Robert Service
LENIN
A Biography
This book was read in draft by Adele Biagi, David Godwin, Heather Godwin, Martyn Rady, Arfon Rees and Tanya Stobbs, and John Klier read the first chapter. Their suggestions made for very welcome improvements. Several helpful tips were also offered by Philip Cavendish, Myszka Davies, Norman Davies, Bill Fishman, Julian Graffy, Riitta Heino, John Klier, Richard Ramage, Arfon Rees, Kay Schiller and Faith Wigzell. I should also like to thank John Screen and Lesley Pitman in the School of Slavonic and East European Studies Library in London and Jackie Willcox in the St Antonys Russian Centre Library in Oxford for their assistance in getting important material on to the stacks. David King generously introduced me to the wonders of his personal collection of Soviet photographs and posters, and I am immensely grateful for his permission to use some here. A particular debt is also owed to the staff of the Russian Centre for the Conservation and Study of Documents of Contemporary History, especially Kirill Anderson, Larisa Rogovaya, Yelena Kirillova, Irina Seleznva and Larisa Malashenko; and to Vladimir Kozlov at the State Archive of the Russian Federation. Russian fellow historians who have given me useful ideas for research include Gennadi Bordyugov, Vladimir Buldakov, Oleg Khlevniuk, Vladimir Kozlov and Andrei Sakharov.
Lenin is a subject of great political and emotional resonance in Russia and I am grateful for the encouragement given by Russian friends to undertake this biography. I am aware that as a foreigner I may be walking into sensitive areas, perhaps even with hobnailed boots. Then again this is perhaps what the biography of Lenin requires.
For several years on my way to work in central London I used to cycle past buildings where Lenin lived, edited or researched. One route took me through Highbury (where Iskra editors had their Russian mail sent) and on to the St Pancras district (where Lenin lived in 1900), across Grays Inn Road (with its pubs where Lenin drank with party comrades in 1905) and along Tavistock Place (where he lived for some months in 1908). It strengthened a feeling that my subject was not quite as exotic as it sometimes appeared. But of course it is in Russia that fuller perspective on his life and times must be obtained. The Kremlin, Red Square and the Smolny Institute are buildings that have to be visited in order to acquire a sense of time and place. I have tried in the following chapters also to give a sense of personality. In this connection it was a pleasure to meet and spend an afternoon with Viktoria Nikolaevna Ulyanova, one of the few people alive who knew the Ulyanov family members mentioned in the book. Her generosity of spirit a trait not shared by Lenin, her husbands uncle demonstrates that not everything that happened in Russia earlier this century was absolutely inevitable.
Lastly, I want to thank my family my wife Adele and our boisterous descendants Emma, Owain, Hugo and Francesca for discussing the contents of the book. Each of them has read lengthy sections and helped with the editing. They have displayed the same attitude as those millions of Soviet citizens who, while acknowledging Lenins huge historical significance, took an interest in his private and occasionally comic foibles. I have tried to write a book that brings together the public and private aspects. Until the opening of the Moscow archives in the 1990s a biography of this kind was unfeasible. And I hope the chapters provide material for my family as well as for readers more generally to go on resolving the enduring questions of Lenins career and impact.
Robert Service
Oxford, May 1999For the paperback edition I have made some corrections, for most of which I am indebted to Israel Getzler.
Note on Transliteration and Calendars
The system of transliteration employed in this book is a simplification of the system developed by the US Library of Congress. The first difference is the dropping of both the diacritical mark and the so-called soft i. Secondly, the yoh sound is rendered here as . By and large I have kept to the Russian versions of Russian proper names, but some sound too exotic in English. Aleksandr Ulyanov, for example, therefore appears as Alexander Ulyanov. The Julian calendar was maintained in Russia until January 1918, when Lenins government introduced the Gregorian version. Unless otherwise indicated, the dates mentioned in this book correspond to the particular calendar in official use at the time.
