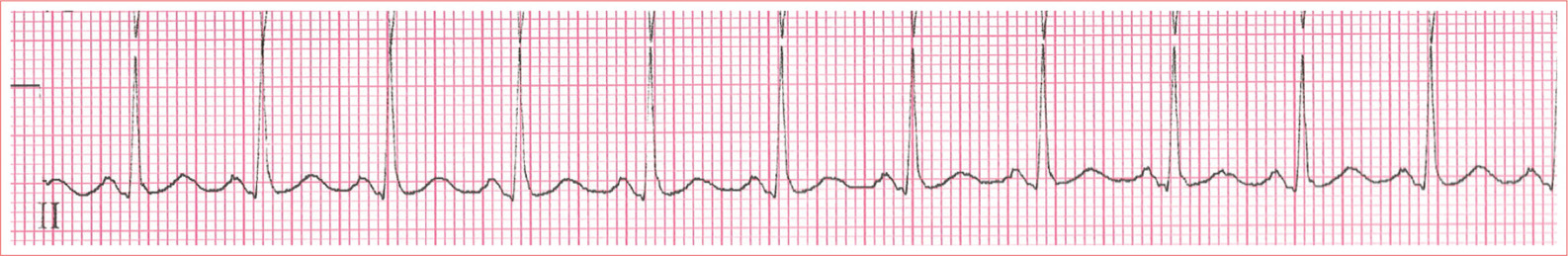
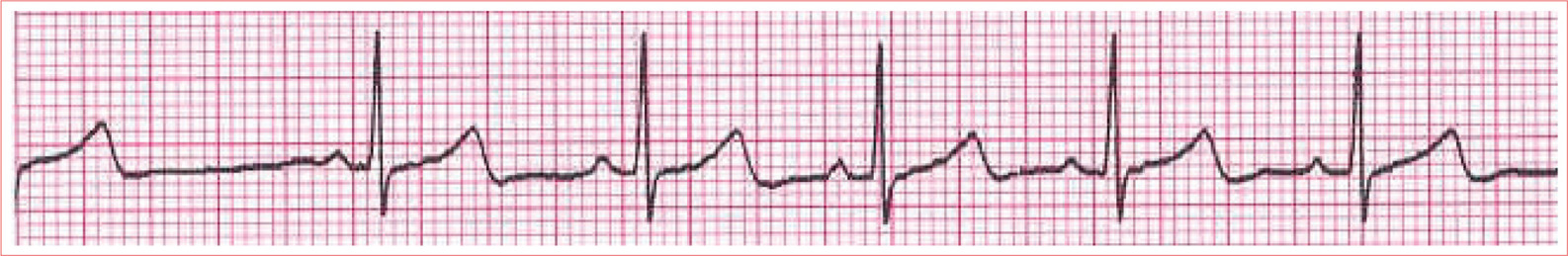
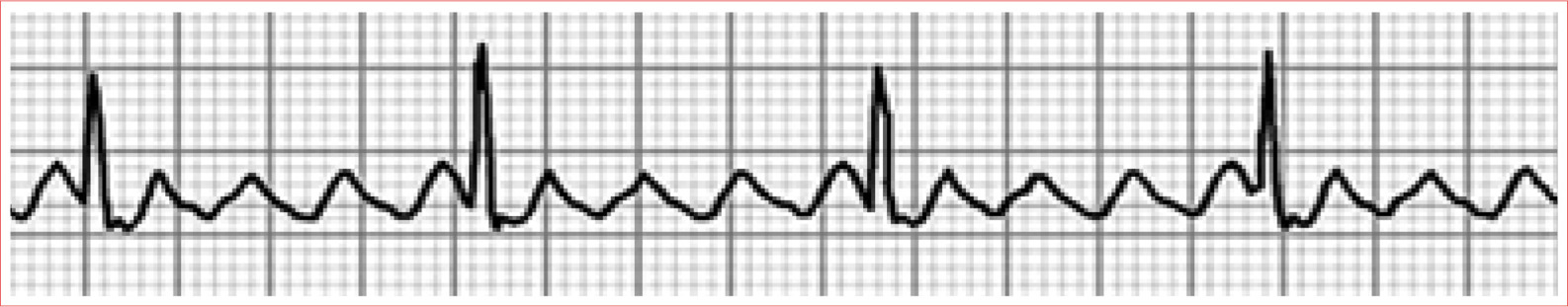
WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome
Short PR interval
Delta wave; slurred upstroke to start QRS
Prolonged QRS complex greater than 0.11 second
ST-T-wave discordance
Pseudo-infarction pattern
Paroxysmal Ectopic Atrial Tachycardia
Regular rhythm
Rate greater than 100 beats/minute
QRS complex is typically narrow (<0.12 second)
P wave has a different morphology than the sinus beat
Isoelectric baseline
Often sudden in onset and sudden stop
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia/Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
Rhythm is irregularly irregular
