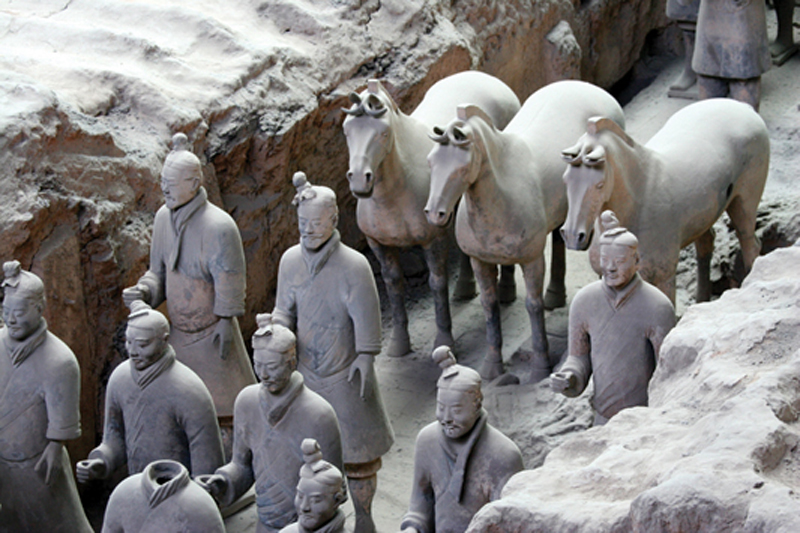
Qin Shi Huangdi ordered the construction of this army of soldiers made of terracotta,a kind of clay pottery. The army was buried underground until it was discovered bya farmer in 1974.
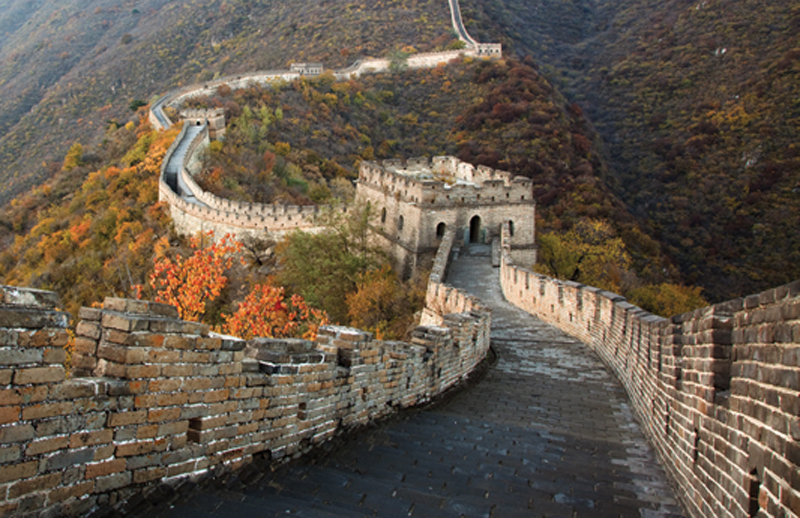
Qin Shi Huangdi began construction of the Great Wall to keep out Mongol invaders.It was built using forced labor, and many workers died.
Later dynasties
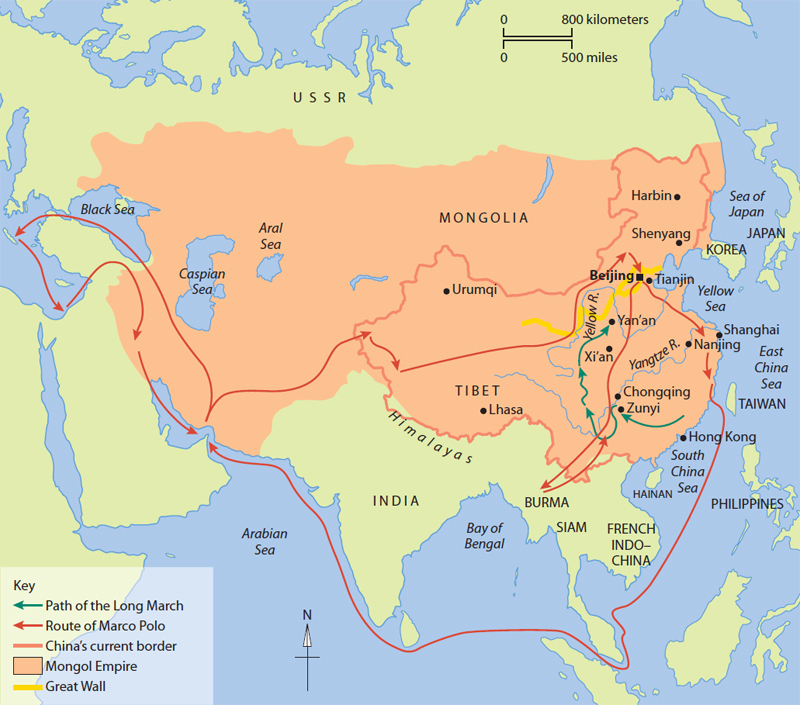
Mongol emperors ruled China from 1279 to 1368 CE. The famous conqueror Genghis Khan(11621227) united Mongolian groups and created a large empire across Asia. KublaiKhan (12151294), a grandson of Genghis Khan, conquered China in 1279, making itpart of the Mongol Empire. This was the beginning of the Yuan Dynasty. The Mongolswere driven from power by the Ming Dynasty (13681644). This was followed by theQing Dynasty (16441911), Chinas last dynasty.
