Introduction
I n this guide you will be introduced to Van Goghs masterpieces, and you will discover some of the ideas and ambitions behind his art .
This comprehensive guide to the Van Gogh museums holdings provides the ideal introduction to the masterpieces from one of the worlds most popular and beloved museums. For the purpose of clarity we will stick to a chronological presentation, while discussing works by Van Gogh and by other artists separately .
The Van Gogh museum houses the world's largest Van Gogh collection, comprising some 200 paintings, 400 drawings and 700 letters .
On display along with these works are masterpieces by Van Gogh's contemporaries, including Paul Gauguin, Emile Bernard, Georges Seurat, Camille Pissarro, Paul Signac and Auguste Rodin .
When Vincent van Gogh died in 1890, he did not leave a will. The artists three sisters Elisabeth, Anna and Willemien decided that all of Van Goghs work would be inherited by Theo, who after all took care of him during his entire career. Thus, the entire collection of Van Gogh paintings, drawings and letters were owned by Van Gogh's brother Theo .
After Theos death, on 25 January 1891, it passed to his widow, Johanna van Gogh-Bonger (1862-1925). She sold some of the works, but the majority stayed in her possession and were inherited by her son, Vincent Willem van Gogh (1890-1978) in 1925. Part of the works she sold are now in the wonderful collection of the Krller-Mller museum in The Netherlands. This museum, set in a beautiful park, holds the second largest collection of Van Goghs in the world, and is definitely worthwhile a visit .
Vincent, an engineer, loaned some of his uncles works to the Stedelijk Museum, Amsterdams premier venue for modern art, in 1930. As the appreciation for the works of the artist Vincent van Gogh exploded, the demand grew for a special museum. At that time, a museum dedicated to a single artist was still something of an anomaly .
A foundation was set up in order to keep Van Gogh's unsold paintings and drawings, but also other artists' work as well as the book and print collections, together as one collection. Various paintings by Van Gogh's friends and contemporaries were part of the collection of contemporary art owned by Vincent and his brother Theo van Gogh .
In 1962, the collection was put in the care of the foundation for 15 million guilders, even though the estimated value of the collection was more than 300 million guilders .
The Dutch state built the Van Gogh Museum and still acts as the collection's administrator. Legally, the collection is on permanent loan to the Dutch state .
In 1973 Queen Juliana of the Netherlands opened the Van Gogh Museum, housed in the same specially designed building that it occupies today .
The collection has substantially grown since the inauguration of the museum, and through the financial support of the Vincent van Gogh Foundation, the Prince Bernhard Fund and many other sponsors, new works of exceptional standing have been acquired. The museum regularly exhibits long-term loans from other institutions .
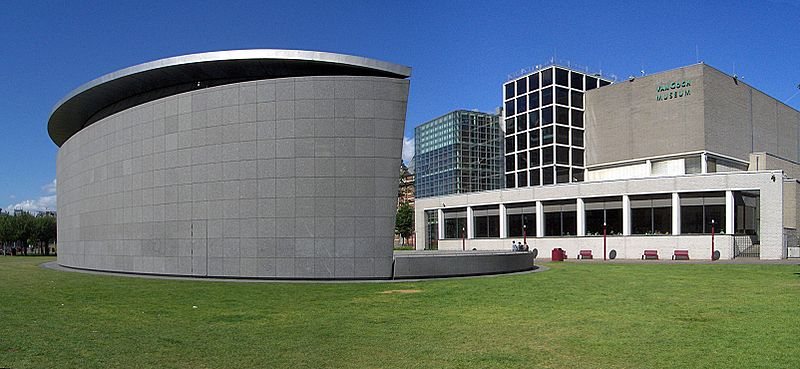
The Building
T he original museum building is designed by one of the most prominent members of the Dutch artistic movement De Stijl, the architect Gerrit Rietveld .
Japanese Wing of the Van Gogh Museum, main building., designed by Gerrit Rietveld. Photography by Minke Wagenaar Wikimedia Commons.
Unfortunately, Rietveld was not able to fully realize his vision, as he died before the completion of the building in 1973. Still, with its clear lines and walls devoid of embellishment, enabling the visitor to focus entirely on the paintings themselves, the Van Gogh Museum is characteristic of Rietveld who was famous for his simplified creations .
The annex was designed by the architect Kisho Kurokawa (1934 - 2007) and built in 1999. It is known as the Kurokawa wing, and is used for temporary exhibitions .
The Kurokawa wing of the Van Gogh Museum. Photography by Wladislav Wikimedia Commons.
