Zsolt Argenyi and Chris H. Jokinen Current Clinical Pathology Cutaneous Neural Neoplasms A Practical Guide 10.1007/978-1-60327-582-8_1 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011
1. The Peripheral Nerve and Cutaneous Neural Tumors: Introduction, Definitions, and Classification
Abstract
Peripheral nerves, brain, and spinal cord comprise the neural organ system, which is traditionally divided by its components into the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. Cutaneous peripheral nerves are responsible for the transmission of sensory information, motor function, and control of multiple functions vital to preservation of the integument and survival of the human. Among these are sensory of the external environment through touch and pressure, and temperature regulation by control over erector pili muscle, eccrine duct secretion for sweating, and constriction or dilation of blood vessels for conservation or release of heat. The peripheral component of the neural organ system includes nerve fibers, nerve fascicles, and various sensory receptors.
Peripheral nerves, brain, and spinal cord comprise the neural organ system, which is traditionally divided by its components into the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. Cutaneous peripheral nerves are responsible for the transmission of sensory information, motor function, and control of multiple functions vital to preservation of the integument and survival of the human. Among these are sensory of the external environment through touch and pressure, and temperature regulation by control over erector pili muscle, eccrine duct secretion for sweating, and constriction or dilation of blood vessels for conservation or release of heat. The peripheral component of the neural organ system includes nerve fibers, nerve fascicles, and various sensory receptors.
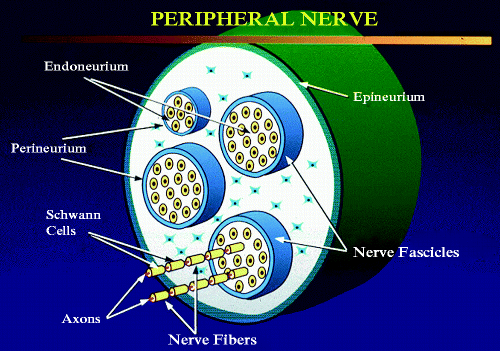
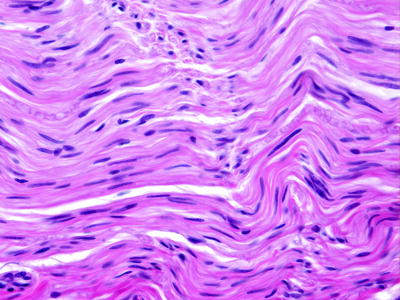
The basic unit of the peripheral nerve is the nerve fiber , which is composed of an axon and Schwann cells (Fig. ). Axons are long cytoplasmic extensions of a neuron whose cell body is located either in the ganglionic chain or central nervous system. Ascending sensory nerve axons attach to cell bodies located in the dorsal root ganglia. Motor axons descend from cell bodies in the ventral horn of the spinal cord, motor nuclei in the brain stem, or sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia. Axons contain microfilaments, specialized intermediate filaments (neural filaments) and microtubules. Schwann cells are specialized neurosustentacular cells that provide support for axons and contribute to the propagation of transmitted stimuli. Schwann cells are encased by a continuous basal lamina and also contain intermediate filaments.
Fig. 1.1
Peripheral nerve: nerve fibers are composed of axons, surrounding Schwann cells, and supportive stromal cells. Individual nerve fascicles are encompassed by perineurium. The nerve fascicles are in turn surrounded by stroma, which is held together by epineurium forming the nerve (artwork by ZA)
Axons can be myelinated or unmyelinated. Myelinated axons are sheathed by multiple rotations of Schwann cell cytoplasmic membranes, resulting in increased velocity of neural transmissions (action potentials). Unmyelinated axons are also bounded by the cytoplasm of the Schwann cells but without the multiple rotations found in myelinated forms. Axons end directly in the epidermis or on cells of the cutaneous adnexal structures or smooth muscle. Sensory axons are connected to specialized mechanoreceptors, such as the corpuscles of Pacini, Ruffini, or Meissner; hair follicle receptors; and Merkel cells.
