Felix S. Chew - Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures
Here you can read online Felix S. Chew - Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. genre: Home and family. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures
- Author:
- Genre:
- Rating:3 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Professor of Radiology
Vice-Chair for Radiology Informatics
Section Head of Musculoskeletal Radiology
University of Washington and Harborview Medical Center
Seattle, WA
Albert Einstein College of Medicine
Chief, Musculoskeletal Radiology
Bronx-Lebanon Hospital Center
New York, NY
Hyojeong Mulcahy, M.D.
Assistant Professor, Musculoskeletal Radiology
Director of Resident Education in Musculoskeletal Radiology
University of Washington and Harborview Medical Center
Seattle, WA
Christin M. Brown, M.D.
Lieutenant Commander, U.S. Navy
Senior Fellow and Acting Instructor, Musculoskeletal Radiology
University of Washington and Harborview Medical Center
Seattle, WA
Seattle, WA
2009
Felix S. Chew, M.D.
DISCLAIMER: The information provided in this work is for educational and informational purposes only, and should not be considered as offering medical advice. If you think that you may have a broken bone or other illness, please check with a qualified physician or other appropriate health care provider.
by Catherine Maldjian, M.D., and Felix S. Chew, M.D.
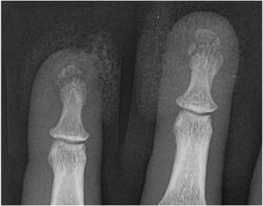
Case 1-01. Phalangeal tuft fractures. PA radiograph of the index and middle fingers centered over the DIP joints. This case demonstrates comminuted phalangeal tuft fractures. Over 50% of all phalangeal fractures involve the distal phalanx, most often involving the ungual tuft. These can be comminuted or non-comminuted. Fibrous septa extending from periosteum to skin resists displacement. Lacerations of the nail bed may occur with this fracture pattern. 42% of phalangeal fractures involve the middle finger [1-3].
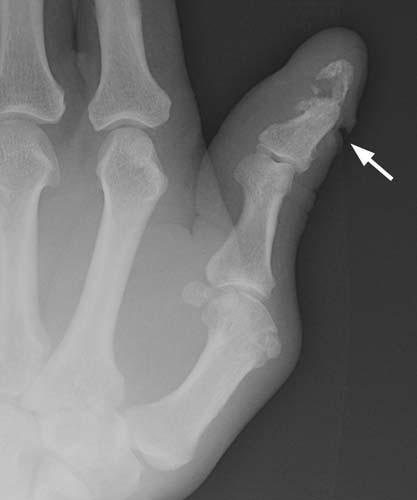
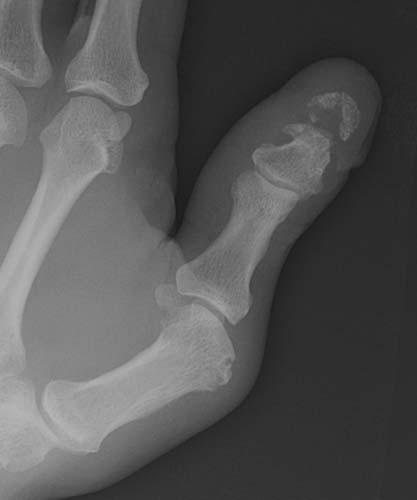
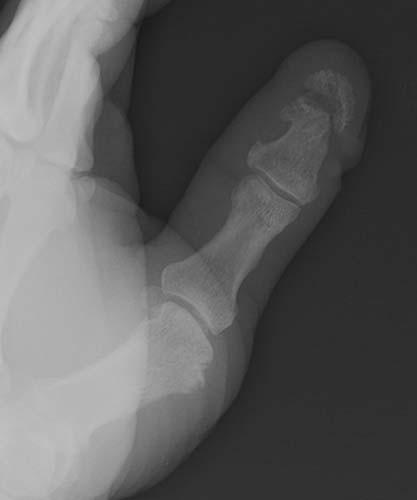
Case 1-02. Phalangeal tuft fracture with nail bed injury. Multiple radiographs of the hand. There is a comminuted fracture of the distal phalangeal tuft of the thumb, as might occur with a self-inflicted, accidental hammer blow. There is a laceration of the nail bed (arrow).
