Bibliografische Information der Deutschen Bibliothek
Die Deutsche Bibliothek verzeichnet diese Publikation in der Deutschen Nationalbibliografie; detaillierte bibliografische Daten sind im Internet ber http://dnb.ddb.de abrufbar
Rangendingen, December 2015
by LIBERTAS - Europisches Institut GmbH
LIBERTAS Europisches Institut GmbH
Lindenweg 37, 72414 Rangendingen, Germany
Tel. +49 7471 984996-0, Fax +49 7471 984996-19
eMail:
Internet: www.libertas-institut.com
ISBN 978-3-946119-73-9 (print)
ISBN 978-3-946119-74-6 (epub)
ISBN 978-3-946119-75-3 (MobiPocket)
ISBN 978-3-946119-76-0 (pdf)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The OSCE has 57 participating states from Europe, Central Asia, and North America, and its area spans from Vancouver to Vladivostok. August 1, 2015 mark ed the 40 th anniversary of the Helsinki Final Act. Since the signing of this agreement, the relevance of the OSCE in the European security architecture has only increased. To understand how it functions, how it is perceived today by the participating states and what their key issues with regard to the organization are, i t is necessary to see how it started.
The OSCE has 57 participating States from Europe, Central Asia and North America:
- Albania
- Austria
- Belgium
- Canada
- Czech Republic
- Finland
- Germany
- Hungary
- Italy
- Latvia
- Luxembourg
- Monaco
- Norway
- Romania
- Serbia
- Spain
- Tajikistan
- Turkmenistan
- United States
| - Andorra
- Azerbaijan
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Croatia
- Denmark
- France
- Greece
- Iceland
- Kazakhstan
- Liechtenstein
- Malta
- Montenegro
- Poland
- Russian Federation
- Slovakia
- Sweden
- The F ormer Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
- Ukraine
| - Uzbekistan
- Armenia
- Belarus
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Ireland
- Kyrgyzstan
- Lithuania
- Moldova
- Mongolia
- Netherlands
- Portugal
- San Marino
- Slovenia
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
|
Source: OSCE Factsheet
Budgethistory
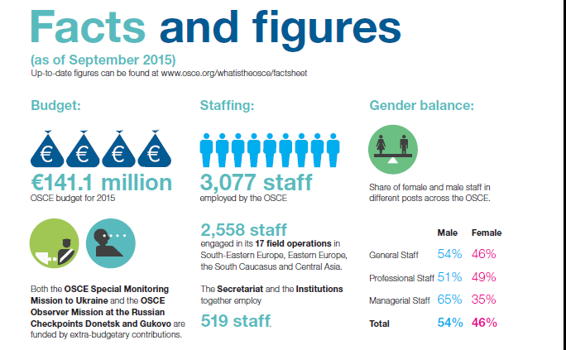
Since 1993, the OSCE's budget by year (in millions of euros,) has been:
- 2015 ... 141.1 million
- 2014 ... 142.3 million
- 2013 ... 144.8 million
- 2012 ... 148.4 million
- 2011 ... 150.0 million
- 2010 ... 150.7 million
- 2009 ... 158.6 million
- 2008 ... 164.1 million
| - 2007 ... 186.2 million
- 2006 ... 186.2 million
- 2005 ... 186.6 million
- 2004 ... 180.8 million
- 2003 ... 165.5 million
- 2002 ... 167.5 million
- 2001 ... 194.5 million
- 2000 ... 202.7 million
| - 1999 ... 146.1 million
- 1998 ... 118.7 million
- 1997 ... 43.3 million
- 1996 ... 34.9 million
- 1995 ... 18.9 million
- 1994 ... 21 million
- 1993 ... 12 million
|
Summits of heads of State and Government
Summit | Date | Place | Decisions |
I | 30.07 - 01.08.1975 | Helsinki | Closing of the Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE). Signing of the Final Act (Helsinki Act) . |
II | 19 - 21.11.1990 | Paris | (Second CSCE Summit). Signing of the Charter of Paris for a New Europe (Paris Charter), the Vienna Confidence and Security Building Measures (CSBM) Document and the CFE Treaty. |
III | 09 - 1992 | Helsinki | Final Document: The Challenges of Change . Creation of the High Commissioner on National Minorities, the Forum for Security Co-operation and the Economic Forum . Suspension of FR Yugoslavia from membership. |
IV | - 0 1994 | Budapest | Final Document: Towards a Genuine Partnership in a New Era . Approval of a multi-national peace-keeping force to Nagorno-Karabakh . Endorsement of the Code of Conduct on politico-military aspects of security. |
V | 02 - 03 . 1996 | Lisbon | (First OSCE Summit). Lisbon Declaration on a Common and Comprehensive Security Model for Europe for the Twenty-First Century . Adoption of a Framework for Arms Control . |
VI | 1819.11.1999 | Istanbul | Signing of the Istanbul Document and the Charter for European Security . |
VII | 0102.12.2010 | Astana | Adoption of the Astana Commemorative Declaration , which reconfirms the Organization's comprehensive approach to security based on trust and transparency. |
The History and Significance of the OSCE
Origins
Following World War II, Europe was divided between theSoviet-led bloc of communist regimes installed in countries it had occupied at the end of the war, grouped together as military allies in the Warsaw Pact; the U.S.-led North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) seeking to contain the spread of communism; and several neutral states.
Since the 1950s, the Soviet Union had advocated holding an a ll-European conference to put a political end to World War II by resolving the "German question," with the goal of ratifying the postwar status quo established in Eastern Europe.
The United States and most of its NATO allies were oppos ed to a conference with such an agenda. The U.S. countered with a proposal for holding a conference between NATO and the Warsaw Pact states dealing with "hard" arms control in Europe, especially reductions of conventional military forces.
On the Way totheHelsinkiFinal Act of 1975
In 1969, neutral Finland offered to host a conference on European security . NATO responded to the Finnish proposal by suggesting that the agenda of a European security conference s hould also include prior notification of military maneuvers and fre er movement of people and ideas across the Cold War divide.
From1972-73in Helsinki preparatory meetings forConference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE)were launched with 35 delegations including: the U.S., Canada, and all the states of Europe, with the exception of Albania. These states tended to gather into three major groups, reflecting the existing political alignments at the time:
Warsaw Pact
NATO / European Community
Neutral / Nonaligned
The preparatory meeting s resulted in a detailed outline of the practical organizational arrangements for the conference.
1973-1975 was the working phaseofnegotiations during which the issues were grouped into three major baskets , also referred to as dimensions of security :