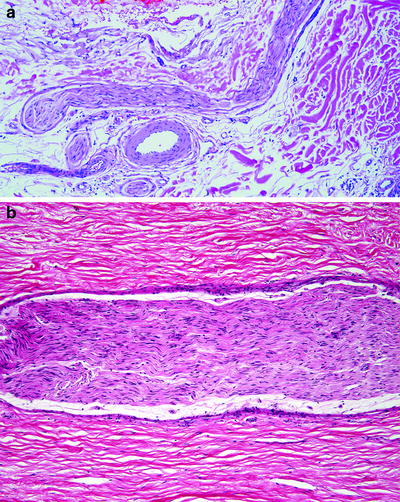
A nerve fascicle is a bundled collection of multiple nerve fibers, which constitutes the tissue-based component of the peripheral nerve upon entering the skin. Nerve fascicles are usually the most evident neural structures at the light microscopic level (Figs..
Fig. 1.2
Peripheral nerve fascicle: longitudinal sections of nerve fascicles in the subcutis ( a ) and soft tissue adjacent to a traumatic neuroma ( b ). The fascicles are composed of closely aligned Schwann cells with elongated slender nuclei. The entire fascicle is surrounded by perineurium
Fig. 1.3
Peripheral nerve fascicles in cross section highlight the dot-like appearance of Schwann cell nuclei when cut perpendicular to the plane of direction. Axons are difficult to visualize but are located by the clear space surrounding them. Individual neural filaments can be viewed with immunohistochemistry. Perineurial cells have slender nuclei with elongated cytoplasmic processes
Fig. 1.4
Schwann cells have slender elongated nuclei with one tapered and one blunt end. The nuclear chromatin is fine and uniform. The cells have eosinophilic elongated cytoplasmic processes
Fig. 1.5
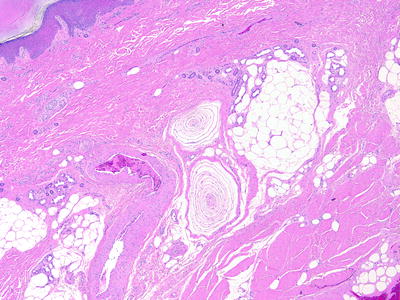
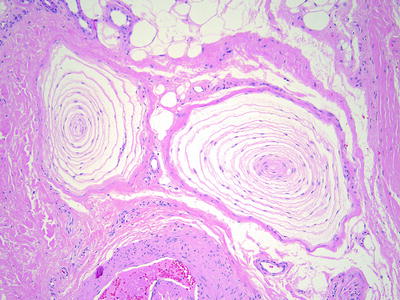
Pacinian corpuscles are located in the reticular dermis of subcutis in acral skin. They are often located near medium-sized muscular blood vessels
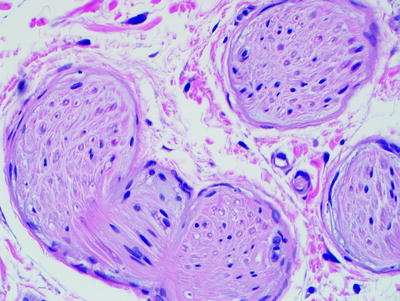
Fig. 1.6
Pacinian corpuscles are composed of a central nerve fiber surrounded by concentric layers of cells with elongated cytoplasmic processes
Fig. 1.7
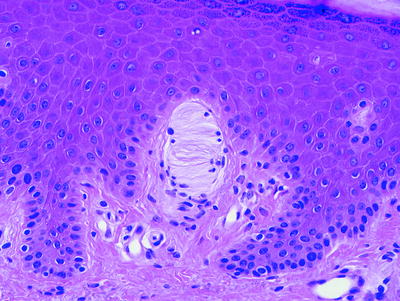
Meissner corpuscles are touch receptors located in the dermal papillae of acral skin. They appear as round or ovoid bodies with small peripheral nuclei and lamellar processes in the center
The space between individual nerve fibers within the fascicle is called endoneurium . The endoneurium is composed of fibrocytes/fibroblasts and mast cells embedded in a collagenous stroma with abundant capillaries. Collagen fibrils of the endoneurium are often partially surrounded by Schwann cell cytoplasmic processes. This suggests that Schwann cells, in part, produce collagen fibrils. Immunohistochemical evidence of type IV collagen in Schwann cells (Chap. 2) and Schwann cell neoplasms further supports this role.