SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering SpringerBriefs in Control, Automation and Robotics
Series Editors
Tamer Baar
Coordinated Science Laboratory, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, USA
Miroslav Krstic
La Jolla, CA, USA
SpringerBriefs in Control, Automation and Robotics presents concise summaries of theoretical research and practical applications. Featuring compact, authored volumes of 50 to 125 pages, the series covers a range of research, report and instructional content. Typical topics might include:
a timely report of state-of-the art analytical techniques;
a bridge between new research results published in journal articles and a contextual literature review;
a novel development in control theory or state-of-the-art development in robotics;
an in-depth case study or application example;
a presentation of core concepts that students must understand in order to make independent contributions; or
a summation/expansion of material presented at a recent workshop, symposium or keynote address.
SpringerBriefs in Control, Automation and Robotics allows authors to present their ideas and readers to absorb them with minimal time investment, and are published as part of Springers e-Book collection, with millions of users worldwide. In addition, Briefs are available for individual print and electronic purchase.
Springer Briefs in a nutshell
50125 published pages, including all tables, figures, and references;
softcover binding;
publication within 912 weeks after acceptance of complete manuscript;
copyright is retained by author;
authored titles only no contributed titles; and
versions in print, eBook, and MyCopy.
Indexed by Engineering Index.
Publishing Ethics: Researchers should conduct their research from research proposal to publication in line with best practices and codes of conduct of relevant professional bodies and/or national and international regulatory bodies. For more details on individual ethics matters please see: https://www.springer.com/gp/authors-editors/journal-author/journal-author-helpdesk/publishing-ethics/14214
More information about this subseries at http://www.springer.com/series/10198
Claudia Califano and Claude H. Moog
Nonlinear Time-Delay Systems
A Geometric Approach
1st ed. 2021
Logo of the publisher
Claudia Califano
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Informatica, Automatica e Gestionale Antonio Ruberti, Universit di Roma La Sapienza, Rome, Italy
Claude H. Moog
Laboratoire des Sciences du Numrique de Nantes, CNRS, Nantes, France
ISSN 2191-8112 e-ISSN 2191-8120
SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering
ISSN 2192-6786 e-ISSN 2192-6794
SpringerBriefs in Control, Automation and Robotics
ISBN 978-3-030-72025-4 e-ISBN 978-3-030-72026-1
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72026-1
Mathematics Subject Classication (2010): 93C10 93B05 93B27 93B18 93B50 93B52
The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021
This work is subject to copyright. All rights are solely and exclusively licensed by the Publisher, whether the whole or part of the material is concerned, specifically the rights of translation, reprinting, reuse of illustrations, recitation, broadcasting, reproduction on microfilms or in any other physical way, and transmission or information storage and retrieval, electronic adaptation, computer software, or by similar or dissimilar methodology now known or hereafter developed.
The use of general descriptive names, registered names, trademarks, service marks, etc. in this publication does not imply, even in the absence of a specific statement, that such names are exempt from the relevant protective laws and regulations and therefore free for general use.
The publisher, the authors and the editors are safe to assume that the advice and information in this book are believed to be true and accurate at the date of publication. Neither the publisher nor the authors or the editors give a warranty, expressed or implied, with respect to the material contained herein or for any errors or omissions that may have been made. The publisher remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This Springer imprint is published by the registered company Springer Nature Switzerland AG
The registered company address is: Gewerbestrasse 11, 6330 Cham, Switzerland
Preface
This book is devoted to nonlinear time-delay control systems. Although they include the class of linear time-delay systems, the specific mathematical tools valid (only) for this subclass of systems will not be developed or used herein.
Thus, in this introductory chapter, a sketch is given of what can be found elsewhere (Richard 2003) and which will not be considered herein.
Linear Time-Delay Systems
For the subclass of linear time-delay systems in continuous time, the use of the Laplace transform yields quasi-polynomials in the Laplace variable 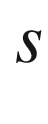 and in
and in 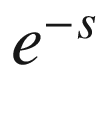 Gu et al. (2003), Michiels et al. (2007), Niculescu (2001). Among those systems, one may distinguish betweem the so-called retarded systems (Fridman 2014) described by differential equations where the highest differentiation order of the output, or the state, is not delayed, and the so-called neutral systems (Fridman 2001) whose equations involve delayed values of the highest differentiation order of the output, or the state.
Gu et al. (2003), Michiels et al. (2007), Niculescu (2001). Among those systems, one may distinguish betweem the so-called retarded systems (Fridman 2014) described by differential equations where the highest differentiation order of the output, or the state, is not delayed, and the so-called neutral systems (Fridman 2001) whose equations involve delayed values of the highest differentiation order of the output, or the state.
Thus, the Laplace transform still enables an inputoutput analysis of linear time-delay systems (Olgac and Sipahi 2002, Sipahi et al. 2011). This approach can hardly be extended to more general nonlinear time-delay systems which are the main focus of this book. Finite dimension approximations may be appealing, but have a limited interest due to stability issues (Insperger 2015).
Discrete-time linear systems with unknown delays are under interest in Shi et al. (1999). Discrete-time linear systems with varying delays are under interest with an ad hoc predictor design in Mazenc (2008).
Stability analysis and stabilization of linear time-delay systems require general tools derived from the Lyapunov theory as in Fridman (2001), Kharitonov and Zhabko (2003).
Stability of linear systems with switching delays is tackled in Mazenc (2021) using trajectory-based methods and the so-called sup-delay inequalities.
Stability and Stabilization of Nonlinear Time-Delay Systems
Some of the most significant historic results obtained for the general class of nonlinear time-delay systems are about the analysis of their stability, thanks to a generalization of the Lyapunov theory, the so-called Krasovskii-type approach (Gu et al. 2003). This approach can hardly be circumvented even in the case of linear time-delay systems (Fridman 2001).













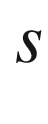 and in
and in 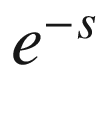 Gu et al. (2003), Michiels et al. (2007), Niculescu (2001). Among those systems, one may distinguish betweem the so-called retarded systems (Fridman 2014) described by differential equations where the highest differentiation order of the output, or the state, is not delayed, and the so-called neutral systems (Fridman 2001) whose equations involve delayed values of the highest differentiation order of the output, or the state.
Gu et al. (2003), Michiels et al. (2007), Niculescu (2001). Among those systems, one may distinguish betweem the so-called retarded systems (Fridman 2014) described by differential equations where the highest differentiation order of the output, or the state, is not delayed, and the so-called neutral systems (Fridman 2001) whose equations involve delayed values of the highest differentiation order of the output, or the state.