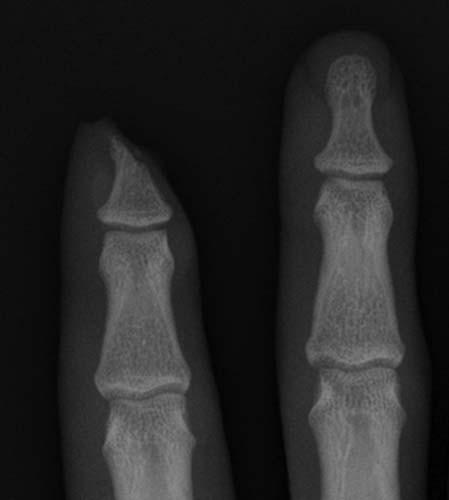
Case 1-03. Fingertip amputation. PA radiograph of the index and middle fingers. There is an amputation of a part of the distal phalanx of the index finger. Fingertip injury is treated with revision amputation if over 50% of the distal phalanx is absent or nail bed is significantly damaged. Bone is resected to the level of the residual nail bed. Complications of surgery include the formation of neuromas.
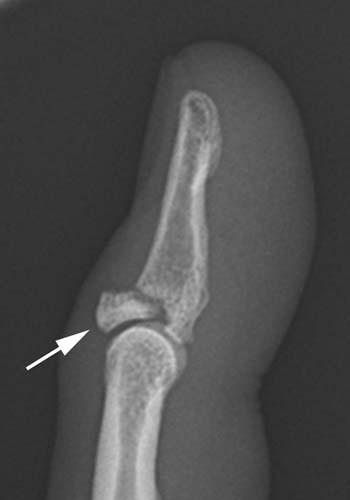
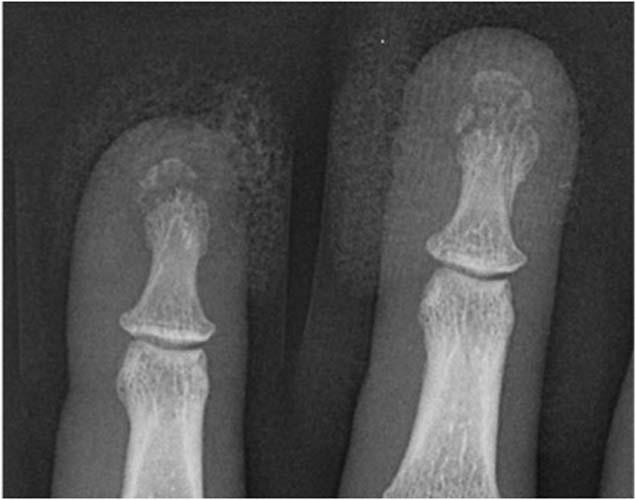
Case 1-04. Mallet finger. Lateral radiograph of a finger centered over the DIP joint. This case demonstrates a fracture at the dorsal aspect of the base of distal phalanx with slight flexion of the DIP joint. This site constitutes the insertion of the common extensor tendon insertion. This injury is a fracture/avulsion of the common extensor tendon insertion at dorsal base of the distal phalanx. A direct blow to the fingertip with forced flexion at the DIP joint, as from a baseball, gives rise to this fracture pattern, also known as baseball finger. On the lateral projection, the resultant unopposed flexion from extensor avulsion resembles a mallet. This injury may also be called a mallet finger. Most cases of mallet finger are pure avulsion of the ligament with no fracture. Only 25 percent of cases of mallet finger will demonstrate an avulsion fracture [4].
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures»
Look at similar books to Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Broken Bones: The X-Ray Atlas of Fractures and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.