Introduction to
Nuclear and Particle Physics
Third Edition
V.K. Mittal
Professor of Physics
Punjabi University, Patiala
R.C. Verma
Professor of Physics
Punjabi University, Patiala
S.C. Gupta
Former Professor and Head
Department of Physics
Punjabi University, Patiala

Delhi-110092
2013
.
INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHYSICS, Third Edition
V.K. Mittal, R.C. Verma and S.C. Gupta
2013 by PHI Learning Private Limited, Delhi. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form, by mimeograph or any other means, without permission in writing from the publisher.
ISBN-978-81-203-4738-0
The export rights of this book are vested solely with the publisher.
Third Printing (Third Edition) April, 2013
Published by Asoke K. Ghosh, PHI Learning Private Limited, Rimjhim House, 111, Patparganj Industrial Estate, Delhi-1100 92 and Printed by Raj Press, New Delhi-110012.
.
Contents
Preface xiii
Preface to the First Edition xv
1.1Introduction
1.2Historical Developments
1.3Constituents of the Nucleus
1.3.1ProtonElectron Hypothesis
1.3.2ProtonNeutron Hypothesis
1.3.3Terms Associated with the Nucleus
1.4Quantitative Facts about Nucleus
1.4.1Size
1.4.2Mass
1.4.3Density
1.4.4Energy
1.4.5Charge
1.5Binding Energy
1.5.1Mass Defect
1.5.2Packing Fraction
1.5.3Fusion and Fission
1.5.4Binding Energy per Nucleon
1.6Nuclear Angular Momentum
1.7Nuclear Moments
1.7.1Magnetic Dipole Moment
1.7.2Electric Quadrupole Moment
1.8Wave Mechanical Properties
1.8.1Parity
1.8.2Statistics
1.9Nature of Nuclear Forces
1.10Yukawa Theory of Nuclear Forces
1.11Mass Spectrometry
1.11.1Bainbridge Spectrograph
1.11.2Bainbridge and Jordan Mass Spectrograph
1.12Determination of Charge by Moseley Law
Numerical Problems
Review Questions
2.1Introduction
2.2Liquid Drop Model
2.2.1Semiempirical Mass Formula
2.2.2Mass of Most Stable Isobar
2.2.3Achievements of Liquid Drop Model
2.2.4Failures of Liquid Drop Model
2.3Shell Model
2.3.1The Square Well Potential
2.3.2The Harmonic Oscillator Potential
2.3.3Spin-Orbit Coupling
2.3.4Predictions of the Shell Model
2.3.5Achievements of the Shell Model
2.3.6Failures of Shell Model
*2.4Fermi Gas Model
2.5Collective Model
Numerical Problems
Review Questions
3.1Introduction
3.2Laws of Disintegration
3.2.1Activity and its Units
3.2.2Half-life
3.2.3Average (Mean) Life
3.3Radioactive Series
3.4Law of Successive Disintegration
3.4.1Radioactive Equilibrium
3.5Alpha Emission
3.5.1Properties of Alpha Particles
3.5.2Alpha Spectrum
3.5.3Range of Alpha-Particles
3.5.4GeigerNuttal Law
3.5.5Gamow Theory of Alpha Decay
3.6Beta Decay
3.6.1Conditions for Spontaneous Emission of -Particles
3.6.2Conditions for Spontaneous Emission of + -Particles
3.6.3Beta-Particle Spectrum
3.6.4Electron Capture
3.6.5Neutrino ( ) and Antineutrino (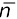 )
)
3.6.6Detection of Antineutrino (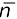 )
)
3.6.7Detection of Neutrino ( )
3.7Gamma Decay
3.7.1Gamma Decay
3.7.2Internal Conversion
3.7.3Internal Pair Conversion
3.8Artificial or Induced Radioactivity
*3.9Applications of Radioactivity
3.9.1Medicine
3.9.2Food and Agriculture
3.9.3Insect Control
3.9.4Reactors
3.9.5Research Reactors
3.9.6Geology and Element Identification
