Bouvet - Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures
Here you can read online Bouvet - Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2017, publisher: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated, genre: Children. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures
- Author:
- Publisher:John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated
- Genre:
- Year:2017
- Rating:5 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Bouvet: author's other books
Who wrote Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.
Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
- 7 Plasticity
- 8 Physics of Aeronautical Structure Materials
- Introduction
- 1 Stress
- 2 Strain
- 3 Behavior Law
- 5 Work-energy Theorem: Principle of Finite Element Method
- 6 Sizing Criteria of an Aeronautical Structure
- 7 Plasticity
- 8 Physics of Aeronautical Structure Materials
- 9 Exercises
- 10 Solutions to Exercises
- Appendix: Analysis Formulas

Christophe Bouvet

First published 2017 in Great Britain and the United States by ISTE Ltd and John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Apart from any fair dealing for the purposes of research or private study, or criticism or review, as permitted under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, this publication may only be reproduced, stored or transmitted, in any form or by any means, with the prior permission in writing of the publishers, or in the case of reprographic reproduction in accordance with the terms and licenses issued by the CLA. Enquiries concerning reproduction outside these terms should be sent to the publishers at the undermentioned address:
ISTE Ltd
27-37 St Georges Road
London SW19 4EU
UK
www.iste.co.uk
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
111 River Street
Hoboken, NJ 07030
USA
www.wiley.com
ISTE Ltd 2017
The rights of Christophe Bouvet to be identified as the author of this work have been asserted by him in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.
Library of Congress Control Number: 2016962010
British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data
A CIP record for this book is available from the British Library
ISBN 978-1-78630-115-4
This book follows a long-standing tradition of mechanical engineering tuition, which is already a century old and comes from the Toulouse mechanical engineering scientific community, now merged into the Institut Clment Ader (www.institutclement-ader.org). Just as all of its illustrious predecessors, this book is very timely and illustrates the specificity and originality of the approaches that we have developed, which have both a high scientific standing and a quasi-permanent connection with the aeronautical industry. This publication provides the reader with the necessary knowledge and techniques to calculate structures and decompartmentalize disciplines and fields. The aeronautical engineer will find all of the helpful information he or she needs within these pages: the basis of continuum mechanics, the finite element method, and knowledge of materials, metals and composites, both within linear and non-linear fields. The information is presented in an extremely clear and educational manner. The reader may draw on an impressive series of exercises with detailed corrections, something which is not so commonly found.
Bruno CASTANI
INSA Toulouse
Institut Clment Adler
This volume, on the mechanics of solids and materials, as well as aeronautical structures, aims to give an overview of the necessary notions for structure sizing within the aeronautics field. It begins by establishing all of the classic notions of mechanics: stress, strain, behavior law and sizing criteria. Also covered are notions that are specific to aeronautics, with a particular emphasis on the notion of limit loads and ultimate loads.
Different problem-solving methods, particularly the finite element method, are then introduced. The methods are not classically presented and instead energy minimization is drawn on in order to minimize the number of equations, all while remaining within a framework that we may comprehend with their hands.
The book then addresses the subject of plasticity, showcasing its influence on structure sizing, and especially the advantages it has for sizing criteria.
Finally, the physics of the two main materials in aeronautics, namely aluminum and composite materials, is discussed, so as to shed light on the sizing criteria outlined in the previous chapters.
The corrected exercises help the student to test their understanding of the different topics.
What is so original about this book is that from the outset, it places itself within the field of aeronautics. Sizing criteria are indeed rather specific to this field. Nevertheless, the notions discussed remain valid for the majority of industrial fields: in Mechanical Engineering and Finite Elements these notions in fact remain the same.
Another original aspect of this work is that it consolidates basic continuum mechanics with a very succinct description of finite elements, and a description of the material aspect of the main materials used in aeronautical structures, that being aluminum and composites. This publication is therefore a summary of the basic knowledge deemed necessary for the (Airbus) engineer working within research departments. The book is simultaneously aimed at both students who are beginning their training and also engineers already working in the field who desire a summary of the basic theories.
Lastly, the publication aims to limit the amount of formulas provided as much as possible, in order to highlight the significance of the physical. Any readers who may be interested in demonstrations are advised to refer to more specific and theoretical works, such as [COI 01, DUV 98, GER 73, HEA 77, KHA 95, LEM 96, MIR 03, SAL 01, UGU 03] and [THU 97], etc.
Christophe BOUVET
January 2017
Let us consider a solid S that is subjected to imposed displacements and external forces.
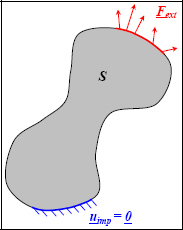
Figure I.1. Outlining the problem. For a color version of this figure, see www.iste.co.uk/bouvet/aeronautical.zip
The aim of the mechanics of deformable solids is to study the internal state of the material (notion of stress) and the way in which it becomes deformed (notion of strain) [FRA 12, SAL 01, LEM 96].
In mechanics, a mechanical piece or system may be designed:
- to prevent it from breaking;
- to prevent it from becoming permanently deformed;
- to prevent it from becoming too deformed, or;
- for any another purposes.
A solid shall be deemed a continuous medium, meaning that it shall be regarded as a continuous set of material points with a mass, representing the state of matter that is surrounded by an infinitesimal volume.
Mechanics of deformable solids enables the study of cohesive forces (notion of stress) at a point M, like the forces exerted on the small volume surrounding it, called a Representative Elementary Volume (REV). For metals, the REV is typically within the range of a tenth of a millimeter.
The matter in this REV must be seen as continuous and homogeneous:
- if it is too small, the matter cannot be as seen homogeneous: atomic piling, inclusion within matter, grains, etc. (for example: for concrete, the REV is within the range of 10 cm);
- if it is too big, the state of the cohesive forces in its center will no longer represent the REV state.
Stress
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures»
Look at similar books to Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and Structures and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.