Powers not granted to the government are reserved for states and the people.
WHAT CAUSED
THE TENTH AMENDMENT?
During the American Revolution (17751783), the colonies had formed a loose . The countrys first constitution, the Articles of Confederation, provided some basic guidelines for the new nation. After the United States won independence, it faced new problems. How would the United States defend its borders? There was no army or navy. What if two states disagreed on an issue? Who was in charge?
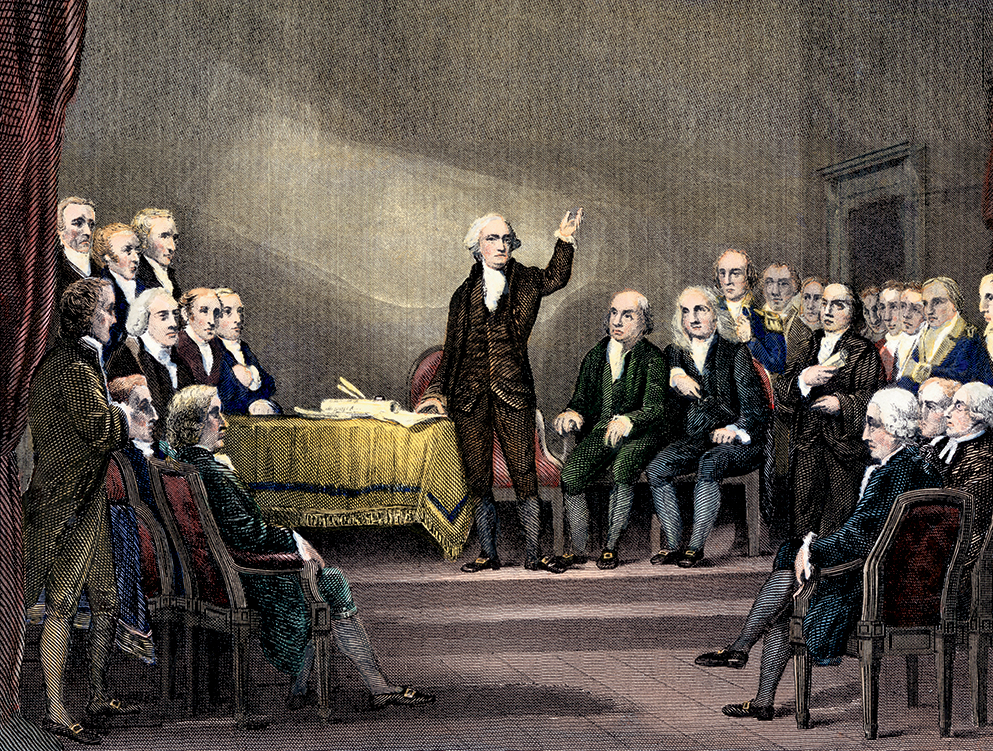
The states sent delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in May 1787. The delegates decided to write a new constitution. Some wanted a powerful federal government. Others wanted most of the power to stay with the states. The constitution would determine the future of the country.
George Washington led the debate at the Constitutional Convention in 1787.
Virginia landowner George Mason wanted to add a bill of rights to the Constitution that would give the people and the states certain rights. A judge and politician, Mason had written Virginias Bill of Rights. Other states had bills of rights as well. The delegates Masons idea for days. In the end, 39 of the 55 delegates voted to approve the Constitution without a bill of rights.
But before the Constitution could take effect, it had to be . Many opposed the new Constitution.
Cause #1: Many Leaders Feared a Powerful Central Government
Many leaders were against the Constitution. They believed that the Constitution gave too much power to the federal government. They feared that the United States would become like Great Britain. They didnt want a powerful government creating cruel laws or charging unfair taxes. They didnt want a second revolution.
FAST FACT:
Rhode Island refused to send delegates to the Constitutional Convention. Rhode Islands leaders feared they would lose power to the federal government.
Reasons for Missing Signatures
For a variety of reasons, several delegates did not sign the Constitution.
- Delegate Patrick Henry (Virginia) - Felt it took away states rights
- Delegate George Mason (Virginia) - Wanted a bill of rights
- Delegate Richard Henry Lee (Virginia) - Wanted a bill of rights
- Delegate Edmund Randolph (Virginia) - Not enough checks and balances among the three parts of the federal governmentthe president, Congress, and courts
- Delegate John Lansing (New York) - Opposed to strong federal government
- Delegate Robert Yates (New York) - Opposed to strong federal government
- Delegate Elbridge Gerry (Massachusetts) - Wanted a bill of rights
- Delegate Caleb Strong (Massachusetts) - Opposed to Electoral College, the group that elects the president and vice president after the general election
- Delegate Luther Martin (Maryland) - Felt it took away states rights
- Delegate John Mercer (Maryland) - Left in protest
Cause #2: The Constitution Seemed to Give Congress Unlimited Powers
Article I, section 8, of the Constitution listed the powers of Congress. The last item gave Congress the power to make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing Powers. It appeared to many state leaders that Congress could make whatever laws it wanted. State leaders feared that Congress might take away the rights of the people or the powers of the states.
Congress serves as the lawmaking body of the United States.
Powers vs. Rights
The Constitution gives certain powers to the government. The Bill of Rights grants certain rights to the people. What is the difference? A power is the ability to act as a legal authority. For example, the federal government has the power to declare war. A state has the power to issue drivers licenses and impose sales taxes. A right, on the other hand, is the legal permission to do something or to act in a certain way. Freedom of speech is a right given to the American people by the Bill of Rights. Generally, governments have powers. People have rights.
The right to protest peacefully is granted in the U.S. Bill of Rights.
Cause #3: The States Wanted to Serve the Needs of Their People
Each of the original 13 colonies was unique. The English had settled some areas. The Dutch and Germans had settled in others. People in various colonies spoke different languages. They practiced various customs. Religious beliefs varied from place to place. People did not consider themselves Americans. Their loyalty was to their states, not to their country. They were Virginians or New Yorkers. They believed their state leaders would make decisions serving their needs. They feared that a federal government would not understand their differing needs.