1.1 Introduction to Global Warming
Global warming involves a temperature change on planet Earth. The temperature is climbing gradually so that the average person does not feel it. However, there are indirect lines of evidence that the average person can see and feel. Increasing unusual weather patterns reported by the news media nearly every day indicate climate change. More floods in parts of the world and more intense droughts in others indicate climate change. Fires raging in some areas and unusual snowfalls in others indicate climate change. A season of intense tornados and more intense hurricanes indicates more energy in the atmosphere and that is climate change. As the Earths global temperature increases, rates of evaporation also increase placing more water in the atmosphere. More evaporation dries out the land, soils, forests and takes more water from the ocean. All are signs of a changing climate. A warming Earth is climate change and it is affecting everyday life throughout the globe. Thus global warming is used to refer to Earths gradually increasing temperature.
1.2 Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is due to a set of chemicals present in Earths atmosphere known as greenhouse gases that trap heat close to the planets surface. As the Suns rays travel through the atmosphere they are in the form of ultraviolet (UV) rays and visible light that warms the Earths surface. The warm surface then emits heat that travels from the surface back toward space as infrared (IR) waves and some of it makes its way back to outer space. The rest of it is trapped by greenhouse gases such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, chlorofluorocarbons, and a few other chemicals and is re-radiated by these chemicals back to the Earths surface. This keeps the lower part of the atmosphere warm enough for humans to survive. If the greenhouses gases increase in the atmosphere, more of this heat is trapped and the Earth warms; if the greenhouse gases diminish in the atmosphere, less of this heat is trapped and the Earth cools. One of these greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide, is so important in trapping and re-radiating this heat energy that it is known as the Earths thermostat. Geologists tell us that throughout Earths history (about 4.5 billion years) there is a direct correlation between carbon dioxide and Earths temperature. Todays climate scientists tell us that models show the temperature increase with the addition of carbon dioxide; and the models do not show the temperature increase without the increase in carbon dioxide. There are other lines of evidence that point to carbon dioxide as the major cause of the most recent global increase in temperature.
The Earth is hurtling through space in its orbit around the Sun while spinning like a top on its axis of rotation. It would be a frozen lifeless place like our moon or the other planets in our Solar System if not for the thin layer of atmosphere that traps solar energy and insulates the Earths surface. The way the atmosphere traps solar energy is called the greenhouse effect because it is similar to a greenhouse or an enclosed car heating up in the Sun. In the case of the car, sunlight comes in through a largely transparent window or windshield and is absorbed by whatever it hits, heating up the interior. Some of that heat is trapped inside, because glass lets heat in but doesnt let it out and the inside temperature of the car increases rapidly in the bright sunlight.
In the Earths atmosphere, sunlight is absorbed by the Earths surface or rooftops or rocks, and that energy is radiated as heat, infrared energy, back toward space. The Earths atmosphere absorbs 531 W/m2 from the Sun plus surface infrared plus thermals plus latent heat, then radiates 333 W/m2 back to the surface and 199 W/m2 back to space. Most of the heat that the atmosphere absorbs doesnt make it to space because it gets reradiated back to the Earths surface by certain gases in the atmosphere, mainly water vapor, carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons, ozone, methane, and a few other gases.
The greenhouse gases consist of more than one atom that are bound together in a way that allows them to vibrate in wavelengths that enable them to capture the infrared radiation on its way back out of the atmosphere. Normally this is a good thing, because without the heat trapped in the atmosphere by these greenhouse gases, planet Earth would be frozen and the temperature would be an uncomfortable 15C. There would be no life on Earth today as we now know it. Life has evolved under CO2 levels of approximately 280 ppm.
If extra carbon dioxide that is not part of the natural carbon cycle is added to the atmosphere, then extra heat is trapped that would otherwise escape to space, and the atmosphere gets warmer.
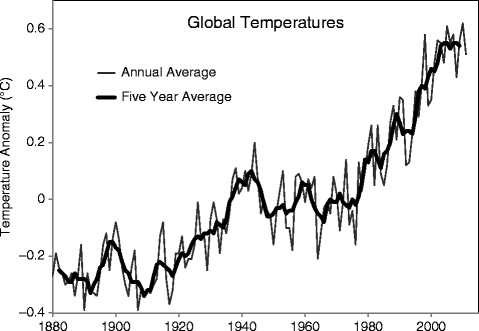
Global warming is an increase in the Earths overall average temperature, since records have been kept, caused by adding extra carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases to the atmosphere that absorb and trap heat. The illustration below (Fig. ) shows the result of this trapped heat during the period 18802009 as compared to the average global temperature for the period 19611990 (stated as a change or an anomaly from the 0 line, either plus or minus in degrees centigrade or Celsius).
Fig. 1.1
Average global temperature during the period 18802009, compiled from various data sources by NASA. The 0-line is the average global temperature for the period 19611990. The smooth curve is a 5-year average (NASA/GISS, Public Domain)
1.3 Climate Sensitivity
We know that Earth is a sustainer of life because it provides us with an environment that has allowed living organisms, including humans, to evolve and thrive on its surface, in its oceans, and in its air. The atmosphere is the main reason life thrives on the planet, at least for humans. It is the air we breathe. It provides water we drink from precipitation. It provides warmth from sunlight captured by molecules that keep the planet warm enough to grow our food and for us to live. It provides us with something called the greenhouse effect that allows us to live on what would be just the third rock from the Sun without it.