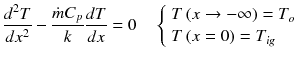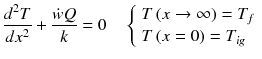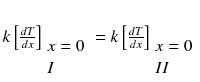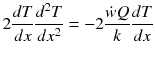Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2017
Nikolai M. Rubtsov Key Factors of Combustion Springer Aerospace Technology 10.1007/978-3-319-45997-4_1
1. Nonlinear Phenomena and Kinetic Mechanism of a Gaseous Branching Chain Process by the Example of Thermal Decomposition of Nitrogen Trichloride
Nikolai M. Rubtsov 1
(1)
Institute of Structural Macrokinetics and Material Science, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
Abstract
The inhibition and promotion of non-thermal NCl3 flame by NOCl and H2, respectively, are explained. The crossover from the non-thermal mode of flame propagation to the thermal one is analyzed for NCl3He mixtures. Calculations based on a kinetic mechanism taking into account energy chain branching are performed, and qualitative agreement between the calculated and observed data is demonstrated. Nonlinear chain branching shortens the time needed for thermal ignition and increases the flammability of the combustible mixture. It is shown that the mechanism of reaction of NCl3 decomposition proposed above is in good qualitative agreement with experimental data. It is established that the conditions sufficient to obtain oscillating solutions are the following: (a) accounting for adsorptiondesorption of NCl3 on reactor walls, (b) accounting for nonlinear chain termination Cl + Cl23ou Cl + Cl21g , (c) accounting for energy chain branching. Therefore, accounting for processes of desorption of NCl3 from the reactor surface during oscillations and the change in a surface state leads to the occurrence of the oscillation modes in a numerical experiment, which are in qualitative agreement with experimental data.
The promotion of the branched-chain decomposition of nitrogen trichloride by molecular hydrogen additives manifests itself in a decrease in the induction period and the acceleration of initial reactant consumption. The emission spectrum of the H2 + NCl3 flame contains the intense bands of NCl (b1+ X3, v = 10, v = 01, and v = 00), and the bands of a hydrogen-free compound. The latter bands can be assigned to electronically excited NCl2 radicals formed in the H + NCl3 reaction. The promotion effect in the system studied should be due to the side reaction of linear branching. The occurrence of the H + NCl3 reaction via two pathways (NHCl + 2Cl and NCl2 + HCl) ensures the qualitative agreement between the experimental data and calculation.
Keywords
Inhibition Promotion Non-thermal flame propagation Nitrogen trichloride Energy chain branching Chemical oscillations Vibronically excited intermediates
Nitrogen trichloride NCl3 (yellow very explosive liquid with 150 Torr vapor pressure under normal conditions) does not require any oxidizer to ignite. Because it is decomposition of individual substance, its detailed mechanism seems to be comparably simple. At the same time, the mechanism shows the very specific peculiarity of chain combustion namely a nonlinear energy branching. The features of thermal decomposition of NCl3 are considered in the following chapter.
1.1 Theories of Flame Propagation in Gases (a Brief Review)
The paragraph is given for better understanding of the material specified below. It is shown that the system of kinetic-diffusion equations includes the propagating wave solution if the nonlinearity in the source term occurs. It is in general Arrhenius nonlinearity for thermal flame propagation or kinetic nonlinearity for non-thermal flame propagation.
- (a)
The theory of thermal flame propagation
One of the remarkable features of exothermic reactions is the existence of the fronts of chemical transformations, which are able to propagate in space with a constant velocity on a limited space interval []. Chemical reactions leading to heat generation and temperature rise are accompanied in the combustion wave by heat and mass transfer. These coupled processes determine the internal structure and velocity of the combustion wave.
A great significance for the development of the combustion wave theory has been the work of Zeldovich and Frank-Kamenetskii [], in which for the first time the structure and velocity of the combustion wave were obtained. Their simple analytical expression for the velocity of flame propagation is known as the Zeldovich and Frank-Kamenetskii (ZFK) formula.
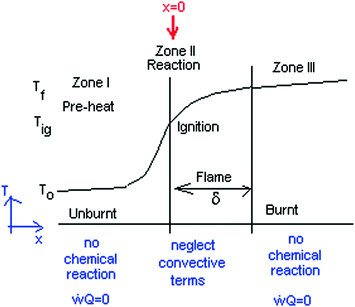
The first important result found in [ illustrates the thermal flame propagation.
Fig. 1.1
The schematic model of thermal flame propagation
Diffusion of molecules (but not free radicals) as well as heat is included.
[A]
molar concentration of reactant
D[d[A]/]/dx
diffusive molar flux

mass flow rate per unit area (mass flux)

[A]/
convected mass
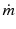
CpT
convected heat
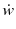
species production or reaction rate
The molar flux (mol/cm2 s) convected into the control volume through a flow cross section of unity:
The molar flux (mol/cm2 s) diffused into the control volume through a flow cross section of unity:
The molar flux (mol/cm2 s) reacting in the control volume:
Conservation of mass: diffusion + convection + sink = 0
Conservation of energy:
- I.
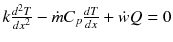
pre-heat zone
- II.
reaction zone
Continuity of heat conduction:
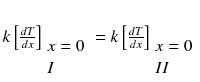
Multiple both sides of the reaction zone II energy equation by 2 dT/dx :













 [A]/
[A]/ 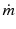 CpT
CpT 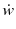
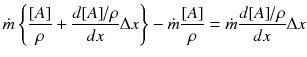
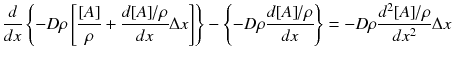


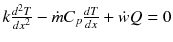 pre-heat zone
pre-heat zone