IDEAS ABOUT THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Science is about finding out how things work. That includes not just the world around us, but the universe, which is everything that exists. We now know the universe is so vast its hard to imagine. But long ago, people thought our tiny corner of the universe was the whole of space.
Scientific Ideas
For hundreds of years, scientists have tried to explain things by coming up with ideas about the way things work. These scientific ideas are known as hypotheses. When scientists believe they have collected enough .
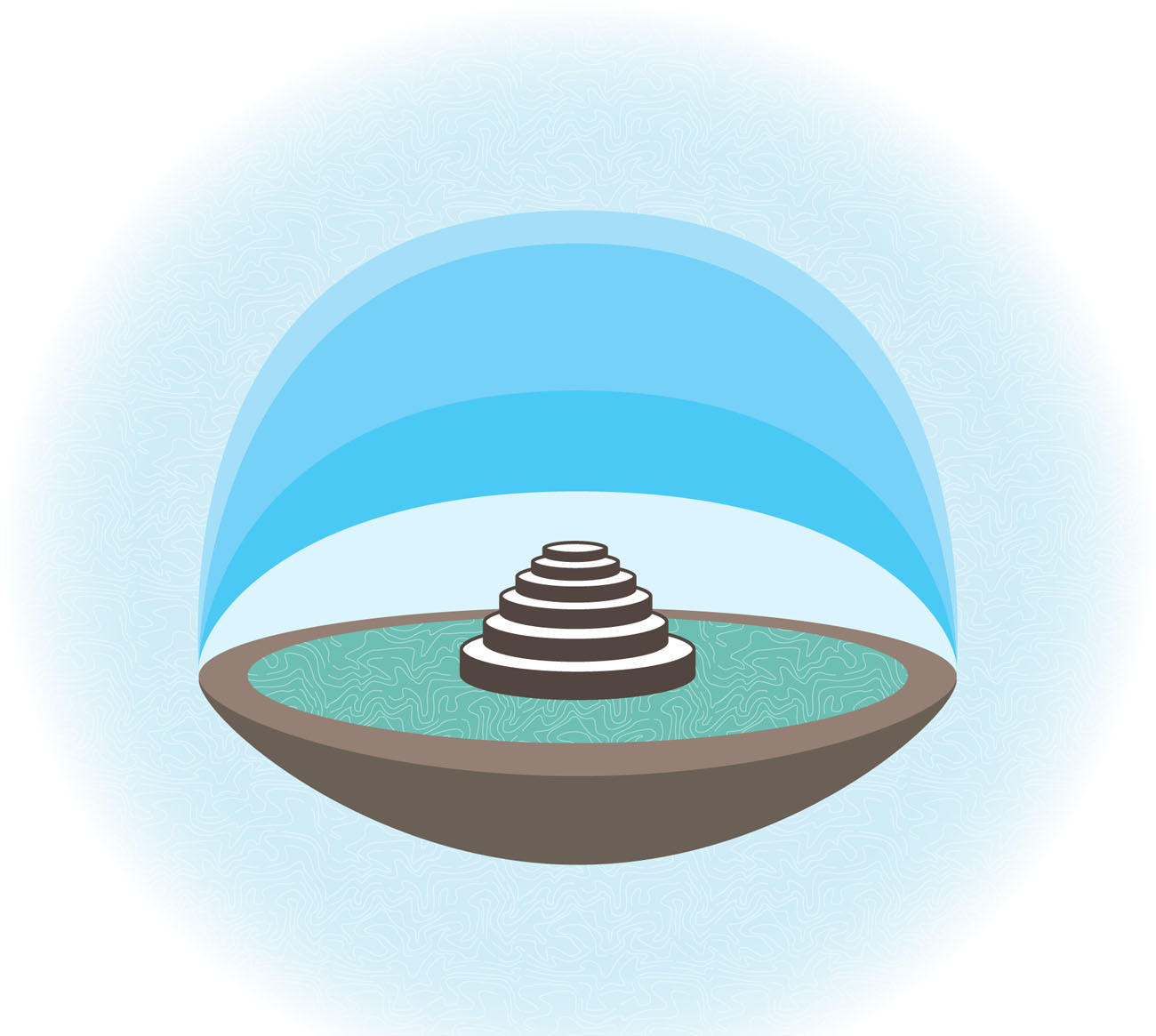
What is the Solar System?
