 The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: Case, Todd and YuTing Tian. 2022. An Introduction to Creating Standardized Clinical Trial Data with SAS. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc. An Introduction to Creating Standardized Clinical Trial Data with SAS Copyright 2022, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA ISBN 978-1-955977-90-6 (Hardcover) ISBN 978-1-955977-95-1 (Paperback) ISBN 978-1-955977-96-8 (Web PDF) ISBN 978-1-955977-97-5 (EPUB) ISBN 978-1-68580-026-0 (Kindle) All Rights Reserved. Produced in the United States of America.
The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: Case, Todd and YuTing Tian. 2022. An Introduction to Creating Standardized Clinical Trial Data with SAS. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc. An Introduction to Creating Standardized Clinical Trial Data with SAS Copyright 2022, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA ISBN 978-1-955977-90-6 (Hardcover) ISBN 978-1-955977-95-1 (Paperback) ISBN 978-1-955977-96-8 (Web PDF) ISBN 978-1-955977-97-5 (EPUB) ISBN 978-1-68580-026-0 (Kindle) All Rights Reserved. Produced in the United States of America.
For a hard-copy book: No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher, SAS Institute Inc. For a web download or e-book: Your use of this publication shall be governed by the terms established by the vendor at the time you acquire this publication. The scanning, uploading, and distribution of this book via the Internet or any other means without the permission of the publisher is illegal and punishable by law. Please purchase only authorized electronic editions and do not participate in or encourage electronic piracy of copyrighted materials. Your support of others rights is appreciated. U.S.
Government License Rights; Restricted Rights: The Software and its documentation is commercial computer software developed at private expense and is provided with RESTRICTED RIGHTS to the United States Government. Use, duplication, or disclosure of the Software by the United States Government is subject to the license terms of this Agreement pursuant to, as applicable, FAR 12.212, DFAR 227.7202-1(a), DFAR 227.7202-3(a), and DFAR 227.7202-4, and, to the extent required under U.S. federal law, the minimum restricted rights as set out in FAR 52.227-19 (DEC 2007). If FAR 52.227-19 is applicable, this provision serves as notice under clause (c) thereof and no other notice is required to be affixed to the Software or documentation. The Governments rights in Software and documentation shall be only those set forth in this Agreement. product or service names are registered trademarks or trademarks of SAS Institute Inc. in the USA and other countries. indicates USA registration. indicates USA registration.
Other brand and product names are trademarks of their respective companies. SAS software may be provided with certain third-party software, including but not limited to open-source software, which is licensed under its applicable third-party software license agreement. For license information about third-party software distributed with SAS software, refer to http://support.sas.com/thirdpartylicenses . Contents About This Book What Does This Book Cover? The purpose of this book is to introduce standardized clinical trial data to anyone interested in understanding the pharmaceutical industry and how that data is collected and created. This book introduces the concept of standardized clinical data, technical terms, and programming practices in the pharmaceutical industry as well as clear and concise explanations with numerous practical examples. We include basic knowledge of the pharmaceutical industry as well as SAS programming practices used in the industry.
This book does not cover how to create define.xml, although we do introduce it to the reader. What Are the Prerequisites for This Book? The only prerequisite for this book is an interest in the pharmaceutical industry. What Should You Know about the Examples? This book includes SAS code and simulated data for the reader to gain hands-on experience standardized clinical data. Visit the author's page at http://support.sas.com/case to access theexample code and data. Software Used to Develop the Books Content SAS Version 9.4 was used to develop the content and examples in this book. Example Code and Data This book includes data and complete programs used to create simulated standardized clinical trial data.
Visit http://support.sas.com/case to access theexample code and data. An example to derive sex in the Demographics domain is demonstrated below: /*Derive SEX*/ if SEX_= "Female" then SEX= "F" ; else if SEX_= "Male" then SEX= "M" ; else if SEX_= "Unknown" then SEX= "U" ; else if SEX_= "Undifferentiated" then SEX= "UNDIFFERENTIATED" ; SAS OnDemand for Academics  This book is compatible with SAS OnDemand for Academics. If you are using SAS OnDemand for Academics, then begin here: https://www.sas.com/en_us/software/on-demand-for-academics.xhtml . Acknowledgments Thank you to CDISC and the technical reviewers who provided feedback: Margaret Hung, Matt Becker, Peter Eberhardt, Laura Elliott, William Kuan, and Crystal Cheng. We Want to Hear from You SAS Press books are written by SAS Users for SAS Users. We welcome your participation in their development and your feedback on SAS Press books that you are using.
This book is compatible with SAS OnDemand for Academics. If you are using SAS OnDemand for Academics, then begin here: https://www.sas.com/en_us/software/on-demand-for-academics.xhtml . Acknowledgments Thank you to CDISC and the technical reviewers who provided feedback: Margaret Hung, Matt Becker, Peter Eberhardt, Laura Elliott, William Kuan, and Crystal Cheng. We Want to Hear from You SAS Press books are written by SAS Users for SAS Users. We welcome your participation in their development and your feedback on SAS Press books that you are using.
Please visit sas.com/books to do the following:
- Sign up to review a book
- Recommend a topic
- Request information on how to become a SAS Press author
- Provide feedback on a book
Chapter 1: Understanding the Industry In the pharmaceutical industry, there is a mandate to create standardized clinical data using very specific rules. These rules are created and governed by the Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC). In this book, we describe and illustrate how to create these required CDISC data sets with SAS code. A statistical programmer should be familiar with the CDISC rules required to create standardized clinical trial data sets. After reading this book, readers will be able to understand CDISC standardized clinical data structures, as well as how to create it. 1.1 Statistical Programmer Work Process In the pharmaceutical industry, the primary goal of a statistical programmer is to create standard data efficiently in order for the clinical trial biostatistician to perform their analysis.
