Introduction
Latent variables play an important role in testing substantive theories in various fields of social sciences including psychology, sociology, and marketing.
As many authors stress, in a formal sense, there is nothing special about latent variables (Bartholomew et al. ) but usually, they form theory-free measurement models in which only the structural part is strongly embedded in theoretical assumptions. Therefore, the measurement models in marketing and social science are less theory oriented and the theoretical framework of measurement part receives usually less attention than the structural part of SEM model.
However, the measurement model and latent variable conceptualization are also connected to theoretical assumptions and stances. This issue in model-building process is often neglected, taking the assumptions that latent variable definition and operationalization is a theory-free process based solely on statistical and numerical assumptions.
Theoretical assumptions of the latent variables and measurement models are based not only on so called small-m-methodology (assumptions of statistical model, sampling size, identification rules, etc.), but also on big-M-methodology connected with the existing paradigms, meta-theoretical assumptions and schools of thought in a given discipline (McCloskey ).
This problem is important in managerial marketing, where latent variables are regarded almost exclusively as a tool-box with the avoidance of discussion about theoretical assumptions and schools of thought in marketing in the context of big-M-methodology.
Marketing Constructs and Latent Variables Models
2.1 The Evolution of Marketing Theory
One of the earliest definitions of marketing says that Marketing is buying and selling activities. This definition was published in Miss Parloas New Cookbook and Marketing Guide around 1880 (Shaw and Jones ). The domain of marketing discipline, its constructs, theories, and methodologies is presented in Hunts three dichotomies model (1976) who tried to summarize the major aspects of the marketing field of research. He depicted three basic criteria that define marketing as a scientific discipline: (1) research objects (profit and non-profit organizations), (2) the level of analysis (micromacromarketing perspectives), and (3) research objectives (positive and normative marketing). Within this framework, the dominant schools of thought in marketing can be located. Three-dichotomy model helps us to understand the self-identity of marketing and provides a broader context of marketing discipline.
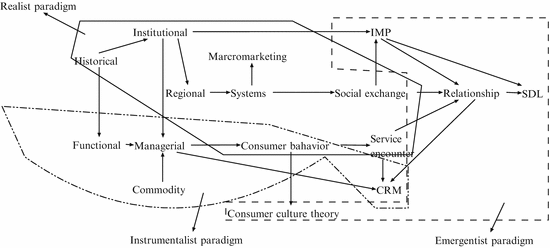
In the evolution of marketing discipline several schools and research paradigms have emerged (Jones et al. presents the dominant schools of thought within the marketing discipline.
Fig. 1
Marketing schools and research paradigms
The variety of approaches can be summarized in three dominant views (paradigms).
The cognitive view, based on the realist paradigm that underlines the problems of causality, functional relations between marketing concepts and, referring to Hunt, takes macro and positive perspective on marketing. Historically, the cognitive view is close to famous Bartels question in the origin era of scientific marketingcan marketing be a science? (Bartels ).
The cognitive view encompassed many schools of thought like distributional, macro-marketing and social exchange, system school, and information processing theory (IPT) in the field of consumer research.
The behavioral view, which is rooted in a predictive-instrumental approach and toolbox analogy of marketing. This approach, mostly popularized and developed by P. Kotler and J. McCarthy textbooks, is more micro and normative oriented. The main schools of thought are managerial, functional, CRM and behavioral perspective models (BPM) in the consumer theory. This view of marketing is labelled also as mainstream or transactional.
The relationship marketing school opens the perspective for contextual, service- and process-oriented view on marketing as a business domain integrator (Vargo and Lusch ). Within this perspective several schools are present i.e. the neo-institutional, Nordic school of relationship marketing, Interactive Marketing and Purchasing (IMP) group and Service-Dominant Logic approach.
2.2 Domains of Marketing Constructs
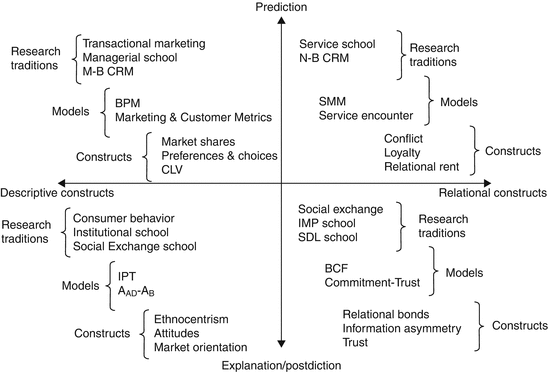
The variety of marketing schools outlined above implies many different methodological orientations, ways of construct definition, and approaches to model building. To simplify this view we can distinguish between two dimensions: (1) the type of causal explanation (predictionpostdiction) and (2) the nature of marketing constructs (descriptiverelational). The first dimension represents the way of causal explanation. In predictive, experimental, and nomothetic approach the objective is to predict future (new) phenomena based on the present (existing) data. In postdictive, historical and idiographic approach, one can explain the past and originated causes on the basis of present data. The second dimension deals with the nature of marketing variables. Descriptive variables are subject-oriented and are used to describe the positional characteristics of subjects under study, like socio-demographic, attitudes, preferences, and values. Relational variables in marketing describe the results of interactions, joint actions of the partners (mutual trust, information asymmetry, loyalty, etc.).
In the classification depicted in Fig., the four basic methodological stances of marketing models can be identified.
Fig. 2
Marketing constructs and research domain
The first (upper left) represents the predictive models based on descriptive marketing constructs. This is the mainstream of managerial marketing, and market-based relationship management (M-B RM). The BPM, consumer metrics indices are defined to measure variables like market shares, preferences and choices, consumer lifetime values (CLV), etc.