John Kuprenas is a registered engineer and LEED professional. He lectures in civil engineering at USC and Cal State Long Beach, and is senior vice president and deputy director of the Construction Management Division at STV Group, Inc. His writings have been published in numerous journals and in The Story of Managing Projects (Praeger Publishers).
Matthew Frederick is an architect, urban designer, instructor of design and writing, and the creator of the acclaimed 101 Things I Learned series. He lives in New Yorks Hudson Valley.

www.101ThingsILearned.com
Insight on insight
An insight is not an observation or invention. It isnt a flash of inspiration or the pinpointing of a missing ingredient. It is the realizing of the essence of a situation.
The search for insight can be tedious and deflating. It requires researching, brainstorming, focusing, refocusing, sifting, resifting, doing, undoing, and often giving up in frustration. But in giving up, one becomes a stranger to his or her situation and may be open to a fresh perspective on it.
When it is eventually found, an insight will be both broad and specific: it will reveal a human truth or cultural-scale experience, yet will connect concretely to the product or product category. It will surprise, inspire, and provide clarity. It will feel like something you had not thought of before yet were aware of all along.
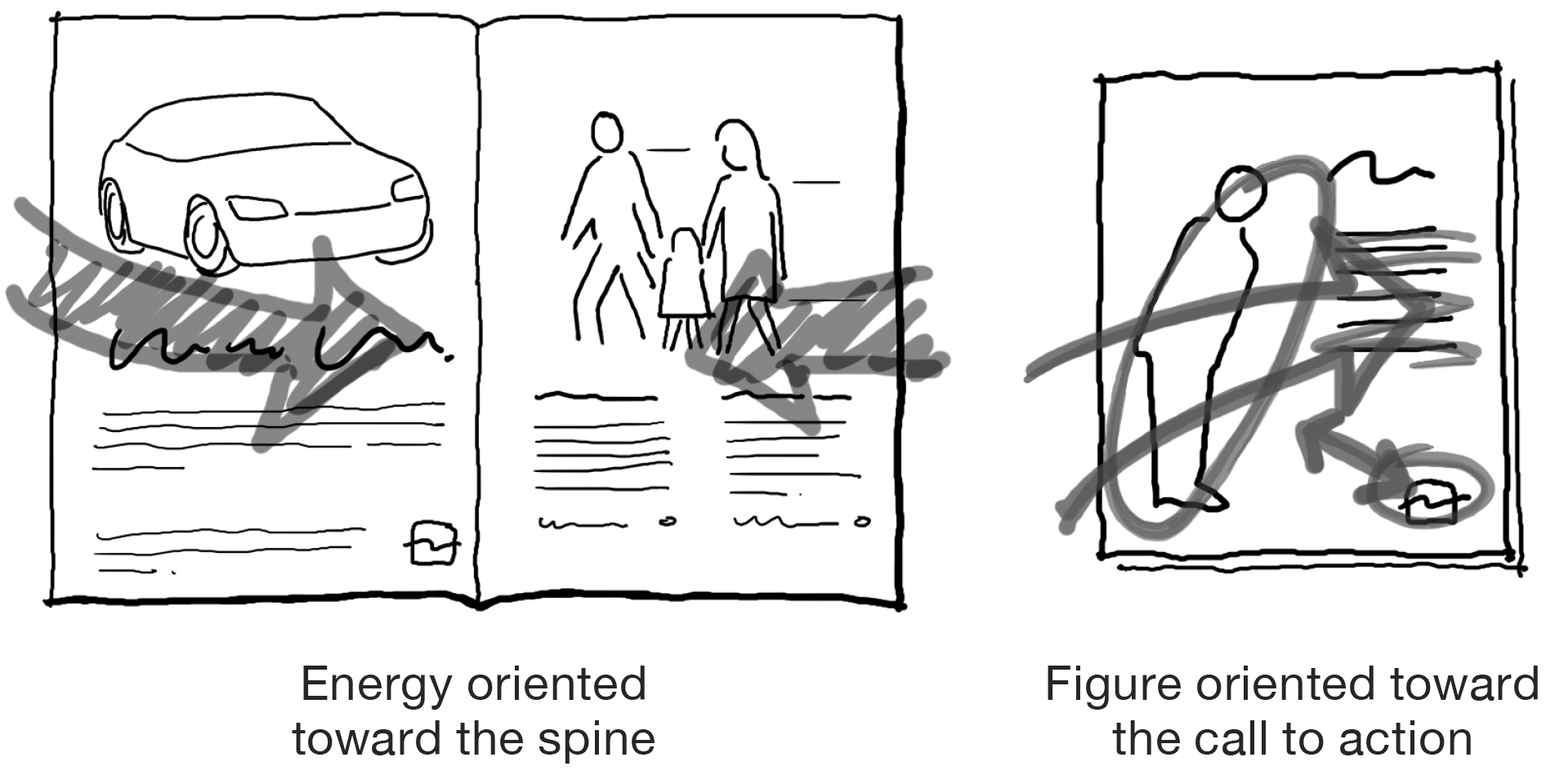
Direct the flow of energy.