Glossary of Names of Lenin and his Family
Lenin
Ilich Respectful nickname for Lenin, used mainly inside the party
Lenin The most famous of the 160 pseudonyms he used
V.I. Lenin. Short version of Vladimir Ilich
Vladimir Ilich Lenins Christian name and patronymic
Vladimir Ilich Ulyanov Lenins name at his christening
Volodya The diminutive of Lenins first name
His Close Family
Alexander Ilich (Ulyanov) First name and patronymic of Lenins elder brother
Anna Ilinichna (Ulyanova) First name and patronymic of Lenins elder sister
Anyuta Diminutive first name of Lenins older sister Anna Ilinichna Ulyanova
Dmitri Ilich (Ulyanov) First name and patronymic of Lenins younger brother
Ilya Nikolaevich First name and patronymic of Lenins father
Manyasha Diminutive of Christian name of Maria Ilinichna (Ulyanova)
Maria Alexandrovna (Ulyanova) First name and patronymic of Lenins mother
Maria Ilinichna (Ulyanova) First name and patronymic of one of Lenins younger sisters
Mitya Diminutive first name of Lenins younger brother Dmitri Ilich Ulyanov
Nadezhda Konstantinovna (Krupskaya) First name and patronymic of Krupskaya, Lenins wife
Nadya Krupskayas diminutive first name
Olga Ilinichna (Ulyanova) First name and patronymic of one of Lenins younger sisters
Olya Diminutive of Christian name of Olga Ilinichna Ulyanova
Sasha Diminutive of Christian name of Lenins elder brother Alexander Ilich Ulyanov
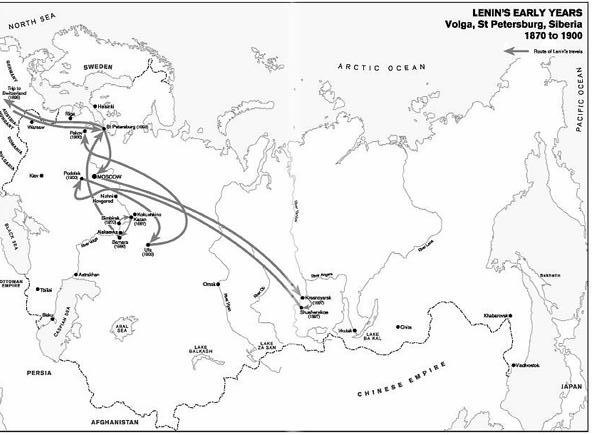
1. Lenins early years: Volga, St Petersburg, Siberia, 1870 to 1900
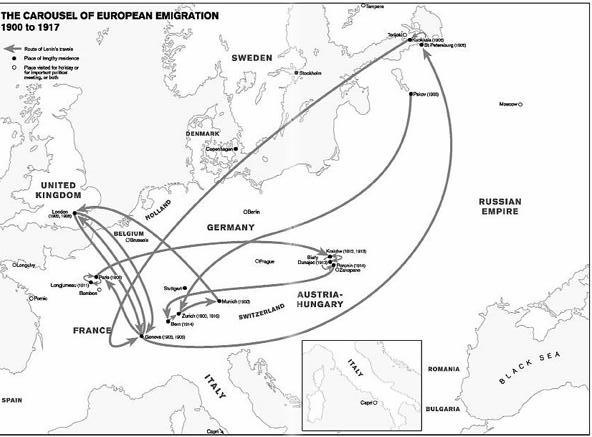
2. The carousel of European emigration, 1900 to 1917
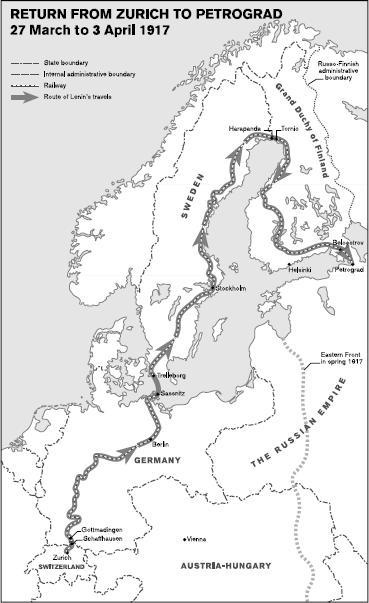
3. Return from Zurich to Petrograd, 27 March to 3 April 1917
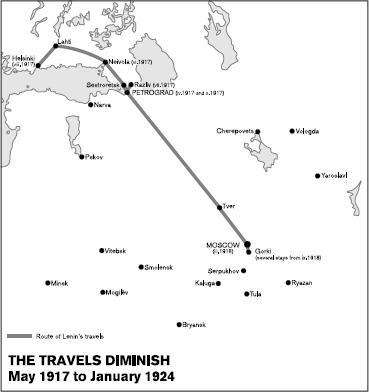
4. The travels diminish, May 1917 to January 1924
Lenin was an exceptional figure. He founded a communist faction, the Bolsheviks, which he turned into a party that made the October Revolution of 1917. The worlds first socialist state was proclaimed. This state which was the territorial core of what eventually became the USSR survived against the odds. Lenin and the communist leadership withdrew Russia from the First World War and won the Civil War. By setting up the Communist International, they imprinted themselves upon politics across the continent. The USSR was a beacon to the worlds far-left socialists and a dangerous rock to conservatives, liberals and other socialists. Lenins interpretation of the doctrines of Marx and Engels became holy writ for communists, and at his death was designated as MarxismLeninism. After the Second World War the communist model the one-party state, ideological monopoly, legal nihilism, militant atheism, state terror and the elimination of all rival institutions of authority was transferred to eastern Europe, China, south-eastern Asia and eventually parts of the Caribbean and Africa. Communism was dismantled in eastern Europe in 1989 and in the USSR at the end of 1991. But no one had made a greater impact upon the development and establishment of the communist order than Lenin.

















 1. Lenins early years: Volga, St Petersburg, Siberia, 1870 to 1900
1. Lenins early years: Volga, St Petersburg, Siberia, 1870 to 1900 2. The carousel of European emigration, 1900 to 1917
2. The carousel of European emigration, 1900 to 1917 3. Return from Zurich to Petrograd, 27 March to 3 April 1917
3. Return from Zurich to Petrograd, 27 March to 3 April 1917 4. The travels diminish, May 1917 to January 1924
4. The travels diminish, May 1917 to January 1924