Our .
Sun at the Center
We now know the sun is the center of our solar system. But for hundreds of years, people thought Earth was at the center. After all, from the planets surface, Earth seems to be still, and the sun, Moon, and stars move across the sky. Then a few scientists dared to disagree. This book looks at these scientists and their theories.
The sun is the center of our solar system.
Sun and Planets
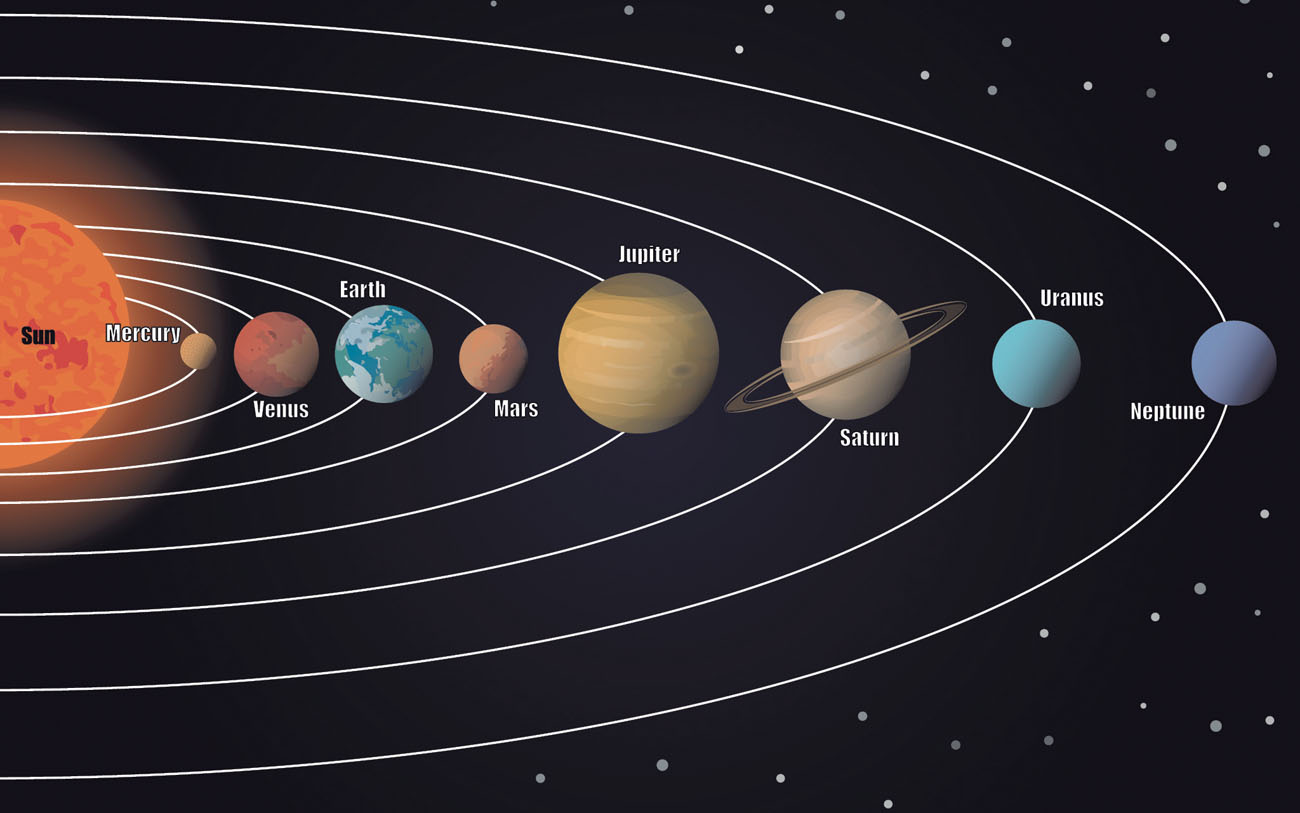
Our solar system includes eight planets. Those nearest to the sun are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These relatively small planets are all made of rock and metal. There are four giant outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These are mostly made of gas and liquid.
