

This edition first published 2013
2013 by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd
Registered Office
John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 8SQ, United Kingdom
Editorial Offices
9600 Garsington Road, Oxford, OX4 2DQ, United Kingdom.
The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 8SQ, United Kingdom.
For details of our global editorial offices, for customer services and for information about how to apply for permission to reuse the copyright material in this book please see our website at www.wiley.com/wiley-blackwell .
The right of the author to be identified as the author of this work has been asserted in accordance with the UK Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, except as permitted by the UK Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, without the prior permission of the publisher.
Designations used by companies to distinguish their products are often claimed as trademarks. All brand names and product names used in this book are trade names, service marks, trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. The publisher is not associated with any product or vendor mentioned in this book.
Limit of Liability/Disclaimer of Warranty: While the publisher and author(s) have used their best efforts in preparing this book, they make no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this book and specifically disclaim any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. It is sold on the understanding that the publisher is not engaged in rendering professional services and neither the publisher nor the author shall be liable for damages arising herefrom. If professional advice or other expert assistance is required, the services of a competent professional should be sought.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Towey, Donald.
Cost management of construction projects / Donald Towey.
pages cm
Includes bibliographical references and index.
ISBN 978-1-118-47377-1 (pbk.)
1. BuildingCost control. I. Title.
TH438.15.T69 2013
624.0681dc23
2013006527
A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library.
Wiley also publishes its books in a variety of electronic formats. Some content that appears in print may not be available in electronic books.
Cover image courtesy of iStockphoto.com
Cover design by Sandra Heath
Dedicated to my late parents, Jim and Peg Towey
Preface
In my first book Construction Quantity Surveying A Practical Guide for the Contractors QS, the role of commercial management of building projects was discussed through the eyes of the contractor. This book is written in contrast and focuses on cost and advisory services a cost manager can provide when engaged by a project client which is independent of the contractor. As clients often strive to obtain buildings for less in terms of the time it takes to design and build a project and the price involved, the cost manager is expected to have a broad understanding of the design, construction and management processes for a range of project types for which this book is intended to act as a guide.
This book will be of value to project managers and contract managers involved with the design and building processes and administration of construction contracts. It will also benefit members of main and principal contracting businesses wishing to undertake design and build projects who seek assistance regarding aspects of cost management. The book will also benefit students enrolled on construction management, quantity surveying and other related courses and anyone with an interest in the construction process.
1
Practice Procedures
1.1 Organisation and structure
In business terms, the term practice is a word used to describe the office of a private firm comprising professional people practising in their dedicated fields of work. In the construction industry, these people practise in the fields of cost management, quantity surveying, project management and the commercial management of construction projects. The services a firm can offer might extend to cost and advisory services for the various engineering disciplines associated with a construction project, and the management of occupied buildings. The firms business potential is driven by demand derived from the number of clients seeking the services, which relies on the economic status of the locality, nation and construction industry at any time.
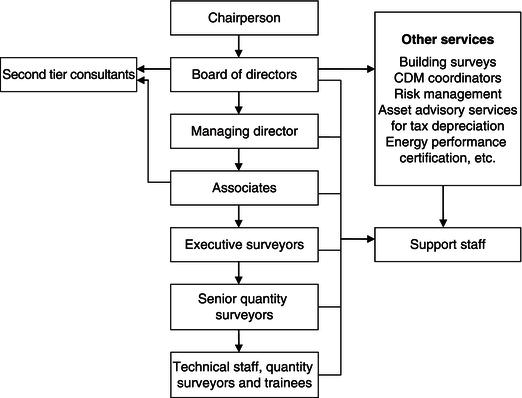
The creation of a firm requires private equity, which is the value of assets less any associated liability and is created from a partnership(s) or investor(s) who buys a portion of equity in the business. Firms or practices vary in size, ranging from partnerships with few employees to large businesses employing staff under a hierarchical management structure. In England, Wales and Scotland, partnerships comprising two or more individuals are required to trade as a corporate body under the Limited Liability Partnerships Act 2000, and in Northern Ireland under the Limited Liability Partnerships Act (Northern Ireland) 2002. These partnerships have legal existence that trade independently of their members; each partner is not personally liable for the others actions by way of negligence or default. Larger practicing firms usually comprise a chairperson, directors, other professionals and technical staff to assist in the running of the business. The hierarchical management structure of a large firm practicing in cost management is shown in .
demonstrates the delegation of authority and levels of responsibility, which usually depend on qualifications, length of service, experience and expertise in certain fields of work. Collaborative teamwork is usually encouraged throughout the structure, with workshops allowing staff members with specialised skills to share their knowledge and aid career development of others, irrespective of their position or title. For example, a senior quantity surveyor who may have experience with infrastructure such as road construction and highway maintenance may provide training on estimating the costs of works to anyone with limited skills in the subject. Support staff includes secretaries, administrators and accountants who have the computer and office skills vital to the business structure and who assist technical and professional staff to set up and run projects. In addition, support staff usually manage the businesss quality control system to handle documents including:
- Logging and recording awarded projects
- Digital and hard copy control of drawings and documentation
- Filing methods for managing computer and office space
- Maintaining records of business development
- Arranging meetings
- Updating the firms policies and procedures file
- Coordinating the flow of information for distribution.
In order to carry out business dealings, a firm requires legal recognition and the acknowledgement of its responsibilities at common law. In order to create a legal identity, it is necessary for the firm to register its business. In the United Kingdom this is with Companies House, a regulatory body for company registration that maintains company records as required by the Companies Act 2006. It might also be necessary to register for value added tax (VAT) if turnover is in excess of the stated threshold, as services tax will be chargeable to clients on invoices raised by the firm. Firm members may be self-employed with each responsible for their own taxation and insurance payments. However, if firm members are not self-employed but are employees, it will be necessary to register them with a system whereby tax is deducted from each wage payment as pay-as-you-earn (PAYE). PAYE addresses tax deductions and national insurance contributions payable to the tax office when they are deducted from the salary payments of employees.
Next page









