Make sure you know how to simplify fractions because answers are generally presented in simplest form. Be able to find the least common denominator of two or more fractions. Know how to multiply and divide fractions as well as use mixed numbers and improper fractions. Be comfortable solving fraction problems that involve variables.
2. Be able to convert between percents, decimals, and fractions. Be able to recognize the meaning of terminology used in percentage problems in order to solve for an unknown. See .
3. EXPONENTS
Familiarize yourself with the exponential notation and know how to apply the rules of exponents, particularly to simplify an expression containing multiple exponents. Avoid common mistakes with exponents, such as incorrectly addressing negative exponents or multiplying exponents when they should be added.
Be aware of rational exponents as well as variables in exponents. See .
4. REAL NUMBERS
Be able to relate the different types of real numbers, and which groups are subsets of other groups. Know the properties of real numbers, including the properties of addition and multiplication. Be able to apply the distributive property.
Review absolute value to know: what it means how it is represented in symbolic form how to solve problems involving absolute value See .
5. RADICALS
Know how to find roots of real numbers. Be aware that some problems have two solutions. Know how to: identify the principal square root use the product and quotient properties of radicals determine the simplest radical form rationalize a denominator containing a radical for both square roots and cube roots use a conjugate, especially when the denominator contains a binomial radical expression See .
Know how to add, subtract, multiply, and factor polynomials. Be familiar with the products of special polynomials, such as
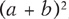
,
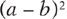
, and
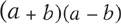
. Be able to recognize perfect square trinomials and the difference of perfect squares. See .
7. QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
Know the meaning of each term in the Quadratic Formula.
Be able to: choose the answer that lists the roots of the quadratic equation determine the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation without actually solving for them use the discriminant to decide if there are two real rational roots, two real irrational roots, one real root, or no roots See .
8. INEQUALITIES
Know the Transitive Property of Inequality as well as the addition and multiplication properties. Inequalities questions may involve conjunctions or disjunctions, as well as absolute values. Be prepared to relate a solution to a graph.
9. Know how to simplify rational expressions and solve equations involving rational expressions. Be familiar with the special products studied with polynomials. Be able to multiply, divide, add, and subtract rational expressions. See .
10. SYSTEMS
Review simultaneous equations and equivalent systems.
Be able to solve systems by substitution or linear combination. Distinguish between the three possible solution sets: one solution, no solution, and infinitely many solutions. Be familiar with word problems with two unknowns. Know how to set up a system and solve it to find the answer. See .
11.
THREE-DIMENSIONAL FIGURES
Study the terminology relating to polyhedra: faces, edges, vertices, or bases. Be able to distinguish among and calculate volume, surface area, and lateral surface area. Review the area formulas for various shapes, such as rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and circles. Know the characteristics of prisms, cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres. Be able to find the ordered triple that describes the vertex of a figure graphed in three dimensions.
12.12.
COORDINATE GEOMETRYLINES
Understand plane rectangular coordinate systems. Know how to: name the ordered pair describing a point find the midpoint of a line segment determine the distance between two points Know how to use these skills to describe a figure, such as finding the area of a parallelogram given a graph. Be able to find the slope of a line and distinguish between positive and negative slopes. Know that parallel lines have the same slope and perpendicular lines have slopes that are opposite reciprocals. Be able to: recognize linear equations in slope-intercept form, point-slope form, and standard form determine the
x and
y intercepts given information about a line See .
13.
COORDINATE GEOMETRYCURVED GRAPHS
Review the standard form for the equation of a circle. Be able to find the
x and
y intercepts from a given equation or to determine the equation given the center and radius of a circle. Know the standard form for the equation of a parabola and be able to identify the vertex. Be able to determine whether the vertex is a maximum or a minimum value. Study the properties of an ellipse and know the standard form for an equation of an ellipse. Be able to find the equation from provided foci of an ellipse and the length of the major axis.
Be able to recognize a hyperbola on a graph and know the standard form for an equation of a hyperbola. Know how to identify the two asymptotes that intersect at the center of the hyperbola. See .
14. POLAR COORDINATES
Be familiar with the polar coordinate system and the relationships you can use to convert between polar coordinates and rectangular coordinates. See .
15. Know the sine, cosine, and tangent trigonometric ratios for an angle. Be able to determine the length of a side of a triangle from a given angle. Know the reciprocal functions of secant, cosecant, and cotangent. Recognize the cofunction identities and be able to use them to solve for unknown values. Know how to use inverse functions, including the arcsine, arccosine, and arctangent. Familiarize yourself with special right triangles.
Also know the trigonometric identities, be able to convert to radian measure, and be prepared to use the laws of sines and cosines. Review the double angle formulas for sine, cosine, and tangent. See .
16. INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONS
Review function notation and know how to determine the domain and range for a given function. Be able to differentiate between linear functions and quadratic functions as well as even and odd functions.
Know how to use the vertical line test to determine if a graph represents a function or a relation. Familiarize yourself with graphs of common functions, such as an identity function, constant function, absolute value function, squaring function, and cubing function. See .



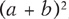 ,
, 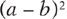 , and
, and 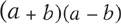 . Be able to recognize perfect square trinomials and the difference of perfect squares. See .
. Be able to recognize perfect square trinomials and the difference of perfect squares. See .