Our solar system contains eight planets.
EARTH-CENTERED UNIVERSE
is the study of the stars and other objects in the sky. From the earliest times, people were in wonder of the night sky.
The First Astronomers
Four thousand years ago, the . In ancient times, travelers used constellations to find their way.
The Babylonians thought that the sky arched over a flat Earth.
Planets
Babylonian astronomers noticed five stars that acted strangely. They wandered across the sky instead of moving in fixed patterns. We now know these are planets. They dont truly shine like stars, but reflect sunlight. The five planets known in ancient times were Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn.
Greek Thinkers
About 2,500 years ago, the ancient Greeks began to think about the world more scientifically. A thinker called Pythagoras suggested that the world was not flat, but ball-shaped. He had noticed that ships heading out to sea disappeared over the horizon. But the Greeks still believed Earth was the center of the universe. The philosopher Aristotle (384322 bc ) wrote that Earth was fixed, and the sun, Moon, and stars circled around it.
Aristotles Pupil
Aristotle was the tutor of a young Greek prince named Alexander. The boy grew up to become a great warrior. Alexander the Great conquered a vast empire, stretching from Greece to India and south into Egypt. In the conquered lands, he founded cities, which were all named Alexandria after him.
A Lone Voice
Aristotles Earth-centered view of the universe was accepted by nearly everyone. But one man thought differently. He was called Aristarchus (about 310230 bc ) and he came from the small Greek island of Samos.
Sun at the Center
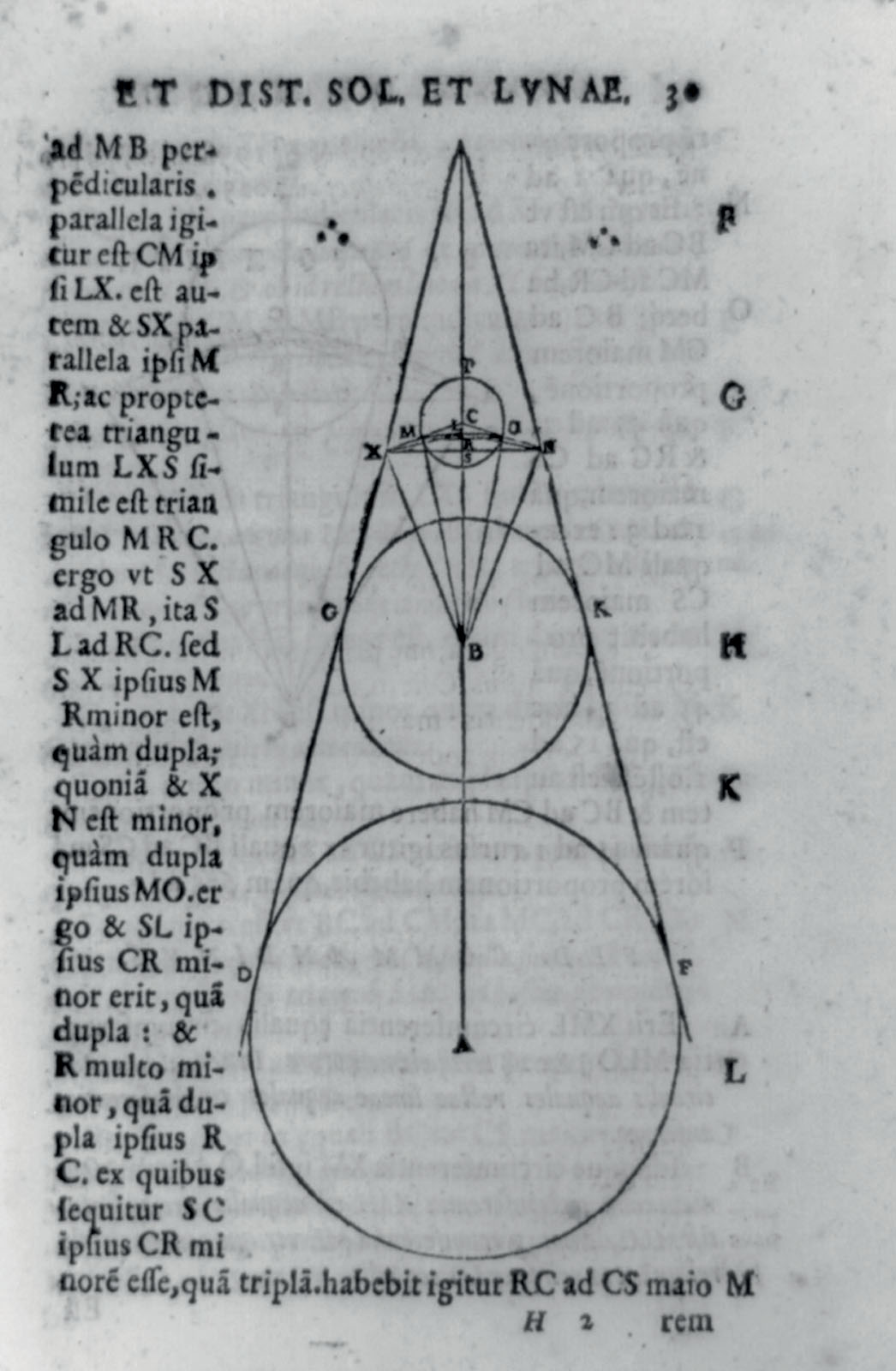
Aristarchus thought that the sun, not Earth, was the center of the universe, and that Earth moved around the sun, not the other way around. He also thought that the stars were very far away. This meant that the universe was much bigger than people had thought.
Aristarchus tried to define the sizes of the Moon (top), Earth and sun (bottom).
Alexandria