Arrange figures and objects to call attention to an ads message. People, animals, and objects usually should face or be inflected toward the body text or call to action. If in motion, they usually should be moving into the ad.
If the placement of the ad on a web page is known, its energy usually should be directed toward the center of the screen. In a print publication such as a magazine or catalog, energy is best directed toward the spine. People or vehicles moving away from the spine may appear disinterested, as if they are leaving the publication, although this can be less problematic on right-hand pages, where movement to the right matches the direction ones eye and attention are usually headed.
As our brain processes images 60,000 times faster than words, we seek out imagery to shortcut the additional work that words require. If a headline needs to be read before one can make sense of an image, place and size the headline so the eye goes to it first.
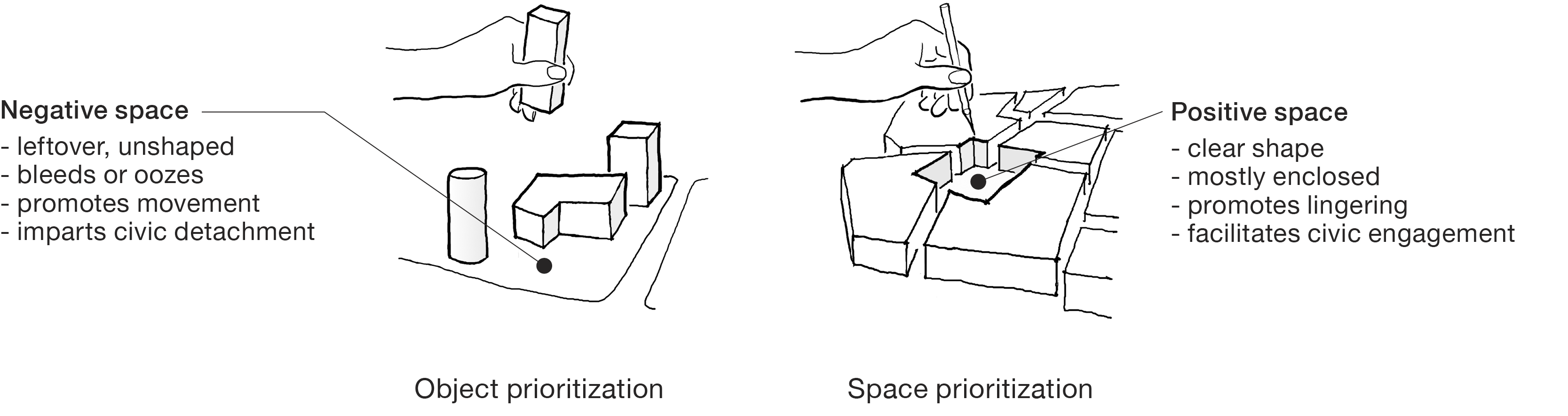
Invert your thinking.
Our culture predisposes us to see and understand reality as an arrangement of objects. To our modern eyes, space is a void within which we create or place objects. We tend not to give space a shape but to treat it as a leftover, or residual, from the placement of objects.
The opposite understanding applies to the making of urban places. Just as one ordinarily gives shape to buildings, the urban designer gives shape to outdoor spaces. Buildings are often the leftover; they are typically sited, configured, formed, and even de formed so that public streets and plazas can have clear, meaningful shape.
