If you are reading this book it means that you are taking the initiative to learn C++. C++ was first developed in 1979 by Bjarne Stroustrup. It is a general and efficient programming language that is highly irreplaceable.
C++ is an extension of the C programming language. Bjarnes knowledge of the SIMULA language and its object oriented model aided him in creating class extensions to C. It was originally named C withClasses. It was later renamed to C++.
C++ has a variety of features. These features include:
Learning C++ is something that can take your resume to a new level. It is still used in many major applications, games, browsers and so much more. People are continuously developing and extending upon the functionality of C++. Open source platforms like Github are home to thousands of C++ repositories.
With C++ growing the opportunities for C++ developers are growing as well. Within these positions one can expect an average salary of $100,000 with thousands of jobs being advertised each month.
Although this book is a perfect starting point, dont expect to learn C++ overnight. This language takes practice, persistence and perseverance. If you were wondering, no, you do NOT need to know C before you can grasp C++.
Use the following chapters and exercises as a roadmap on your C++ programming journey, the knowledge awaits.
Chapter 1 Beginning C++

Before you begin to develop in C++ you must first set up an environment that allows you to do effectively. With this being said, you will need a way to run and compile your C++ programs. This can be done in a plethora of ways. These ways include the following:
- Online: Running and compiling programs online is an easy way to avoid excessive downloads or new software. It is also a good option when running programs quickly. There are a good number of sites which allow for this. Due to ease of use, this is the option which will be utilized in this book. Ideone.com is an excellent option for doing so.
- Mac OS X: Programs can be run on a MAC operating system using a program called XCode. This can be downloaded from the Apple developer page. The latest version is highly recommended.
- Linux: In order to run programs effectively with a Linux machine, you will need to install a compiler. GNU GCC is a recommended compiler for beginners or users new to programming in this operating system. You must also download a text editor. Gedit, being one example.
- Windows: Being that Windows is a standard and widespread platform there are several options available for use with it. These may include Code::Blocks, JGrasp or Eclipse.
In order to better understand the structure of a C++ program, Hello World will be used as a template. Hello World programs are generally used for beginners in a various programming languages.
 The first line of the program is used to include the header file within your program. This allows for you to use the operations included in them. The namespace std is needed in order to accurately reference a variety of operations. It also aids you in not having to write the std in front of every cout statement. This line basically refers to the use of a standard namespace.
The first line of the program is used to include the header file within your program. This allows for you to use the operations included in them. The namespace std is needed in order to accurately reference a variety of operations. It also aids you in not having to write the std in front of every cout statement. This line basically refers to the use of a standard namespace.
 The third line simply refers to this being the main function of your program. The body of the program resides inside of the brackets. The cout statement simply prints the items within the quotes or in some cases variable names. This would depend on what is listed in the cout statement. The last line before the bracket is important because it essentially closes or terminates the programs main function.
The third line simply refers to this being the main function of your program. The body of the program resides inside of the brackets. The cout statement simply prints the items within the quotes or in some cases variable names. This would depend on what is listed in the cout statement. The last line before the bracket is important because it essentially closes or terminates the programs main function.
If you are familiar with other programming languages, it is easy to understand that all programs are simply a series of ordered instructions or commands for a computer to perform. These instructions are made up of statement. A statement is the smallest unit of a programming language which is equivalent to a sentence in the English language. In C++, a semicolon is used to complete a statement instead of a period. The notion of a variable is also one that is widespread and heavily used when programming. A variable is a name given to a space in memory that can be changed based on the instructions of the program.
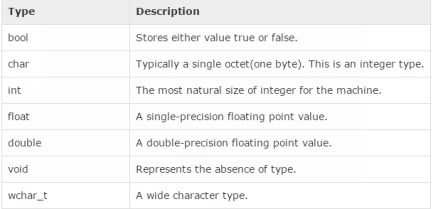
Variables can have a variety of types. These types indicate what can be stored within that specific variable. Variable types include:
Integer (int) This variable type stores only single integers with no decimals. Examples include 5 or 4509. They must be at least 16 bits long. Examples of this include 7854 or 34,
Character (char) This type refers to a single character, like a and is at least 8 bits long.
float - Stores floating point values such as 3.1555. Is usually 32 bits long.
double - Similar to float but with twice the precision. Is usually 64 bits long.
Boolean (bool) - Stores true/false values.
void - Cannot store data directly, but acts a bit like a placeholder.

Using Variables
A variable is a very fundamental piece of a program. They can be of alphanumeric nomenclature but must always begin with a letter. Variables are used in a variety of statements within a program.
There are 3 types of statements. These types include declaration statements , assignment statements and output statements . Examples of all are provided below.
 Before a variable can be used in a program it must first be declared with a declaration statement. A declaration statement gives a name and type to a place in memory where a specific value will be held. In the above example, the name
Before a variable can be used in a program it must first be declared with a declaration statement. A declaration statement gives a name and type to a place in memory where a specific value will be held. In the above example, the name
is y and the type is double.
An assignment statement assigns a specific value to a variable, y. In the example, y is being assigned a value of 20.5
An output statement simply prints the value of a specific item or variable. The example above would have an output of 20.
 Declaration and assignment of a variable can also take place together; this is referred to as initialization . It is important to remember that the only time to initialize a variable is when it is being defined.
Declaration and assignment of a variable can also take place together; this is referred to as initialization . It is important to remember that the only time to initialize a variable is when it is being defined.













 The first line of the program is used to include the header file within your program. This allows for you to use the operations included in them. The namespace std is needed in order to accurately reference a variety of operations. It also aids you in not having to write the std in front of every cout statement. This line basically refers to the use of a standard namespace.
The first line of the program is used to include the header file within your program. This allows for you to use the operations included in them. The namespace std is needed in order to accurately reference a variety of operations. It also aids you in not having to write the std in front of every cout statement. This line basically refers to the use of a standard namespace. The third line simply refers to this being the main function of your program. The body of the program resides inside of the brackets. The cout statement simply prints the items within the quotes or in some cases variable names. This would depend on what is listed in the cout statement. The last line before the bracket is important because it essentially closes or terminates the programs main function.
The third line simply refers to this being the main function of your program. The body of the program resides inside of the brackets. The cout statement simply prints the items within the quotes or in some cases variable names. This would depend on what is listed in the cout statement. The last line before the bracket is important because it essentially closes or terminates the programs main function.

 Before a variable can be used in a program it must first be declared with a declaration statement. A declaration statement gives a name and type to a place in memory where a specific value will be held. In the above example, the name
Before a variable can be used in a program it must first be declared with a declaration statement. A declaration statement gives a name and type to a place in memory where a specific value will be held. In the above example, the name Declaration and assignment of a variable can also take place together; this is referred to as initialization . It is important to remember that the only time to initialize a variable is when it is being defined.
Declaration and assignment of a variable can also take place together; this is referred to as initialization . It is important to remember that the only time to initialize a variable is when it is being defined.