Aristarchus moved from Samos to Alexandria in Egypt, which was part of the Greek world. Alexandria had become a great center for learning, and had the worlds finest library. In Alexandria, Aristarchus talked with other , but almost no one accepted his idea.
Ptolemy of Alexandria
In the 2nd century bc , the Romans took over the Greek world. They also took over Greek learning. In Alexandria, a scholar named Ptolemy ( ad 85165) collected all the Greek ideas about astronomy and put them into one big book called the Great Treatise . Ptolemys book repeated Aristotles view of an Earth-centered universe. Aristarchuss idea was forgotten.
Ptolemys Book
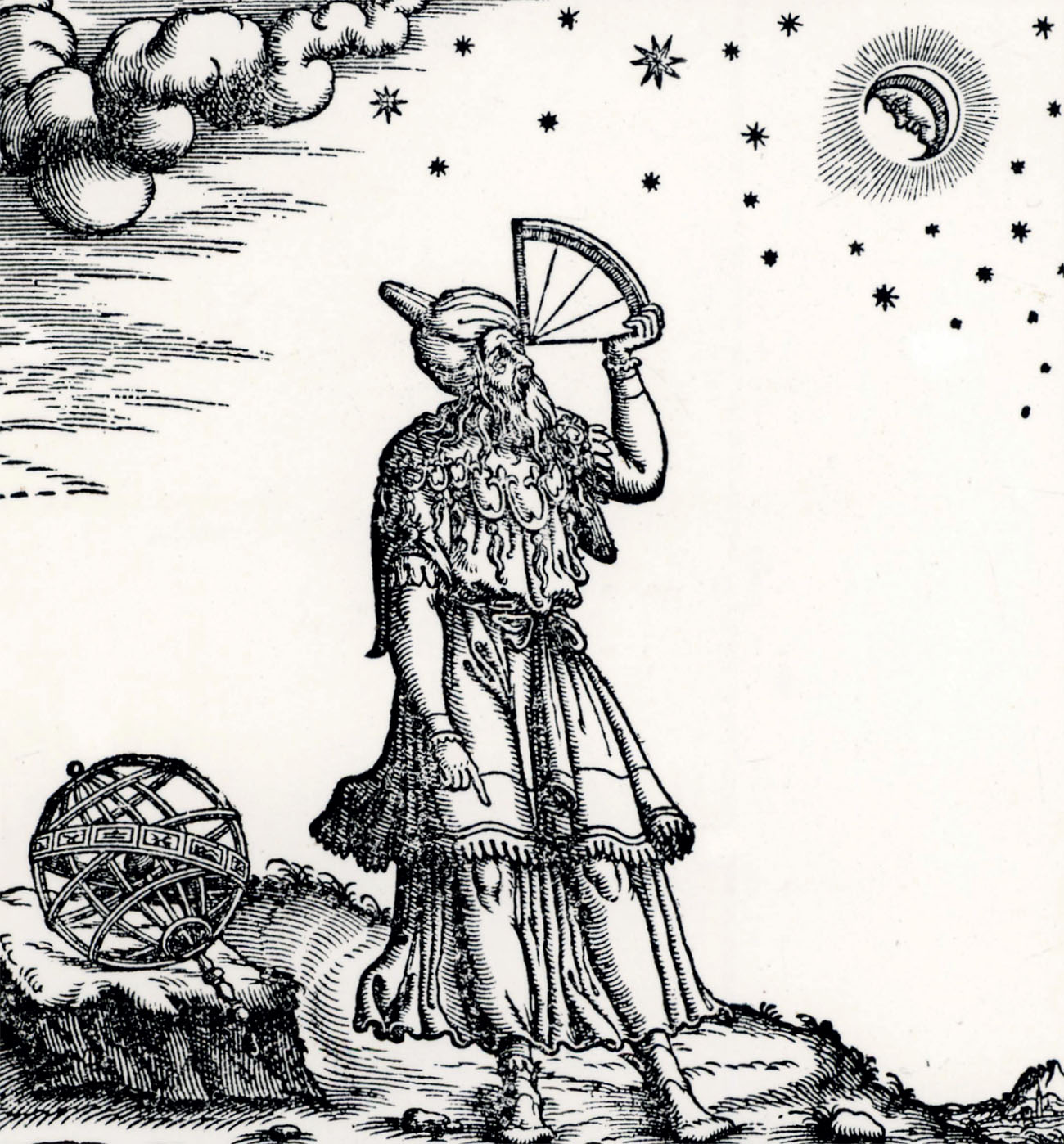
In the 4th century ad , the Roman Empire was attacked by northern tribes. The great library of Alexandria burned to the ground during a battle. Luckily, Ptolemys book had been copied, or it would have been lost forever. One copy was translated into Arabic. Arab scholars called it the Almagest, which simply means the Greatest.
This illustration shows Ptolemy observing the stars. He is using an instrument called a quadrant.