A simplified illustration of the process workflow for the statistical programmer is shown in . shows that the work process starts from the Case Report Form (CRF), which is designed for a specific study to collect clinical trial raw data from a site. Often, studies are global having sites in countries all over the world. The Data Management group creates the CRF by working with the statistical programmer and other functions to ensure that the appropriate data is collected for the purpose of that study. After the CRF is created and data is entered into it by the sites, the statistical programmer uses this data to create CDISC Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) domains to group collected information from the CRF in a way that facilitates standardization. The statistical programmer then creates CDISC Analysis Data Model (ADaM) data sets from the SDTM domains to support clinical trial analysis.
Figure 1.1: Statistical Programmer Process Workflow 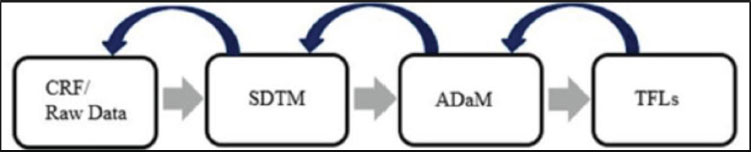 Note: When we refer to SDTM, we use the term domain, and for ADaM, we use the term data set. To be crystal clear, both models generate standardized clinical data using SAS. Creating SDTM and ADaM data sets ensure that data will meet the criteria to be accepted by regulatory agencies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Finally, the statistical programmer generates the Tables, Figures, and Listings (TFLs), which are used to support analysis presented in the Clinical Study Report (CSR). The CSR is used to provide evidence to regulatory agencies about the safety and efficacy of the study drug. Note: This workflow actually represents a much more complicated process.
Note: When we refer to SDTM, we use the term domain, and for ADaM, we use the term data set. To be crystal clear, both models generate standardized clinical data using SAS. Creating SDTM and ADaM data sets ensure that data will meet the criteria to be accepted by regulatory agencies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Finally, the statistical programmer generates the Tables, Figures, and Listings (TFLs), which are used to support analysis presented in the Clinical Study Report (CSR). The CSR is used to provide evidence to regulatory agencies about the safety and efficacy of the study drug. Note: This workflow actually represents a much more complicated process.
Next page









 The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: Case, Todd and YuTing Tian. 2022. An Introduction to Creating Standardized Clinical Trial Data with SAS. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc. An Introduction to Creating Standardized Clinical Trial Data with SAS Copyright 2022, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA ISBN 978-1-955977-90-6 (Hardcover) ISBN 978-1-955977-95-1 (Paperback) ISBN 978-1-955977-96-8 (Web PDF) ISBN 978-1-955977-97-5 (EPUB) ISBN 978-1-68580-026-0 (Kindle) All Rights Reserved. Produced in the United States of America.
The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: Case, Todd and YuTing Tian. 2022. An Introduction to Creating Standardized Clinical Trial Data with SAS. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc. An Introduction to Creating Standardized Clinical Trial Data with SAS Copyright 2022, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA ISBN 978-1-955977-90-6 (Hardcover) ISBN 978-1-955977-95-1 (Paperback) ISBN 978-1-955977-96-8 (Web PDF) ISBN 978-1-955977-97-5 (EPUB) ISBN 978-1-68580-026-0 (Kindle) All Rights Reserved. Produced in the United States of America. This book is compatible with SAS OnDemand for Academics. If you are using SAS OnDemand for Academics, then begin here: https://www.sas.com/en_us/software/on-demand-for-academics.xhtml . Acknowledgments Thank you to CDISC and the technical reviewers who provided feedback: Margaret Hung, Matt Becker, Peter Eberhardt, Laura Elliott, William Kuan, and Crystal Cheng. We Want to Hear from You SAS Press books are written by SAS Users for SAS Users. We welcome your participation in their development and your feedback on SAS Press books that you are using.
This book is compatible with SAS OnDemand for Academics. If you are using SAS OnDemand for Academics, then begin here: https://www.sas.com/en_us/software/on-demand-for-academics.xhtml . Acknowledgments Thank you to CDISC and the technical reviewers who provided feedback: Margaret Hung, Matt Becker, Peter Eberhardt, Laura Elliott, William Kuan, and Crystal Cheng. We Want to Hear from You SAS Press books are written by SAS Users for SAS Users. We welcome your participation in their development and your feedback on SAS Press books that you are using. Note: When we refer to SDTM, we use the term domain, and for ADaM, we use the term data set. To be crystal clear, both models generate standardized clinical data using SAS. Creating SDTM and ADaM data sets ensure that data will meet the criteria to be accepted by regulatory agencies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Finally, the statistical programmer generates the Tables, Figures, and Listings (TFLs), which are used to support analysis presented in the Clinical Study Report (CSR). The CSR is used to provide evidence to regulatory agencies about the safety and efficacy of the study drug. Note: This workflow actually represents a much more complicated process.
Note: When we refer to SDTM, we use the term domain, and for ADaM, we use the term data set. To be crystal clear, both models generate standardized clinical data using SAS. Creating SDTM and ADaM data sets ensure that data will meet the criteria to be accepted by regulatory agencies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Finally, the statistical programmer generates the Tables, Figures, and Listings (TFLs), which are used to support analysis presented in the Clinical Study Report (CSR). The CSR is used to provide evidence to regulatory agencies about the safety and efficacy of the study drug. Note: This workflow actually represents a much more complicated process.