The Complete Works of
FRIEDRICH NIETZSCHE
(1844-1900)

Contents
Delphi Classics 2015
Version 1

The Complete Works of
FRIEDRICH NIETZSCHE

By Delphi Classics, 2015
COPYRIGHT
Complete Works of Friedrich Nietzsche
First published in the United Kingdom in 2015 by Delphi Classics.
Delphi Classics, 2015.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, without the prior permission in writing of the publisher, nor be otherwise circulated in any form other than that in which it is published.
Delphi Classics
is an imprint of
Delphi Publishing Ltd
Hastings, East Sussex
United Kingdom
Contact: sales@delphiclassics.com
www.delphiclassics.com
Other classic non-fiction authors by Delphi Classics

Delphi Classics is proud to present the most comprehensive collections of these important writers, with beautiful illustrations and the usual bonus material.
www.delphiclassics.com
The Philosophical Writings
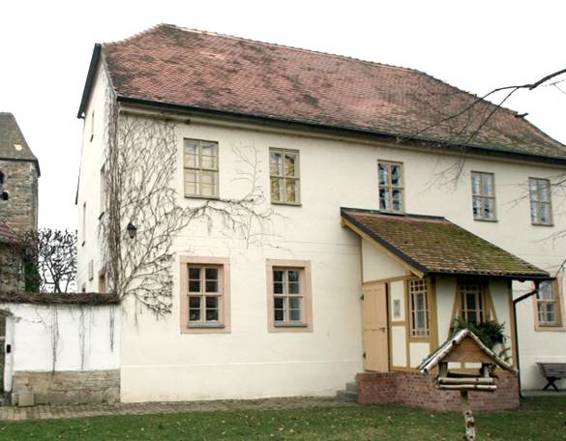

Nietzsches birthplace born on 15 October 1844, he grew up in the small town of Rcken, near Leipzig, in the Prussian Province of Saxony.

Nietzsche in 1861, aged 17
HOMER AND THE CLASSICAL PHILOLOGY
Translated by J. M. Kennedy
( Inaugural Address delivered at Ble University, 28th of May 1869. )
At the present day no clear and consistent opinion seems to be held regarding Classical Philology. We are conscious of this in the circles of the learned just as much as among the followers of that science itself. The cause of this lies in its many-sided character, in the lack of an abstract unity, and in the inorganic aggregation of heterogeneous scientific activities which are connected with one another only by the name Philology. It must be freely admitted that philology is to some extent borrowed from several other sciences, and is mixed together like a magic potion from the most outlandish liquors, ores, and bones. It may even be added that it likewise conceals within itself an artistic element, one which, on sthetic and ethical grounds, may be called imperatival an element that acts in opposition to its purely scientific behaviour. Philology is composed of history just as much as of natural science or sthetics: history, in so far as it endeavours to comprehend the manifestations of the individualities of peoples in ever new images, and the prevailing law in the disappearance of phenomena; natural science, in so far as it strives to fathom the deepest instinct of man, that of speech; sthetics, finally, because from various antiquities at our disposal it endeavours to pick out the so-called classical antiquity, with the view and pretension of excavating the ideal world buried under it, and to hold up to the present the mirror of the classical and everlasting standards. That these wholly different scientific and sthetico-ethical impulses have been associated under a common name, a kind of sham monarchy, is shown especially by the fact that philology at every period from its origin onwards was at the same time pedagogical. From the standpoint of the pedagogue, a choice was offered of those elements which were of the greatest educational value; and thus that science, or at least that scientific aim, which we call philology, gradually developed out of the practical calling originated by the exigencies of that science itself.
These philological aims were pursued sometimes with greater ardour and sometimes with less, in accordance with the degree of culture and the development of the taste of a particular period; but, on the other hand, the followers of this science are in the habit of regarding the aims which correspond to their several abilities as the aims of philology; whence it comes about that the estimation of philology in public opinion depends upon the weight of the personalities of the philologists!
At the present time that is to say, in a period which has seen men distinguished in almost every department of philology a general uncertainty of judgment has increased more and more, and likewise a general relaxation of interest and participation in philological problems. Such an undecided and imperfect state of public opinion is damaging to a science in that its hidden and open enemies can work with much better prospects of success. And philology has a great many such enemies. Where do we not meet with them, these mockers, always ready to aim a blow at the philological moles, the animals that practise dust-eating ex professo , and that grub up and eat for the eleventh time what they have already eaten ten times before. For opponents of this sort, however, philology is merely a useless, harmless, and inoffensive pastime, an object of laughter and not of hate. But, on the other hand, there is a boundless and infuriated hatred of philology wherever an ideal, as such, is feared, where the modern man falls down to worship himself, and where Hellenism is looked upon as a superseded and hence very insignificant point of view. Against these enemies, we philologists must always count upon the assistance of artists and men of artistic minds; for they alone can judge how the sword of barbarism sweeps over the head of every one who loses sight of the unutterable simplicity and noble dignity of the Hellene; and how no progress in commerce or technical industries, however brilliant, no school regulations, no political education of the masses, however widespread and complete, can protect us from the curse of ridiculous and barbaric offences against good taste, or from annihilation by the Gorgon head of the classicist.
Whilst philology as a whole is looked on with jealous eyes by these two classes of opponents, there are numerous and varied hostilities in other directions of philology; philologists themselves are quarrelling with one another; internal dissensions are caused by useless disputes about precedence and mutual jealousies, but especially by the differences even enmities comprised in the name of philology, which are not, however, by any means naturally harmonised instincts.
Science has this in common with art, that the most ordinary, everyday thing appears to it as something entirely new and attractive, as if metamorphosed by witchcraft and now seen for the first time. Life is worth living, says art, the beautiful temptress; life is worth knowing, says science. With this contrast the so heartrending and dogmatic tradition follows in a theory , and consequently in the practice of classical philology derived from this theory. We may consider antiquity from a scientific point of view; we may try to look at what has happened with the eye of a historian, or to arrange and compare the linguistic forms of ancient masterpieces, to bring them at all events under a morphological law; but we always lose the wonderful creative force, the real fragrance, of the atmosphere of antiquity; we forget that passionate emotion which instinctively drove our meditation and enjoyment back to the Greeks. From this point onwards we must take notice of a clearly determined and very surprising antagonism which philology has great cause to regret. From the circles upon whose help we must place the most implicit reliance the artistic friends of antiquity, the warm supporters of Hellenic beauty and noble simplicity we hear harsh voices crying out that it is precisely the philologists themselves who are the real opponents and destroyers of the ideals of antiquity. Schiller upbraided the philologists with having scattered Homers laurel crown to the winds. It was none other than Goethe who, in early life a supporter of Wolfs theories regarding Homer, recanted in the verses
Next page