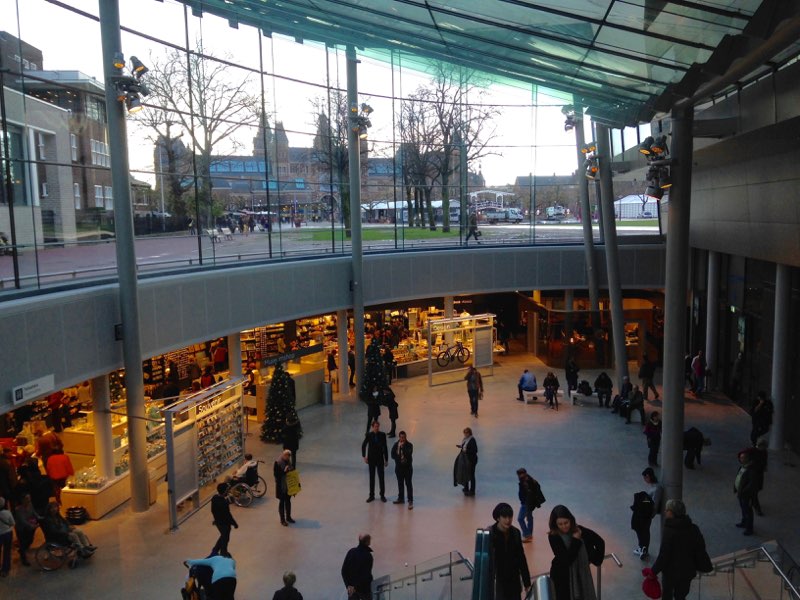
More recent alterations to the building include the construction of a new entrance hall. Since September 2015, visitors enter the museum through a glass building on Museumplein. The new transparent structure gave the museum another 800 square meters, improving the experience for the ever growing number of visitors.. Due to time-slotted admission tickets, visitor do not perceive the museum as overcrowded, even in the rather busy summer months. There is a new spacious and light reception area with cloakrooms, and a completely redesigned museum shop .
Having long been a dream of the museum, the new entrance hall was designed by Kisho Kurokawa Architect & Associates from Tokyo, the same agency that worked on the annex .
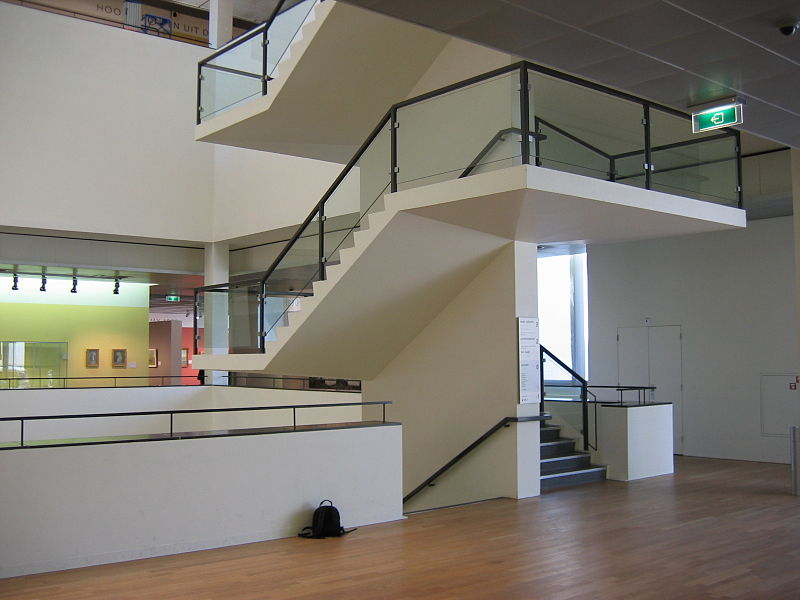
Interior of the new entrance hall with the Rijksmuseum in the back. Photograph by the author.
The Van Gogh Museum is one of the most popular museums in Amsterdam. In 2016 the total number of visitor was more than 2 million, coming from over 125 countries in the world, The majority of visitors were from the Netherlands, followed by the United States, Italy, France and Great Britain .
Short Biography of Vincent van Gogh
W hen comparing Vincent van Gogh's career with those of other artists, it soon becomes clear that his was one of the shortest in art history. It was not until the age of twenty-seven that he began work as a full-time professional painter, and he died a mere ten years later .
Yet in this short window of time, Vincent van Gogh (1853 - 1890) produced a body of works that is not only impressive in size, but also marks the origin of several modern art movements .
From the years following his death up until present day, artists have been inspired by his vibrant and innovative use of color, his expressionism, as well as his uncompromising attitude towards art and life .
Vincent van Gogh, 18 years old.
Born in the small town of Groot-Zundert (Brabant) in The Netherlands in 1853, Vincent Willem van Gogh was a shy and introverted child. At the age of sixteen he began work as an assistant at the art dealership Goupil & Co. in The Hague, a company his brother Theo would also join a few years later .
During this time, Van Gogh was reassigned to various major cities including London and Paris, before eventually losing his job in 1876. Although he loved art, he did not especially like his job in the art world. After his dismissal, he took an unpaid job at a boarding school in Ramsgate (England). Various other jobs followed, not terribly successful. In 1878 he relocated to Belgium to work as a layman minister, and ended up realizing his artistic calling .