A REVOLUTIONARY IDEA
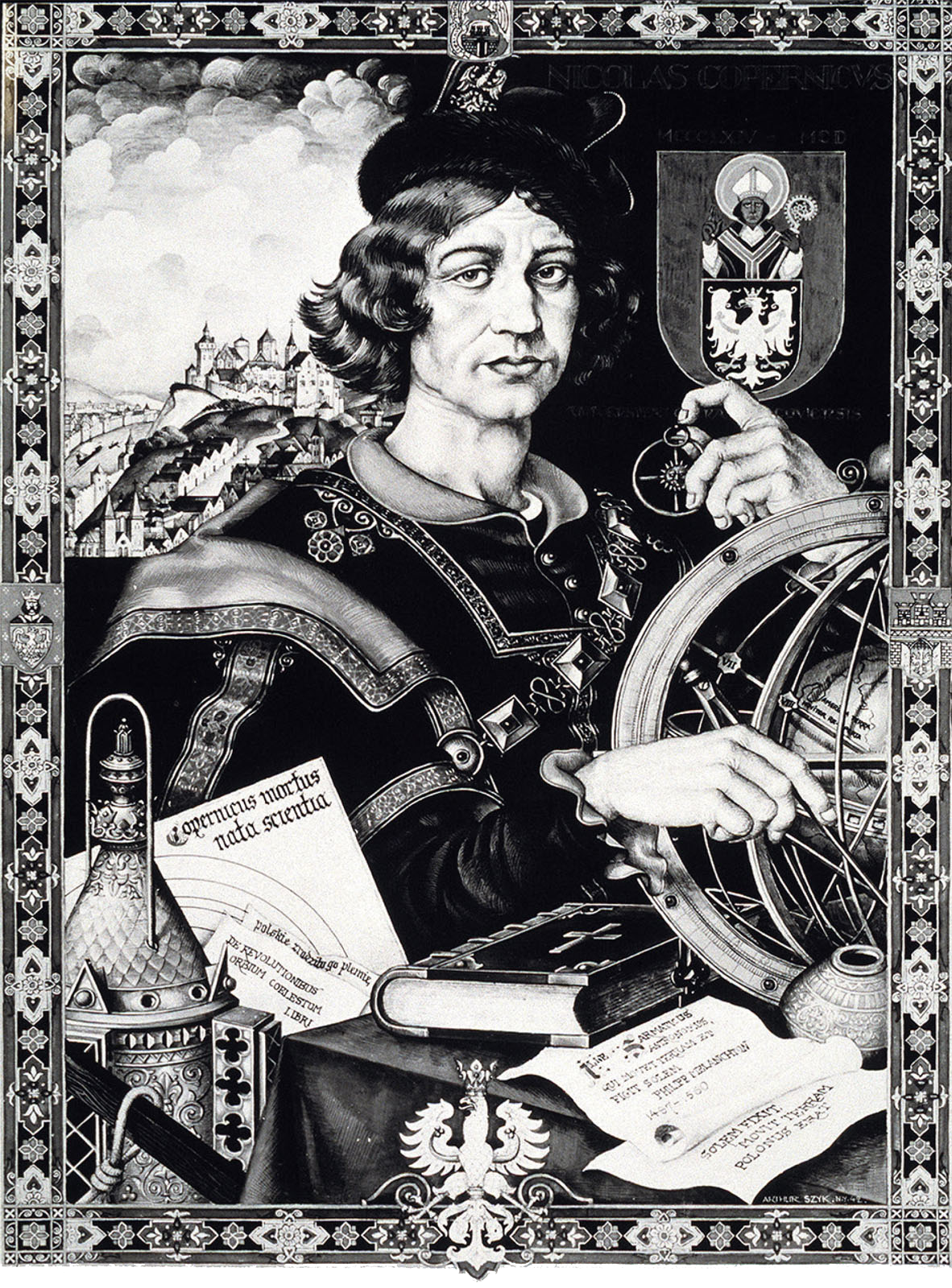
In the 1100s, Ptolemys book was translated into European languages. It soon became the main textbook for astronomy. Scholars everywhere accepted Aristotles view that Earth was the center of the universe. Everyone, that is, until a Polish astronomer called Nicolaus Copernicus (14731543) challenged the idea.
NICOLAUS COPERNICUS
Copernicus was very well-educated. He spent 12 years at the university in Poland and then Italy, studying law, medicine, mathematics, and astronomy. In Italy, he lodged with the professor of astronomy Domenico Navara. Every night, the two studied the stars, and Copernicus became a great astronomer.
A Passion for Astronomy
Copernicus lived in a town in northern Poland, where he worked as a .
Observing the Heavens
At this time, there were no Earth.