MAT rate greater than 100 beats/minute
WAP rate less than 100 beats/minute
Narrow QRS complex
Three or more distinct P waves in a single lead
Isoelectric baseline
Atrial Escape Beat/Rhythm
Occurs after delay in sinus activity
P wave with different morphology than sinus beat, may be inverted
Rhythm is regular
Rate typically less than 60 beats/minute
Narrow QRS
PR interval greater than 0.12 second
Junctional Escape Beat/Rhythm
Occurs after delay in sinus activity
Rhythm is regular
Narrow QRS complex
P waves are absent or inverted immediately before or after QRS complex in lead II
PR is less than 0.12 second, when present
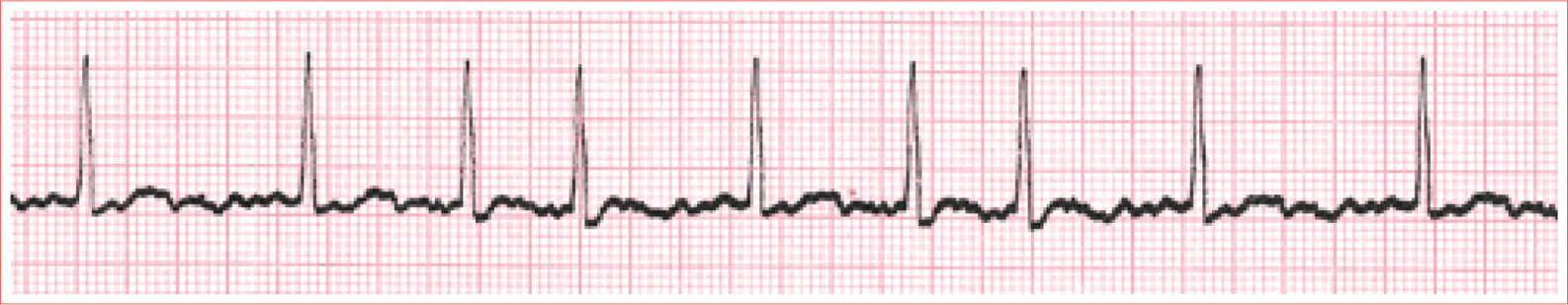
Atrial Fibrillation
Irregularly irregular ventricular response
