If this is your first time to install Linux, I suggest that you install it into a virtual machine (VM) so that you dont have to dedicate an entire piece of hardware for a learning system and so that you dont potentially render your system inoperable by attempting to install Linux in parallel to your current system creating a multi-boot computer. (Setting up multi-booting is a more advanced concept and out of the scope of this book.)
A good place to start with virtualization, if you dont already have it installed, is to download and install the latest version of VirtualBox (https://www.virtualbox.org/). VirtualBox is an application that allows your current computer to act as a virtual machine host system where you may install virtual guests, such as Linux into what amounts to a separate functioning computer system. Virtualbox runs on many different host operating systems (OSs) and supports a variety of guest operating systems including Linux. The host OS and guest OS can be different from one another. Your computer (host OS) can be a Windows, Mac, or Linux-based system but have guest Linux systems installed on it as VirtualBox VMs.
Downloading and Installing Linux
Next, youll need to select a Linux distribution (distro) to install so that you can practice issuing commands, changing configurations, rebooting, installing software, creating users, and so on. I suggest that you should select a Linux distro based on the one that your current employer uses. If your company doesnt use Linux yet or youre not employed in a system administrator role, then select from one of the popular distributions described below:
Debian
Debian is a top-level distribution from which many other distributions are derived. Debian is community-supported, open source, and free.
OpenSUSE
OpenSUSE is a community-supported, top-level distribution that has many faithful followers worldwide. Its commercial version SUSE Linux Enterprise has widespread adoption.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Red Hat is a commercially-supported Linux that enjoys worldwide enterprise adoption and is now owned by IBM.
Ubuntu
Ubuntu is a very popular, Debian-derived community and commercially-supported distribution. Ubuntu also offers ready-made VirtualBox (and other) virtual machines to help you get a quick start.
The downloaded ISO file is a bootable Linux image. You dont have to do anything to it if you use it to create a virtual machine. A virtual machine will boot from the ISO image and begin the installation process. After youve configured your virtual machine in VirtualBox, select Settings from the Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager, as shown in .
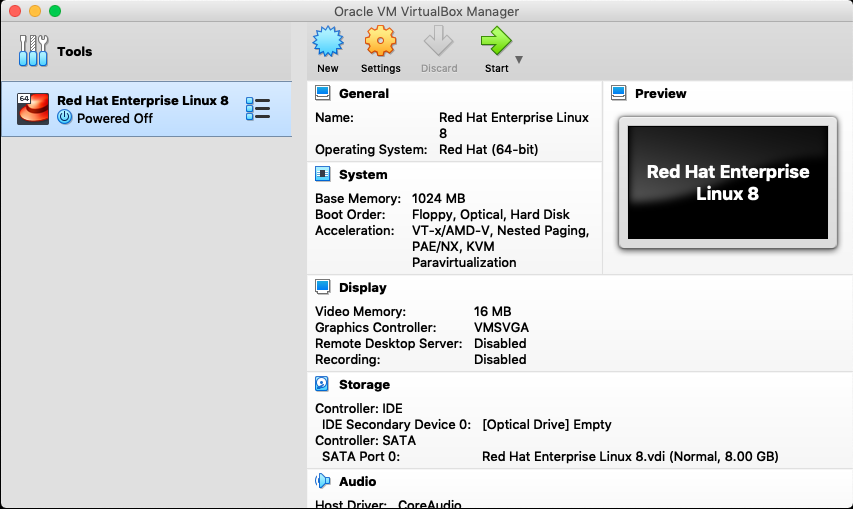
Figure 1-1. The Oracle VirtualBox Manager application and a configured virtual machine.
Then, select Storage, as shown in .
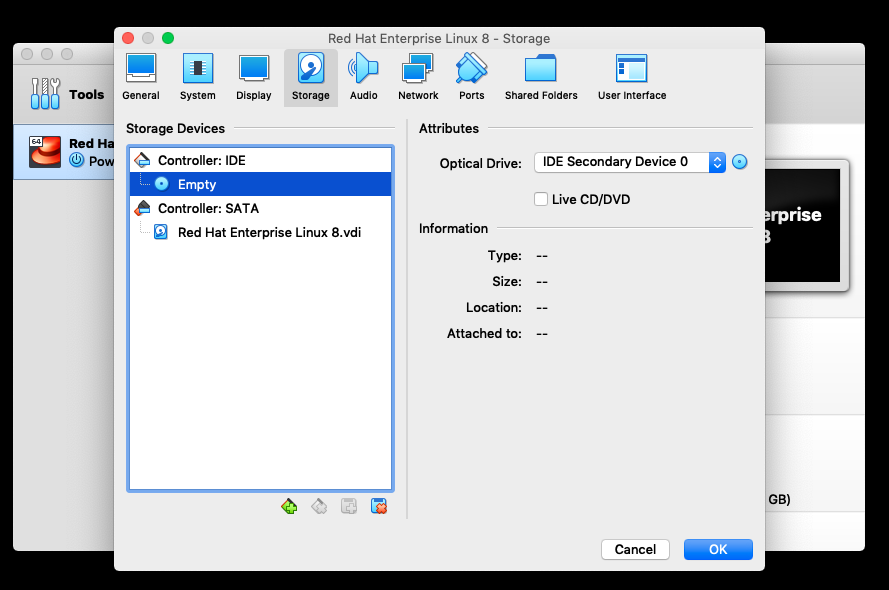
Figure 1-2. Virtual machine settings with Storage settings selected.
Select the empty optical disk drive under the IDE Controller in the Storage Devices pane and then select the optical disk icon in the Attributes pane to browse for your ISO image file. See .















