
CENTER STAGE
EVERYTHING IN OUR SOLAR SYSTEM ORBITS THE SUN. It is the center of our solar system, and affects everything in it. Sometimes the Sun creates powerful storms and solar winds. How do we know all this? Spacecraft from Earth have visited the Sun. These robotic explorers have taught us a lot about the star at the center of our solar system. Learn about the amazing missions, the dedicated scientists who plan them, and more far-out facts about the Sun. All thefacts you need, and lots more, are included in this up-to-date book.
The Far-Out Guide to the Solar System series provides valuable information about the solar system, its planets, and mankind's quest in exploring them. This series is an excellent resource for young scientists and amateur astronomers.
Bahram Mobasher, PhD, Series Science Consultant
Professor of Physics and Observational Astronomy, University of California, Riverside
About the Author
Award-winning author MARY KAY CARSON has written many nonfiction books for young people and their teachers. In 2009, she received the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Children's Literature Award.
Image Credit: Shutterstock
The Sun makes up 99.8 percent of the total mass of our solar system. More than one million Earths could fit inside the Sun.
When you look at stars in the night sky, you are actually seeing thousands of suns. A sun is the star in the center of a solar system. Like all stars, our solar systems sun is a ball of glowing gas. Our sunwe call it the Suneven has a star name. Its name is Sol. Sol is a yellow star of medium size. It seems big to us because it is so much closer than other stars. But our sun is a pretty ordinary star. There are billions of others like it in the universe. You will learn lots more far-out facts about the Sun in this book. Just keep reading!
The Sun bathes our planet in light. Plants use the Suns energy to make food. Sunlights heating of Earth creates wind. The Suns rays evaporate water into clouds that make rain. Without the Sun, life could not exist on Earth. In fact, without the Sun, there would be no solar system at all. The planets, moons, comets, and asteroids all formed from the leftovers of Sols birth. More than 99 percent of the mass in our entire solar system is the Sun.

Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/S. Stolovy (SSC/Caltech)
This illustration shows a swirling cloud of gas and dust surrounding a newly born star. Planets, moons, asteroids, and other solar system stuff will eventually form when chunks of leftovers clump together.
The Sun seems unchanging to us. It rises each day and sets each night. But all stars are born, live, and eventually die. Our sun has a long life, thankfully. It formed out of a cloud of dust and gas about 5 billion years ago. It will shine like it does now for another 5 billion years or so, and then slowly begin to die.
Yet the Sun changes from year to year as it spins and speeds through space. Sometimes it is calm. But other times it rages and boils with solar flares and storms that can hurl danger toward Earth. What causes these storms? How dangerous are they to us? Scientists have found out a lot about the Sun. But they still have much to learn about the star of our solar system.

Image Credit: NASA, ESA, and K. Noll (STScI)
This Hubble Space Telescope image shows a star much like our own Sun at the end of its life. It has shed its outer layer of gas.
FAR-OUT FACT
Nothing lasts forever, not even the Sun. In about 5 billion years, the Sun will start to grow old. It will swell up and get hotter for a while, swallowing up Mercury and cooking Earth. Toward the end of its life, the Sun will blow off its outer layers. Its center will shrink into a dense ball. From then on Sol will grow cooler and its light fainter and fainter as it runs out of fuel.

Image Credit: Shutterstock
At 2:45 a.m. on March 13, 1989, a powerful storm knocked out power in Quebec, Canada. Six million people lost electricity. Some were stuck in elevators or dark offices. Many woke up in freezing-cold homes without heat. Others had to drive on roads without traffic lights. The subway and airport shut down. Schools and businesses closed. It took nine hours to get the lights back on and cost the power company 10 million dollars.
What kind of storm caused such a big blackout? Not a blizzard, tornado, or any other kind of earthly weather. The blackout was triggered by a storm on the Sunso-called space weather. It can be difficult for people to believe that space weather can affect life on Earth, said scientist Larry Combs. Combs is a space weather forecaster. But in fact it can have a tremendous impact on communication and navigation systems, satellites, electric power grids, and astronauts working and living in space.
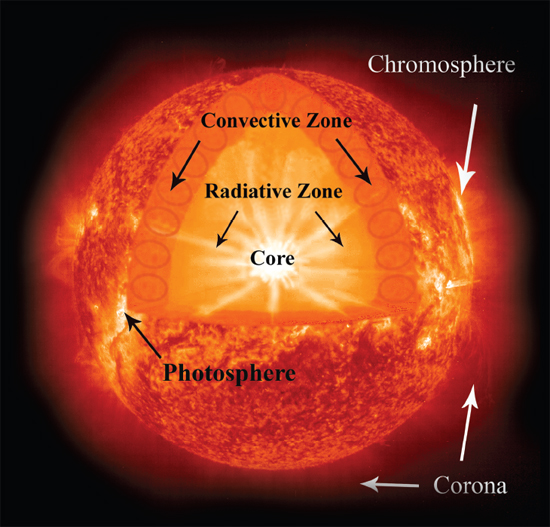
Image Credit: SOHO (ESA & NASA)
The core is where the Sun makes its energy. All the pressure and heat in the core smashes the Suns hydrogen fuel, changing it into helium. This releases energy that slowly travels outward through the radiative zone. In the convective zone, rising and falling hot gases carry heat to the Suns surface, or photosphere. Just above the surface is the chromosphere, where solar flares happen. The corona is the Suns outer atmosphere. It is a halo of hot gas, hotter than the Suns surface.
FAR-OUT FACT
Earth spins on a tilt, which creates our seasons. The part of the Earth that is having summer is tilted toward the Sun. It gets more than twelve hours of sunlight per day. Summer sunlight is also stronger. The summer Sun is higher in the sky, like a lamp directly overhead. The part of Earth that is having winter is tilted away from the Sun. Wintry parts of Earth have fewer than twelve hours of sunlight a day. Winter sunlight is weaker because the Sun is lower in the sky. It comes in at an angle, which spreads out the light.
A storm is a violent burst of activity. Tornadoes are bursts of wind. Blizzards are bursts of snow. Solar storms are bursts of activity on the Sun. How the Suns activity affects Earth is called space weather. Solar storms can shoot clouds of invisible particles toward Earth. These can mess up electric and telephone lines, block out radio signals, and damage orbiting satellites. Stormy space weather can interfere with and damage some of the modern technology we depend on.
Solar storms are just part of living with an ever-changing star. The Sun is not a simple ball of gas hanging in space. It has an atmosphere, a surface, middle layers, and a center core. Within the Sun, hot dense gases somersault. This constant churning makes electric currents that create a magnetic field. The Sun is a huge, powerful spinning magnet!
The Sun also has eleven-year seasons, called solar cycles or sunspot cycles. A sunspot is a dark patch on the Suns surface. Sunspots are areas where the Suns magnetic field is concentrated. When there are more sunspots, there is more unstable magnetic energy. More unstable magnetic energy creates more solar storms. The solar maximum is the part of the solar cycle when the most sunspots appear. And it is also when the most solar storms happen. Sunspot groups often cause severe solar storms, so scientists track them carefully.
Next page






