Ventricular rate is commonly between 90 and 170 beats/minute
QRS complex is narrow
Absence of isoelectric baseline
No identifiable P waves
Atrial Flutter
May have regular or irregular ventricular response
Ventricular rate is commonly 140 to 160 beats/minute, but variable
Ventricular rate is a ratio of atrial rate, most commonly a 2:1 AV ratio
Narrow QRS complex
Flutter or sawtooth waves
Absence of isoelectric baseline
VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS
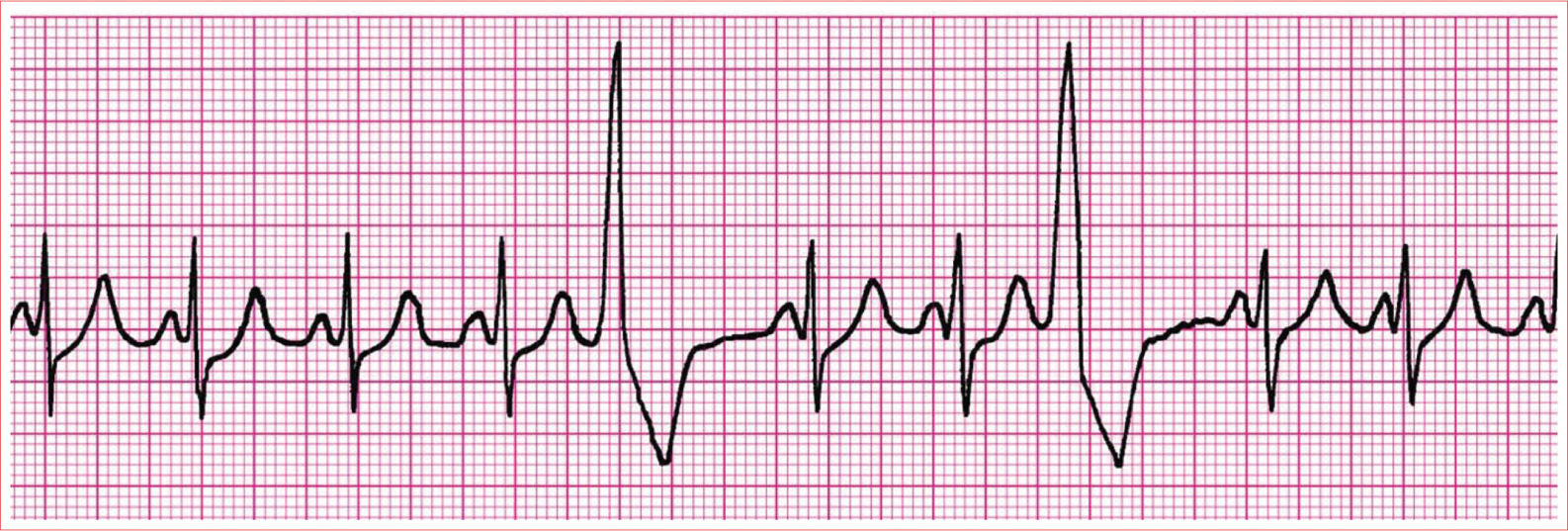
Premature Ventricular Complexes
No apparent P wave
Premature QRS complex
Wide QRS (>0.12 second)
Bizarre
ST-T-wave discordance
Compensatory pause
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Three or more consecutive PVCs with same morphology
