Object Oriented Programming System is referred to as OOPS in programming.
To create a programme using classes and objects is a paradigm for or methodology for programming. Every entity is treated as an object by OOPS. Python's object-oriented programming is focused on objects. Any OOPS-based programming that is developed solves our problem but takes the shape of objects. For a particular class, we are free to produce as many objects as we choose. What then are things? Anything with characteristics and certain behaviours is an object.
The terms "variables of the object" and "functions of the object" are frequently used to describe an object's properties and behaviours, respectively. Objects might be conceptual or actual objects. Let's say that a pen exists in the real world. A pen's characteristics are its colour and type (gel pen or ball pen). Additionally, the pen's behaviour may include the ability to write, draw, etc. A logical object might be any file on your computer.
Files can retain data, be downloaded, shared, and have other behaviours. They have properties like file name, file location, and file size.
4 Difference between procedural and object-oriented programming
Python adheres to four different programming paradigms, did you know that? Imperative, functional, procedural, and object-oriented programming are some of them. Procedural Oriented Programming (POP) and Object-Oriented Programming are two of the most significant programming paradigms in Python (OOP).
Let's start.
- What Are They, First?
Let's examine the methodology each paradigm employs: Suppose you want to prepare Maggie for dinner! Then you follow a series of stages, including Warm up some water in a pan. Include Maggie in it add masala Prepare and serve. Similar to this, POP needs to follow a specific set of steps in order to function. POP is made up of functions. There are different parts of a POP programme called functions, each of which is responsible for a different job.
The functions are set up in a particular order, and the programme control happens one step at a time. OOP: Object-oriented programming. The programme is divided into items. These objects are the entities that blend the traits and workings of things found in the real world. 2. Which Locations Do They Prefer? POP is only appropriate for little jobs.
Because the code becomes more difficult as the program's duration increases and becomes bloated with functions, Debugging gets even more challenging. OOP works well for bigger issues. Recursion can be used to make the code reusable, which makes it simpler and cleaner. 3. Which Offers Greater Security? POP offers the functions along with all the data, which makes it less secure. Thus, our data are not secret.
If you wish to protect your login passwords or any other secret information, POP is not a recommended solution! OOP offers security by data hiding, making it more secure. Encapsulation is a unique idea in OOP that grants it the ability to hide data (we will read about this further). 4. Programming approach POP adheres to programming from the top down. The top-down method of programming focuses on dissecting a complex issue into manageable units of code. The minor portions of the problems are then resolved.
OOPS principles adhere to the Bottom-up method of programming. The Bottom-Up method prioritises resolving the smaller issues at their most fundamental level before incorporating them into a comprehensive and entire solution. 5. Utilization of Access Modifiers: When applying the ideas of inheritance, access specifiers or access modifiers are used in Python to restrict the access of class variables and class methods outside of the class. The keywords Public, Private, and Protected can be used to do this. No access modifiers like "public," "private," or "protected" are used in POP.
To employ the aforementioned modifiers, POP lacks the concepts of classes and inheritance. Modifiers for access are supported by OOP. They understand inheritance, so they can use terms like "public," "private," or "protected." Note: The access modifiers in Python come in quite handy when working with inheritance ideas. Class methods can make use of this idea as well.
5 Python's Class and Objects
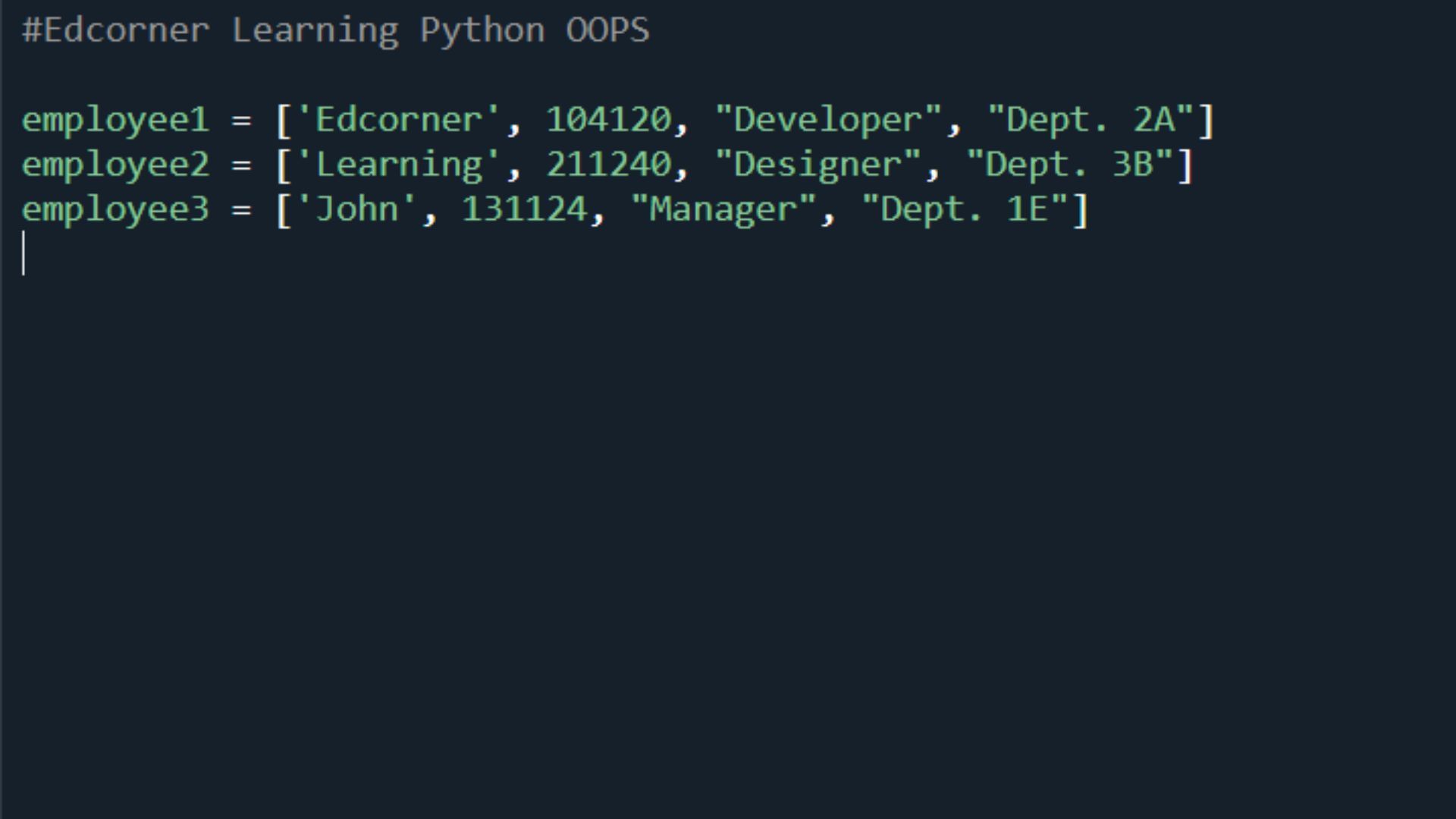
Let's say you want to keep track of how many books you own. You can easily do that by utilising a variable.
Also possible is to compute the sum of five numbers and save the result in a variable. Simple values are intended to be stored in a variable using primitive data structures like numbers, characters, and lists. Consider your name, the square root of a number, or the quantity of marbles (say). But what if you need to keep a record of every employee in your business? For instance, if you try to put all of your employees in a list, you can later become confused about which index of the list corresponds to which individual details (e.g. which is the name field, or the empID or age etc.)