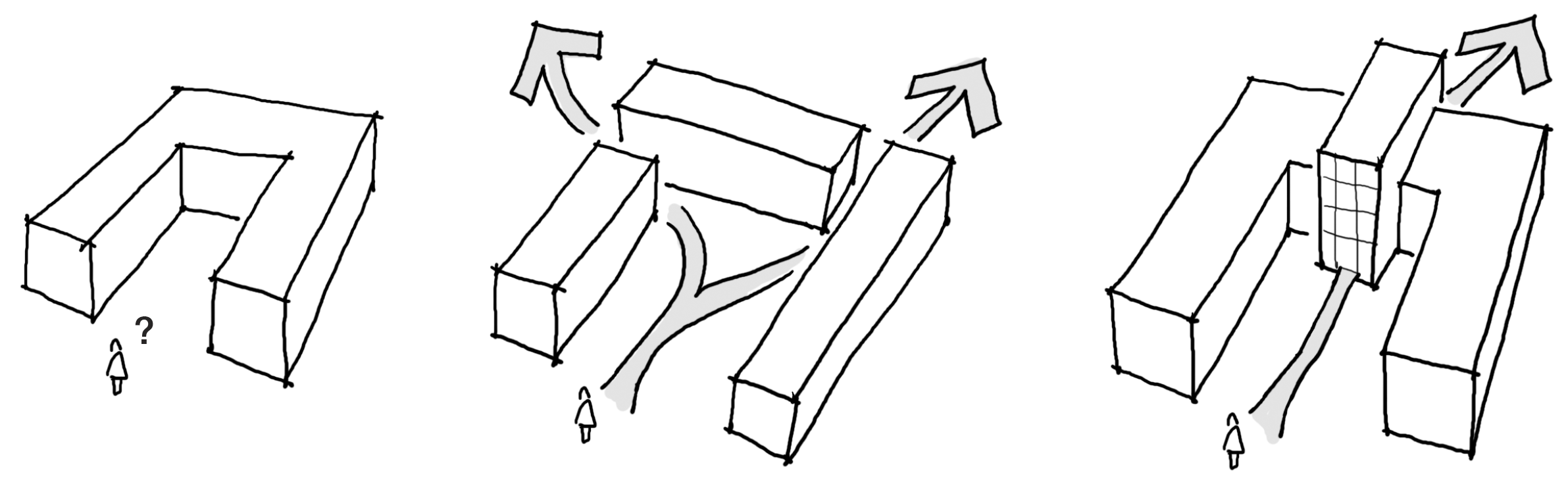
As we enter, we look for the exit.
A public space lacking an apparent exit at the end opposite from where one enters will dissuade many people from using iteven if they do not intend to pass all the way through the space. A dead end subconsciously invokes our defensive instincts: if we are pursued from behind, we will lack an escape route. A street, alley, public mall, or interior corridor lacking a through-connection will have fewer people, fewer things of interest, and less vitality than one with a through-passage. A physical dead end is an experiential dead end is a social dead end is a cultural dead end is an economic dead end.
Notes
Illustration adapted from Mark Holtzapple, W. Reece, Foundations of Engineering (McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math, 2nd ed., 2002), p. 9.
Illustration with regard to Ralph Caplan, By Design: Why There Are No Locks on the Bathroom Doors in the Hotel Louis XIV and Other Object Lessons (St. Martins Press, 1982).
Illustration adapted from Frederick Gould, Managing the Construction Process (Prentice Hall, 4th ed., 2012), p. 64.
Gary T. Schwartz, The Myth of the Ford Pinto Case, Rutgers Law Review , vol. 43, p. 1029.
Illustration adapted from John Elkington, Cannibals with Forks: The Triple Bottom Line of 21st Century Business (Capstone Publishing, 1999).
The Possibility of Life in Other Worlds by Sir Robert Ball, Scientific American Supplement no. 992, January 5, 1895, pp. 1585961.
After Jane Jacobs, The Death and Life of Great American Cities (Random House, 1961), pp. 43031.
Illustration data adapted from Global Fatal Accident Review, 19972006, UK Civil Aviation Authority.