Regular rhythm
Rate greater than 120 beats/minute
Wide QRS
AV dissociation
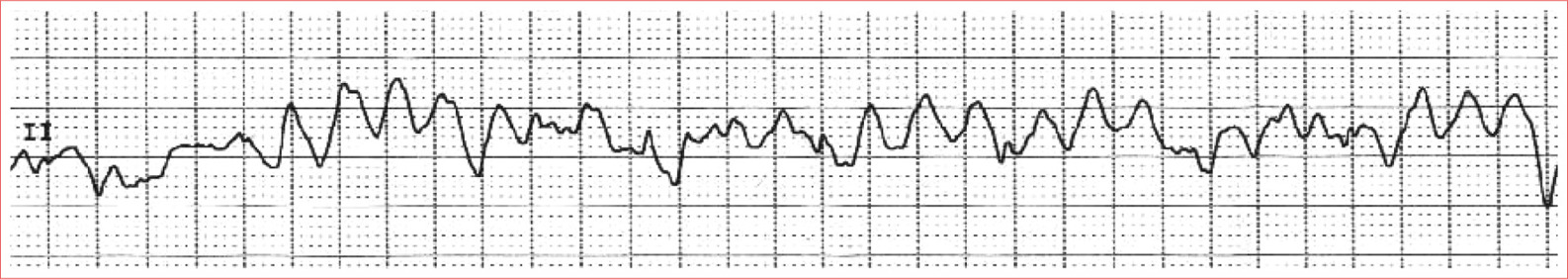
Ventricular Fibrillation
Fibrillatory waves
Irregular
Rate 150 to 500 quivers/minute
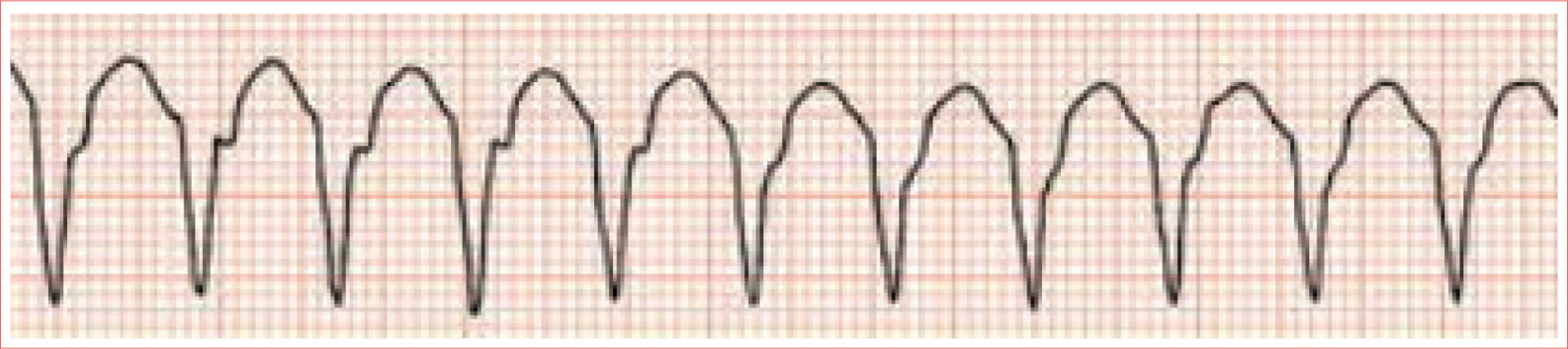
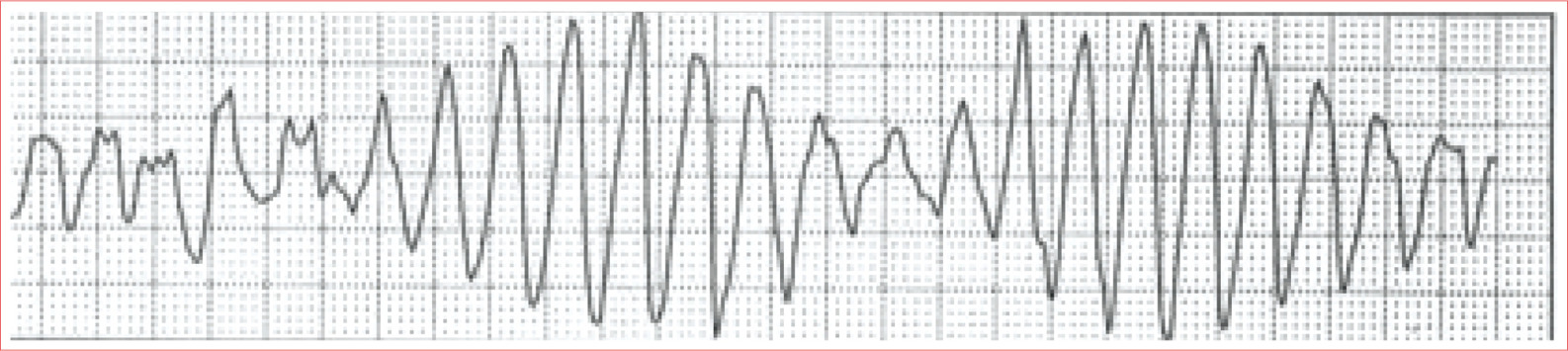
Torsades de Pointes
Irregular rhythm
Rate 150 to 200 beats/minute
Gradual shift in both axis and amplitude of QRS complexes
QT prolongation was cause
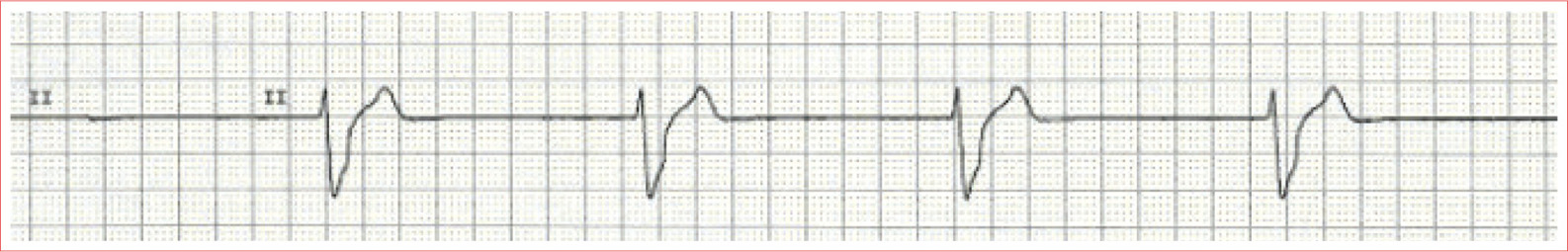
Ventricular Escape Rhythm
Regular rhythm
No P waves
Wide QRS
Rate is 20 to 50 beats/minute
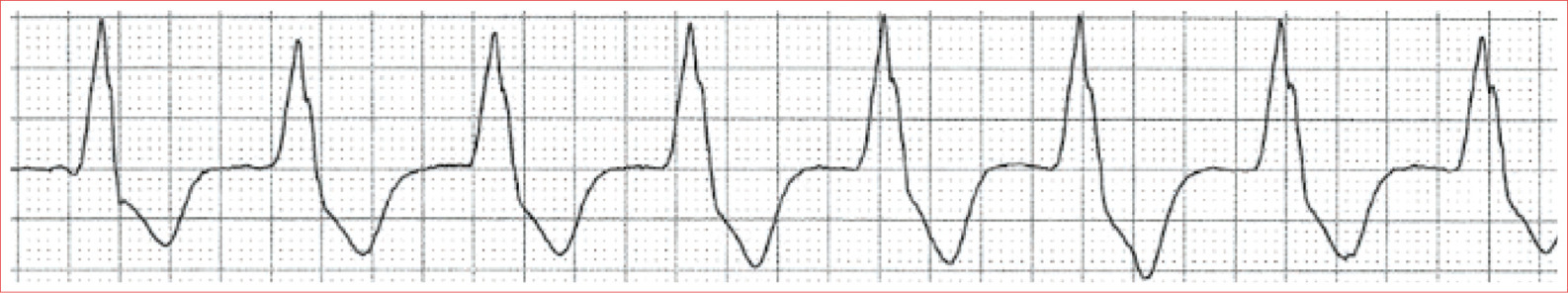
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
Regular rhythm
Absence of P waves
Next page