THE SHAPE OF BODY TO COME
WOMAN AND FITNESS
Female body recomposition:
workout and diet
2021 Andrea Raimondi
www.fitnessedintorni.it
AREdit.com
All rights reserved
Contacts: info@aredit.com

2021 Andrea Raimondi
AREdit.com
info@aredit.com
Dedicated to Silvia.
INDEX
Introduction 7
Differences Woman / Man 11
Female Biotypes 14
Water Retention 16
Cellulite 20
Body Fat 22
Energy systems 33
Kilocalorie 41
Energy Balance 43
Food Categories 47
Macronutrients 51
Micronutrients 57
Supplements 59
Lean Mass 63
Muscle Physiology 67
Mechanisms of Hypertrophy 70
Mechanical Tension 72
Metabolic Stress 73
Muscle Damage 74
Training Variables 75
Volume 77
Frequency 79
Intensity 81
Type Of Exercises 83
Progression 85
TUT 86
Rest Between Sets 88
Training Techniques 89
Periodization 97
Major Muscle Groups 103
PART II Practice 121
Dieting 125
Food Diary 125
Why We Eat Too Much? 128
Meal Plan 130
Meal Plan In Practice 135
Esempi di diete 138
Training Exercises 153
Aerobic Activity 195
Training Protocol 199
Adaptation Phase 200
Strenght Phase 210
Recovery Phase 219
Hypertrophy Phase 224
Strenght Phase #2 228
Hypertrophy Phase #2 247
Leg Metabolism Activation 260
Lunch Break Training 261
Lockdown 263
Functional Evaluation 266
Measurements and Indices 268
Motivation 280
Body Recomposition 286
Short Term Body Recomposition 292
Long-term body recomposition 302
Bibliografia 307
Introduction
The physical and biochemical structure of the woman certainly presents differences from that of the man. These differences must be taken into account in creating training plans and eating plans, but they are not so marked that you have to review the theory and practice of a scientific method that aims at body recomposition. The process that leads to the reduction of fat mass and the increase of lean mass is the same in both sexes.
If you want to lose weight, that is, to consume the accumulated fat, we have only two ways: to introduce fewer calories with the diet, eat less than you are used to, or to consume more calories with physical activity, with the same calories introduced. If you combine the two elements, diet, and physical activity, the process is faster and leads to better body composition and to maintain the results obtained over time. The same is true if you want to improve your muscle mass: you have to combine the right caloric intake and the correct training.
The contradiction, in terms of fitness, of the current opulent society, characterized by the great availability of food and the increase in free time, lies in the fact that it proposes as an example of a desirable body the lean and muscular body of models, while on the other keep people standstill in front of a screen, large or small.
The point is that you don't move your body enough: you just need to walk for half an hour a day to improve your fitness.
A better, more toned physique, with less fat, is within everyone's ability. There are few "rules" to know: the theory is simple. The problem is to put it into practice. With the exercises proposed in the book and the training plan described, which serves as the basis for creating your plan, you try to reach the goal for which "fitness" stably enters your life, becomes a habit. Knowing how the human body works help not to be dazzled by the bright mirrors of the fitness and supplement industry and the food industry. There are no miracle diets, there are no diet pills. There is the will that allows achieving the established objectives, through a path built over time.
In the book we highlight the differences between women and men, we will see the fundamental theory for the increase of lean mass and therefore the training theory and its variables, we will also see the food theory, the energy systems of the human body, the role of the various macronutrients. And we will apply the theory to both training and nutrition, using the role of some measurements and some fundamental indices to understand the starting point and the direction of the path. We will conclude with an example of body recomposition for weight loss and an increase in muscle mass.
In this book, you will find everything you need to understand how to build a training plan and a food plan. You can write to me at info@fitnessedintorni.it to join a personalized body recomposition program for you at a discounted price.
Differences Woman / Man
Differences Woman / Man
In this chapter, we describe the main differences between women and men, intending to determine whether they are such as to cause significant changes in the diet and training approach.
Let's start with the amount of body fat . In general, a woman has a higher percentage of body fat than a man. The amount of essential fat , that is essential for living, is on average 10-13% of body weight for women, while for men it is 2-5% of body weight. Below is a summary table:
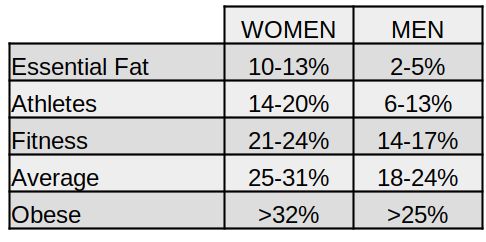
In nature, nothing happens by chance, the presence of double the amount of visceral fat is the result of the evolution of the human-animal. In this case, the fundamental reason is to be found in the woman's ability to reproduce the human species. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, fat reserves are essential to ensure greater chances of surviving mother and child. The distribution of fat is also different, on average, between women and men. This distribution derives from the different hormonal profiles: from the presence of higher levels of estrogen and is accumulated on average in the area of the thighs and buttocks.
The bone structure also has differences that are a result of the evolution of our species: the bones of the pelvis develop in width, while those of man develop in height. Also in this case this conformation is evident to guarantee the survival of the species.
On average, a woman has less muscle mass than a man, therefore fewer muscle cells, myofibrils, and mitochondria. In general, less muscle power than in men.
The different role in the reproductive phase has led women to have a different hormonal profile from men (and vice versa), with higher levels of estrogen and lower testosterone.
In the table the differences between women and men in estrogen and testosterone.
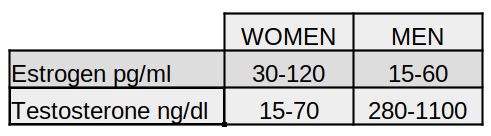
Estrogen, as we said, among other things regulates the distribution of body fat, favoring its deposit in the hips, buttocks, thighs, and abdomen below the navel. In the female body, about two-thirds of estrogen production occurs in adipose tissue thanks to an enzyme that converts the androgens produced by the adrenal glands into estrogen. Their role is of primary importance in all phases of the menstrual cycle with production and absorption of progesterone, estradiol, FSH, LH, and all the changes that this entails at the ovarian and uterine level and in body temperature. In any case, I want to assure all women that there is currently no research that leads to a correlation between the different phases of the menstrual cycle and greater or lesser training capacity. For the record, I report that someone hypothesizes instead a greater increase in strength and the relative amount of training to undergo during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle (before menstruation) and a lighter workout during the post-ovulatory phase.
Next page














