
Table of Contents
List of Tables
- Chapter 1
- Chapter 8
List of Illustrations
- Chapter 1
- Chapter 2
- Chapter 3
- Chapter 4
- Chapter 5
- Chapter 6
- Chapter 7
- Chapter 8
- Chapter 9
Guide
Pages
Carbonyl Compounds
Reactants, Catalysts and Products
Feng Shi
Hongli Wang
Xingchao Dai

Authors
Feng Shi
State Key Laboratory for Oxo Synthesis and Selective Oxidation
Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics
Chinese Academy of Sciences
No.18, Tianshui Middle Road
Lanzhou 730000
China
Hongli Wang
State Key Laboratory for Oxo Synthesis and Selective Oxidation
Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics
Chinese Academy of Sciences
No.18, Tianshui Middle Road
Lanzhou 730000
China
Xingchao Dai
State Key Laboratory for Oxo Synthesis and Selective Oxidation
Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics
Chinese Academy of Sciences
No.18, Tianshui Middle Road
Lanzhou 730000
China
Cover: Andreas Prott/Shutterstock
All books published by WILEYVCH are carefully produced. Nevertheless, authors, editors, and publisher do not warrant the information contained in these books, including this book, to be free of errors. Readers are advised to keep in mind that statements, data, illustrations, procedural details or other items may inadvertently be inaccurate.
Library of Congress Card No.:
applied for
British Library CataloguinginPublication Data
A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library.
Bibliographic information published by the Deutsche Nationalbibliothek
The Deutsche Nationalbibliothek lists this publication in the Deutsche Nationalbibliografie; detailed bibliographic data are available on the Internet at .
2022 WILEYVCH GmbH, Boschstr. 12, 69469 Weinheim, Germany
All rights reserved (including those of translation into other languages). No part of this book may be reproduced in any form by photoprinting, microfilm, or any other means nor transmitted or translated into a machine language without written permission from the publishers. Registered names, trademarks, etc. used in this book, even when not specifically marked as such, are not to be considered unprotected by law.
Print ISBN: 9783527347360
ePDF ISBN: 9783527825608
ePub ISBN: 9783527825615
oBook ISBN: 9783527825622
Preface
Chemical industry has made a great contribution to the development of human society because it creates a great range of products such as dye, pesticides, paints, pharma drugs, fertilizers, and plastic, etc. Among the different chemicals, the carbonyl compounds represent one of the most basic chemicals in the chemical industry. Carbonyl compounds include CO, CO2, aldehydes, ketones, carboxyl acids, ester, amides, carbamate, urea, carbonate, and so on. Carbonyl compounds are typical building blocks in myriad of natural products, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and functional materials, etc. In addition, they are indispensable precursors for the preparation of functional molecules and materials. It is considered that about 60% chemical processes are involving the building and transformation of the carbonylcontaining molecules. Thus, the building and transformation of carbonylcontaining molecules hold a very important position in chemical industry process and organic synthesis. Normally, the synthesis of carbonylcontaining molecules and transformation of carbonylcontaining molecules are independently discussed. In fact, many reactions simultaneously involve building and transformation of the carbonylcontaining molecules, for example, borrowinghydrogen reactions, direct amination of toluene via benzaldehyde intermediate, hydroaminomethylation of olefins, etc. So, the two parts should be looked as a whole. Integration of building and transformation of the carbonyl containing molecules will not only promote exploration of novel catalytic reactions and synthetic methods but also facilitate development of new processes and catalysts and innovation of chemical industry and technology. It eventually will contribute greatly to efficient utilization of resources and the sustainable development of the chemical industry. Nevertheless, we could NOT find any books that look at two individual topics as a whole on the building and transformation of the carbonylcontaining molecules. In this context, we began to prepare a book on this topic in order to fill the gap in this area.
Considering that the building and transformation of the carbonylcontaining molecules involve many contents, we were unable to include every detail involved in these fields in this short volume. This book will highlight the importance of carbonylcontaining molecules, which can be served as a link between reaction, chemicals, and materials. The book is intended to describe and convey the concept of building and transformation of carbonylcontaining molecules and its application in catalysis. The book is divided into four chapters and organized according to the sequence of the synthesis and application of carbonyl compound. Part I focuses on the methods of synthesis of carbonyl compounds. A variety of carbonyl sources, such as CO, carbon dioxide, other C1 carbonyl molecules, and nonC1 carbonyl molecules, in situ generated carbonyl molecules, are described for the synthesis of carbonyl molecules. The application of carbonyl compounds as catalysts for the synthesis of fine chemicals is summarized in Part II. Part III presents the applications of carbonyl compounds in the synthesis of functional molecules and materials. The book ends with our personal outlook on this field.
It is a pleasure to be the authors of this book because it provides us with the opportunity to survey the field of the building and transformation of the carbonylcontaining molecules. We gratefully acknowledge the WILEYVCH editorial staff and extend special thanks to Lifen Yang. We are very grateful to all of our colleagues for their excellent contributions to this book. Contributors include: Xinzhi Wang (), Dongcheng He (Chapters 2 and 3), Kang Zhao (Chapters 4 and 7), and Shujuan Liu (Chapters 5, 6, and 8).
We truly hope this book will be of interest to all those involved in this field, from graduate students to independent catalytic and organic researchers in both academic and industrial sectors. We also hope that it will stimulate a wider general interest and promote further development in the subject.
Feng Shi, Hongli Wang, and Xingchao Dai
Lanzhou, China
July 2020
Part I
Carbonyl Molecules as Reactants
Carbon Monoxide
1.1 Hydroformylation of Alkenes and Alkynes
Hydroformylation is one of the most important reactions for the preparation of aldehydes and alcohols from alkenes and synthesis gas .
The key consideration of hydroformylation is the selectivity of normal vs. iso. For example, the hydroformylation of propylene can afford two isomeric products, butyraldehyde or isobutyraldehyde ().
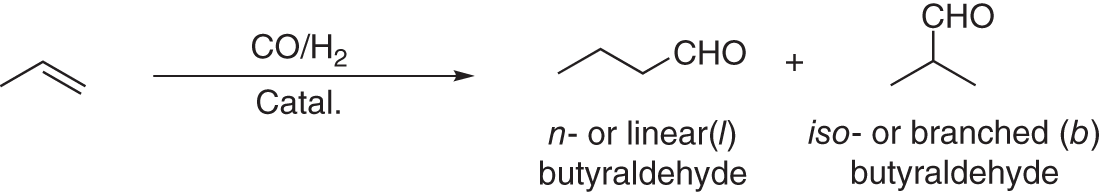
Example of hydroformylation.
These isomers are related to steric hindrance and the rate of CO migration insertion. In addition, they also reflect the regiochemistry of the insertion of alkene into the MH bond. For example, the reaction mechanism begins with dissociation of CO from hydridometaltetracarbonyl complex (1) to give the 16electron species HM(CO)3 (2). Then, the alkene starts to coordinate with the HM(CO)3 complex. The complex (3) is converted into the corresponding complex (4); the 18 electron species are formed by adding CO (5). In the next step of the reaction cycle, the CO is inserted into the carbonmetal bond (6). Once again, CO is associated to end up in the 18 electron species (7). In the last step of the reaction cycle, the catalytically active hydridometaltetracarbonyl complex (1) is released by adding hydrogen. Moreover, the aldehyde is formed by a final reductive elimination step (. In this section, we will summarize the history and recent advances of catalysts for hydroformylation.
Next page