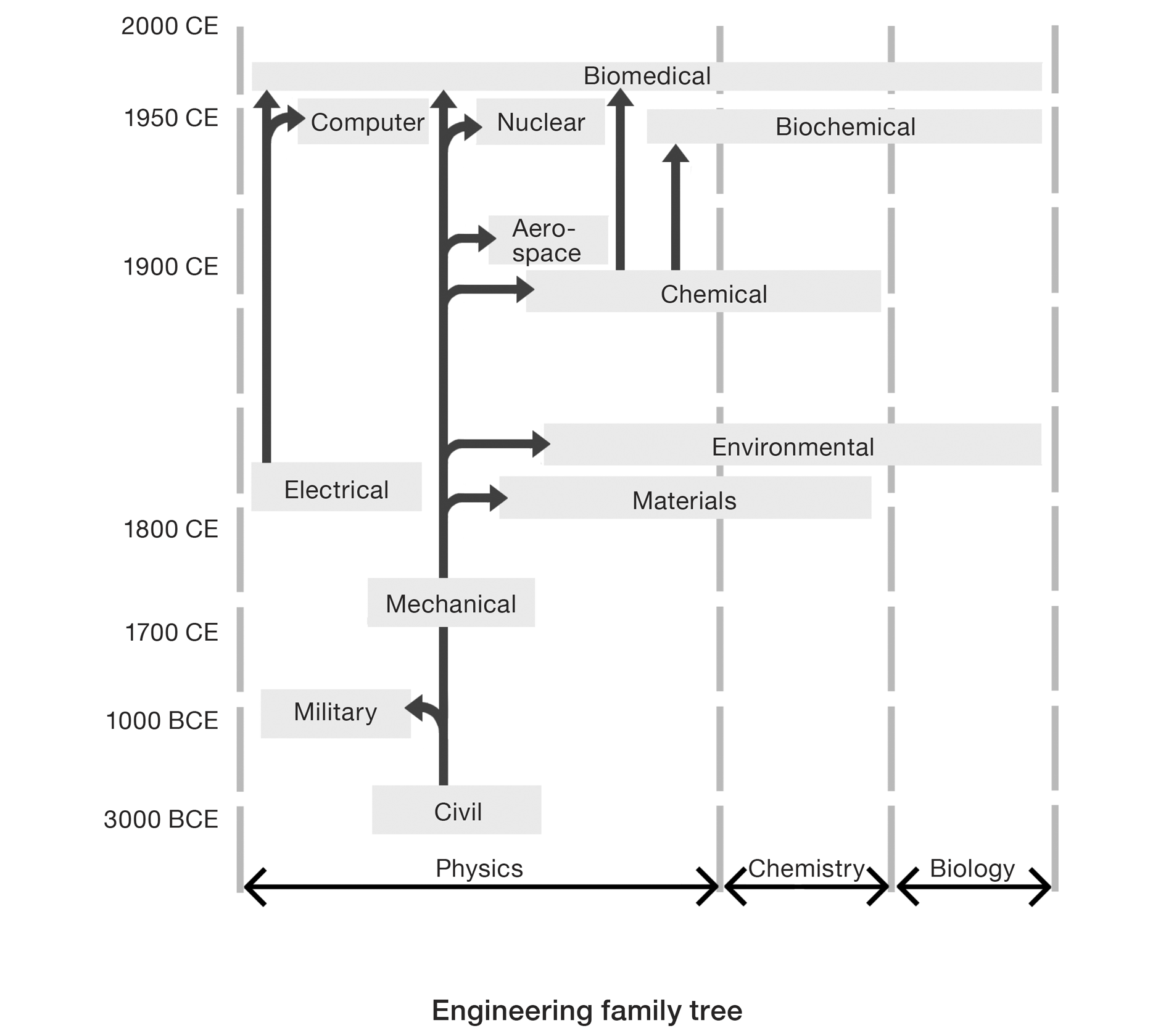
Civil engineering is the grandparent of all engineering.
In its early days during the Roman Empire, civil engineering was synonymous with military engineering. Their kinship was still strong when the first engineering school in America was founded in 1802 at the U.S. Military Academy at West Point, New York. USMA graduates planned, designed, and supervised the construction of much of the nations early infrastructure, including roads, railways, bridges, and harbors, and mapped much of the American West.
Engineering succeeds and fails because of the black box.
Engineering is a field of specialties, with different individuals or teams working on different aspects of a project. A black box conceptually contains the knowledge and processes of an engineering specialty. On multidisciplinary design teams, the output from one disciplines black box becomes the input for the black boxes of one or more other disciplines. The designer of a fuel system, for example, works within a fuel system black box that produces an output for the engine designer; the engine designers black box outputs to the automatic transmission designer, and so on.
Design solutions arent created linearly, however; teams work in complex, interconnected ways. Hence, the black box model works best when employed as a momentary ideal that is adjusted and redefined throughout the design process as constraints become evident, opportunities emerge, prototypes are tested, and goals are clarified. It fails when expected to be permanent and orderly.