
Series Editors
Pierre-Nol Favennec and Frdrique de Fornel
Elastic Waves in Solids 2
Radiation, Scattering, Generation
Tony Valier-Brasier
Daniel Royer

First published 2022 in Great Britain and the United States by ISTE Ltd and John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Apart from any fair dealing for the purposes of research or private study, or criticism or review, as permitted under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, this publication may only be reproduced, stored or transmitted, in any form or by any means, with the prior permission in writing of the publishers, or in the case of reprographic reproduction in accordance with the terms and licenses issued by the CLA. Enquiries concerning reproduction outside these terms should be sent to the publishers at the undermentioned address:
ISTE Ltd
27-37 St Georges Road
London SW19 4EU
UK
www.iste.co.uk
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
111 River Street
Hoboken, NJ 07030
USA
www.wiley.com
ISTE Ltd 2022
The rights of Tony Valier-Brasier and Daniel Royer to be identified as the authors of this work have been asserted by them in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s), contributor(s) or editor(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of ISTE Group.
Library of Congress Control Number: 2022931520
British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data
A CIP record for this book is available from the British Library
ISBN 978-1-78630-815-3
Preface
In Volume 1 (Royer and Valier-Brasier 2022), the propagation of elastic waves was studied in isotropic, anisotropic, piezoelectric or viscoelastic solids. The phenomena of reflection and transmission of bulk waves at one or more interfaces were analyzed in detail. A wide variety of elastic waves propagating on a free surface or at the interface between a solid and a fluid, or between two solids, were presented. Finally, the properties of various types of waves guided in most usual structures (plate, ribbon, cylinder) were established. In addition to these general developments, the objective of this second volume is to analyze the radiation, scattering and generation of elastic waves.
Plane waves are not physically realizable because, in practice, sources are of finite dimensions. Acoustic waves generated by a real device diverge, so that their amplitude decreases with the distance from the transmitter. The understanding of radiation from sources is therefore necessary to predict the acoustic field emitted by the transducers used in imaging and measurement systems. In , we start by studying the acoustic radiation in a fluid emitted by a vibrating surface having the shape of a disc or a spherical cup, respectively, modeling a planar or a focused transducer. Then, we study the radiation emitted by a multi-element antenna such as those used in ultrasound imaging systems. In the second section, we analyze the radiation of elastic waves, in an isotropic or anisotropic solid, by sources located on its surface. The generation of bulk and Rayleigh waves by a linear distribution of normal or tangential impulsive forces, modeling a seismic or a thermoelastic source, is examined. The last section is devoted to the radiation of an elementary spherical source embedded in an isotropic matrix.
Phenomena related to the scattering of elastic waves by various targets are developed in . The scattering theory accounts for different phenomena observed in Volume 1 (refraction, transmission, absorption) in a global way. The scattered waves propagate away from the target, possibly in preferred directions, even if the medium is isotropic. As in other areas of physics, scattering phenomena are characterized by a cross-section, which can be calculated in the case of cylindrical or spherical scatterers. In the first section, the target is a cylinder immersed in a perfect fluid; the incident wave is therefore longitudinal. The two examples studied explain some phenomena, such as the shadow behind a rigid cylinder in the geometric regime, or the existence of circumferential waves propagating around an elastic cylinder in the resonant regime. The second section is devoted to the scattering of elastic waves by a cylinder buried in a solid matrix, and the third section is devoted to the scattering by a sphere. In the case of a sphere, strong monopolar and dipolar resonances are highlighted. The multiple scattering by a set of particles is discussed at the end of this chapter, with the determination of the effective wave number of coherent waves propagating in heterogeneous media. For small concentration of particles, this effective wave number is close to that of the host medium and contains information on the scattering by a single particle.
In , we investigate the generation and detection of bulk and surface elastic waves. The most efficient and widespread technique for generating and detecting free bulk waves in a solid or a liquid, and also elastic guided waves in a plate or a cylinder, is to exploit the inverse and direct piezoelectric effects. The operating principle and the structure of transducers are described according to the frequency range. Their performances and their domain of application are specified. The properties of active materials commonly used (polarized piezoceramic or piezocomposite, piezoelectric polymer or single crystal) are given. In the second section, we analyze the generation and detection of surface acoustic waves, directly on a piezoelectric substrate, by transducers composed of two comb-shaped electrodes. Several models are developed to explain how these interdigital transducers operate. Their impulse and frequency responses, and their efficiency, are evaluated. The last two sections are devoted to optical methods, first the excitation of elastic waves by photothermal effects and second the detection of mechanical displacements by laser interferometry. The spatiotemporal characteristics of transmitted bulk and Rayleigh waves are given. These laser-based ultrasonic techniques present some advantages: they do not require any mechanical contact with the propagation medium; they can reach very high frequency domains and very small wavelengths. Therefore, they can be used for material evaluation at a large distance or with a high spatial resolution.
The authors would like to thank for their assistance in the preparation of this book:
- Claire Prada, Director of Research at the CNRS, at the Institute Langevin Ondes et Images;
- Jean-Marc Conoir, Director of Research at the CNRS, at the Institute Jean le Rond dAlembert.
Tony VALIER-BRASIER
Daniel ROYER
February 2022
List of Main Symbols
- a,b: amplitude of the waves.
- cijkl (CI J): stiffnesses (Voigt notation).
- D: directivity factor.
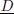 : electric induction (displacement) vector.
: electric induction (displacement) vector.- E: Young modulus.
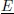 : electric field vector.
: electric field vector.- ek(ep): kinetic (potential) energy per unit volume.
- eijk (ij): piezoelectric (dielectric) constants.
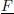 : force density per unit mass.
: force density per unit mass.
Next page













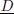 : electric induction (displacement) vector.
: electric induction (displacement) vector.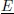 : electric field vector.
: electric field vector.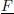 : force density per unit mass.
: force density per unit mass.