Chinas dynasties
The following are approximate dates for some major dynasties that ruled China:
| Years | Dynasty |
| 1046256 BCE | Zhou |
| 221207 BCE | Qin |
| 206 BCE220 CE | Han |
| 581618 CE | Sui |
| 618907 | Tang |
| 9601279 | Song |
| 12791368 | Yuan (Mongol) |
| 13681644 | Ming |
| 16441911 | Qing (Manchu) |
The Italian trader Marco Polo visited China during the Yuan dynasty, when KublaiKhan ruled.
Foreign influence in China
During the late Qing Dynasty, China chose to be isolated, cutting itself off fromthe rest of the world. But in the early 1800s, the British came to China, demandingto trade in goods such as tea, spices, silk, and porcelain. In return, the Britishbrought a drug called opium . Many Chinese people became addicted to opium. When Chinatried to ban the drug, the British fought and won wars to continue their trade. Witheach defeat, China gave up further rights and territory. In 1842 the Chinese gaveBritain the island of Hong Kong.
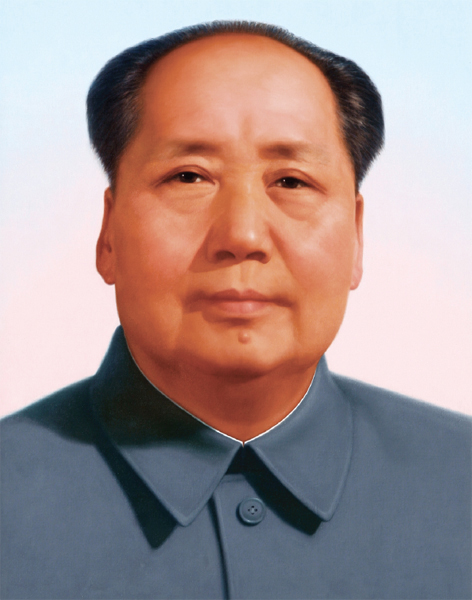
Mao Zedong (18931976)
Mao Zedong was an important Communist Party leader duringthe 1930s and 1940s. When surrounded by Nationalists in 1934, Mao famously led tensof thousands of followers thousands of miles to safety. This became known as theLong March.
The Nationalists and Communists
In 1911 groups opposed to Qing leadership rose up in rebellion. Emperor Puyi wasforced to give up his position as ruler in 1912. Sun Yat-sen, leader of the victoriousNationalist Party, declared China a republic and became its president. At the sametime, a new Communist Party grew in opposition to the Nationalists. Communists believethe state, rather than individuals, should own and control property and resources.
Japanese invasion
In the 1930s Japanese troops invaded China, taking over Beijing in 1937. The ChineseCommunists and Nationalists, led by Chiang Kai-shek, decided to work together toforce out the Japanese. However, civil war began again in 1945 between the Nationalistsand Communists.
Communist victory and the Cultural Revolution
The Communists defeated the Nationalists in 1949. Mao Zedong proclaimed the PeoplesRepublic of China and became its leader. In defeat, more than two million Nationalistsfollowed Chiang Kai-shek to the island of Taiwan. They continued the government ofthe Republic of China there. Meanwhile, in 1950 Mao and the Peoples Republic ofChina invaded neighboring Tibet and took control there.
Deng Xiaoping, pictured here on a billboard, began Chinas Open Door Policy, whichhas brought the country great wealth and increasing international power.
In 1966 Mao began the Cultural Revolution. This was an effort to get rid of foreigninfluence and ancient Chinese ideas, while also strengthening Communist Party ideals.Students and young people became Red Guards, enforcing these goals. Millions of peoplewere sentenced to forced labor, and many were tortured or killed. The Cultural Revolutionended with Maos death in 1976.