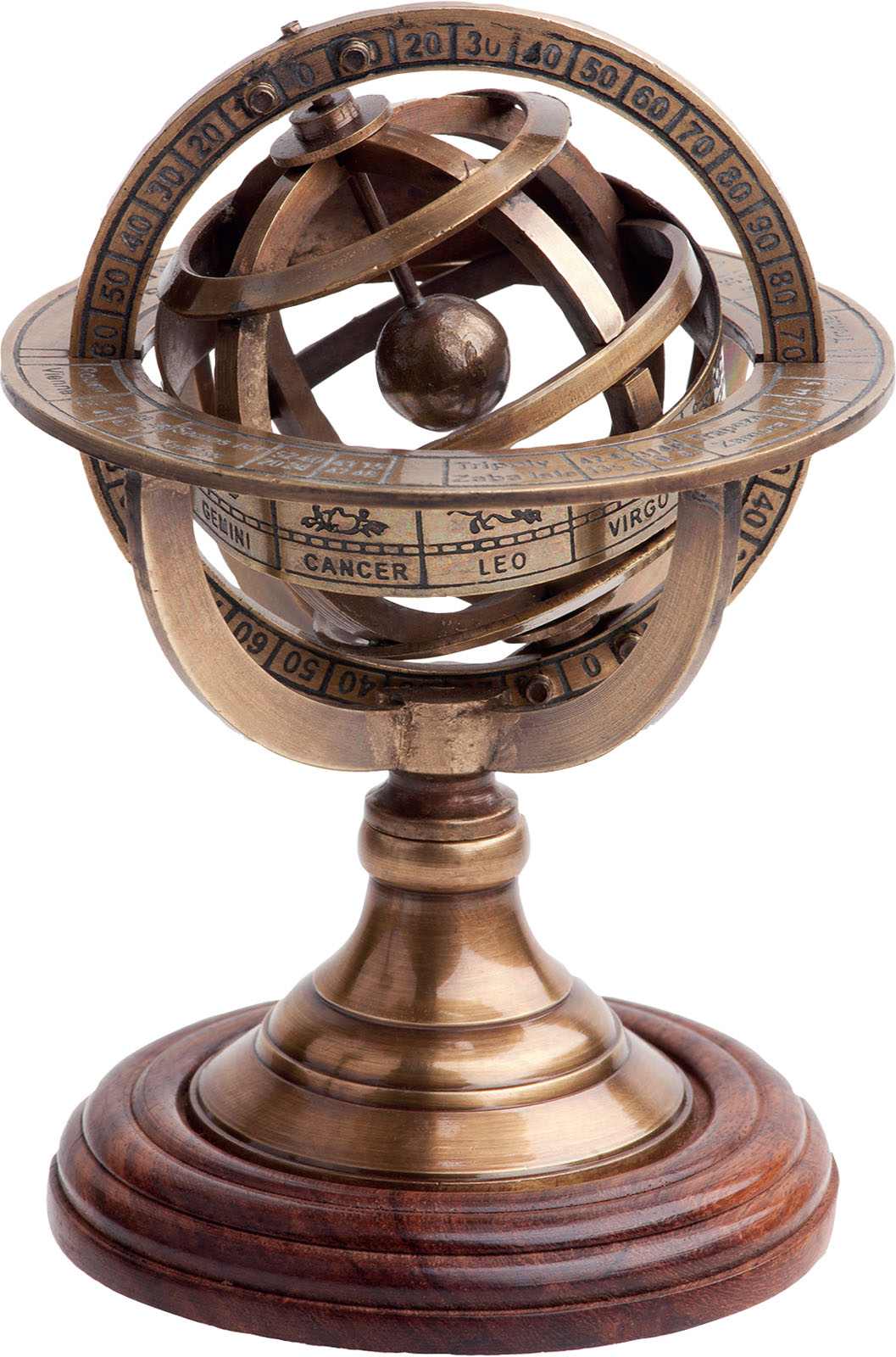
This is an armillary sphere. Astronomers adjusted the rings to measure the positions of the planets and stars relative to the Earth.
Crystal Spheres
For many years, Copernicus observed the night sky from his little tower. As he did, he became more and more frustrated with the traditional view of the universe. According to sun and planets. The outer sphere with the stars marked the edge of the universe. But what Copernicus saw just didnt fit the model or the accepted view of space.