Acknowledgments
M y thanks to a superb editor, Claire Abramowitz, and my assistant Patricia Wagner, who both helped me put this book together. I am also forever indebted to my clients for their support and inspiration.
APPENDIX I
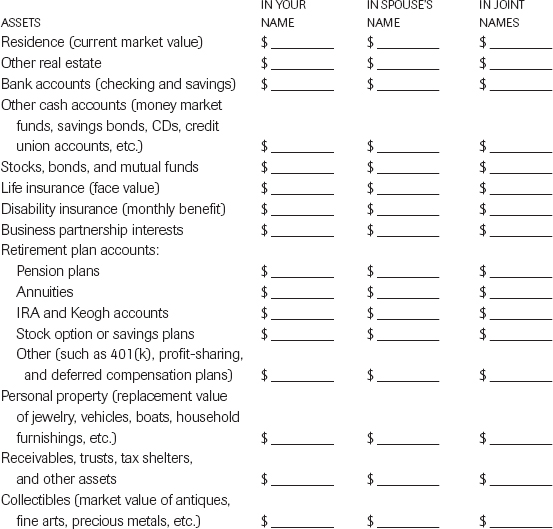
Net Worth Worksheet
D etermining your net worth is the first step in preparing an estate plan. This worksheet will help you to organize your inventory for easy reference.

APPENDIX II
Glossary of Terms
abatement: A priority system of reducing or eliminating bequests that an estate cannot afford to pay.
actuary: One who calculates various insurance and property costs; particularly, one who computes the cost of life insurance risks and insurance premiums.
ademption: Property left to a beneficiary in a will that is no longer in the decedents estate upon death.
adjusted gross estate: During administration, debt administration expenses and losses are deducted. What is left is the adjusted gross estate.
administration of the estate: When the court supervises the distribution of the probated estate.
administrator: A personal representative appointed by the court to administer the estate of an intestate.
alternate valuation date: A date six months after the date of the decedents death.
alternative minimum tax: A way of computing income tax disallowing certain deductions, credits, and exclusions.
annual exclusion: Under gift tax laws, each person may give as much as
$10,000 per year to whomever he or she wishes.
annuity: A right to receive fixed, periodic payments, either for life or for a term of years, payable at specific intervals.
ascendant or ancestor: A person related to an intestate or to a claimant to an intestate share in the ascending lineal line.
attested will: A will signed by a witness.
augmented estate: Property owned at the time of a persons death as well as the value of any property transferred during his or her lifetime without consideration (gifts).
basis: What one has invested or put into property, real or personal. For tax purposes, subtract the basis from the proceeds of a property sale to determine the net gain.
beneficiary: A person or entity selected by the testator to receive a portion of the estate upon the testators death.
bequest: A clause in a will directing the disposition of personal property.
bypass trust: Also known as a credit shelter trust. This is an estate tax-skipping trust used in conjunction with the unlimited marital deduction.
charitable lead trust: Trust in which a charitable organization receives income for a certain period with the remainder passing to the donors beneficiaries after a set period.
charitable remainder trust: Trust created to pay income to beneficiary for a certain period and assets remaining in the trust pass to a charitable organization. There are three types of charitable remainder trusts.
charitable trust: A trust created for the benefit of a charitable organization. There are several different kinds of charitable trusts that can be created.
closely held corporation: A corporation with less than twenty-five shareholders. Usually, all the issued shares are held by only those who work in the corporation.
codicil: A testamentary instrument, which, after it has been properly executed, is added to the will.
community property: A property system premised on the belief that everything acquired during marriage belongs equally to each spouse.
compromise settlement: In a civil action, where two or more persons mutually bind themselves to refer their legal dispute to a third-party arbitrator.
contingency beneficiary: An alternative beneficiary selected by the testator in case the primary beneficiary dies prior to the testator.
contingent remainder: A remainder interest that does not become possessory until a certain specified event takes place.
corpus: Property the settlor/transferor places in the trust. (Also known as the trust res or trust principal.)
credit shelter trust: Also known as the bypass trust. This is an estate tax-skipping trust used in conjunction with the unlimited marital deduction.
Crummey power: The right of a beneficiary of a trust to withdraw a portion of a gift made to the trust equal to the lesser of the annual exclusion ($10,000) or the value of the gift made to the trust that year.
custodian: General term to describe anyone who has charge or custody of property. Also, person named to care for property left to minor under Uniform Gift to Minors Act.
death taxes: Taxes on the estate of the decedent. Federal death taxes are called estate taxes and state death taxes can be termed inheritance taxes, among other names.
devise: A clause directing the disposition of real property in a will. The person named to take the real property is called the devisee.
discretionary trust: A trust that allows the trustee to distribute as much trust income to the beneficiary as he or she deems proper.
disinheriting: When a testator cuts someone out of his or her will. A spouse cannot legally disinherit another spouse, but a parent can dis-inherit a child or another by stating so specifically in his or her will or living trust.
distributee or next of kin: That person or persons who are or who may be entitled to the property of an intestate.
domicile: The permanent residence of a person or the place to which he intends to return even though he may reside elsewhere.
dower or curtesy: A statutory right to inherit a certain portion of the estate of the deceased spouse.
elective share: A portion of the estate that a surviving spouse is entitled to by statute.
escheat: A reversion of property to the state if no relatives are living to inherit.
estate planning: The development of a plan to provide for effective and orderly distribution of an individuals assets at the time of death.
estate tax: Tax imposed on the fair market value of the net asset value of a decedents estate.
execution: Making a written document complete by meeting the legal requirement of the completion, usually signing, witnessing, and notarizing.
executor or personal representative: The administrator named in a will.
executory interest: Interests that will take place in the future.
exemption: A deduction allowed to a taxpayer because of his status (i.e., over sixty-five, being blind, particular dependents, etc.)
fair market value: The average value that can be placed on an asset as determined by market forces.
family limited partnership: A legal entity that can provide asset protection and allows for management and control of assets.
fee simple absolute: The complete, outright right to ownership of land, present and future.
fiduciary: A person having a duty created by his, her, or its undertaking to act primarily for the benefit of others, such as an executor, personal representative, or trustee.
generation-skipping tax: Tax imposed to prevent you from passing property to two or more generations below you without paying a transfer tax.