3.9.7Radioactive Dating
3.9.8Radioactive Tracers
3.9.9Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
3.9.10In Space Flights
3.9.11In Sea
Numerical Problems
Review Questions
4.1Introduction
4.2Types of Nuclear Reactions
4.2.1Reactions Based on the Reaction Mechanism
4.2.2Reactions Based on the Mass of Projectile
4.3Nuclear Reaction Cross-Section
4.3.1Measurement of Cross-Section
4.3.2Units of Cross-Section
4.3.3Different Types of Cross-Sections
4.4Conservation Laws in Nuclear Reactions
4.4.1Conservation of Mass-Energy
4.4.2Conservation of Linear Momentum
4.4.3Conservation of Charge/Atomic Number
4.4.4Conservation of Nucleons/Mass Number
4.4.5Conservation of Angular Momentum
4.4.6Conservation of Spin
4.4.7Conservation of Statistics
4.4.8Conservation of Parity
4.4.9Conservation of Lepton Number
4.5Kinematics of Nuclear Reactions
4.5.1Exoergic or Exothermic Reactions
4.5.2Endoergic or Endothermic Reactions
4.5.3Threshold Energy
4.6Compound Nucleus
*4.7Nuclear Fission
4.7.1Neutron-Induced Fission
4.7.2Energy Released in Fission
*4.8Nuclear Fusion
4.8.1Energy Released in Fusion
4.8.2Hydrogen Burning and Solar Energy
4.8.3Helium Burning in Stars
Numerical Problems
Review Questions
5.1Introduction
5.2Energy Loss by Heavy Charged Particles
5.3Interaction of Electrons with Matter
5.4Range of Charged Particles
5.5Interaction of Gamma Rays with Matter
5.5.1Radiation Length
5.5.2Half-thickness
5.5.3Experimental Determination of Attenuation Coefficient
5.6Photoelectric Effect
5.6.1Experimental Verification of Photoelectric Effect
5.7Compton Effect
5.7.1Experimental Verification of Compton Effect
5.8Pair Production
5.8.1Positron Annihilation
Numerical Problems
Review Questions
6.1Introduction
6.2Cockcroft and Walton Accelerator
6.2.1Principle
6.2.2Construction
6.2.3Working
6.2.4Advantages
6.2.5Limitations
6.3Van de Graaff Accelerator
6.3.1Principle
6.3.2Construction
6.3.3Working
6.3.4Advantages
6.3.5Limitations
6.4Tandem Accelerator
6.4.1Principle
6.4.2Construction and Working
6.4.3Advantages
6.4.4Limitations
6.5Linear Accelerator ( linac ) or Drift Tube Accelerator
6.5.1Principle
6.5.2Construction
6.5.3Working
6.5.4Advantages
6.5.5Limitations
6.6Wave-Guide Accelerators
6.7Magnetic Resonance Accelerators or Cyclotrons
6.7.1Principle
6.7.2Construction
6.7.3Working
6.7.4Theory
6.7.5Advantages
6.7.6Limitations
6.8Betatron
6.8.1Principle
6.8.2Construction
6.8.3Working
6.8.4Average Energy per Orbit
6.8.5Calculation of Final Energy of Electrons
*6.9Synchrocyclotrons or Frequency Modulated Cyclotrons
6.9.1Principle
6.9.2Construction
6.9.3Theory
6.9.4Advantages
6.9.5Limitation
*6.10Azimuthally Varying Field (A.V.F.) or Sector Focusing Cyclotrons
6.10.1Principle
6.10.2Construction
6.11Synchrotrons
6.11.1Proton Synchrotron
Numerical Problems
Review Questions
7.1Introduction
7.2Gas-Filled Detectors
7.2.1Principle
7.2.2Construction and Working
7.2.3Concept of Average Energy Required for Creating ElectronIon
Pair ( W -value)
7.3Ionization Chamber
7.3.1Principle
7.3.2Construction
7.3.3Working
7.3.4Main Uses
7.3.5Main Drawback
7.4Proportional Counters
7.4.1Principle
7.4.2Construction
7.4.3Working
7.4.4Uses
7.4.5Main Disadvantage
Next page













 )
) )
)