Bibliografische Information der Deutschen Nationalbibliothek
Die Deutsche Nationalbibliothek verzeichnet diese Publikation in der Deutschen Nationalbibliografie; detaillierte bibliografische Daten sind im Internet ber www.dnb.de abrufbar.
2017 Dipl.- Ing. Roland Prsch, Dipl.- Inf. Aikaterini Daskalaki-Prsch
Email:
Production and publishing: BoD - Books on Demand GmbH, Norderstedt, Germany
Cover design: Anne Prsch
Cover fotos: Mike Hhn, Roland Prsch
Printed in Germany
Webpage: www.frequencymanager.de
ISBN 9783744805858
Acknowledgement:
Thanks for those persons who have supported us in the preparation of this book.
Aikaterini Daskalaki-Prsch
Disclaimer:
The information in this book have been collected over years. The main problem is that there are not many open sources to get information about this sensitive field. Although we tried to verify these information from different sources it may be that there are mistakes. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you discover any wrong description.
Content
1. List of Pictures
2. List of Tables
3. General
The Technical Handbook for Radio Monitoring HF is meanwhile well known and used by many radio listeners (official or private) worldwide.
Due to the high amount of systems we decided to separate the description of signals in the VHF/UHF range from those heard on HF. We also moved the part of satellite signals to a new book called Technical Hadbook for Satellite Monitoring.
This book has been written to help the listener in identifying the different modes or waveforms which are active throughout the VHF/UHF band.
It will never be complete.
But it will give a good overview which techniques are state of the art today. It has to be mentioned that most of the pictures are a result of the decoder HOKA CODE 300-32 and PROCITEC PROCEED and go2DECODE. For the wide band spectra we have used an AOR5000 with NetSDR or PERSEUS on the IF-frequency of 10.7 MHz.
This book is divided in four main parts:
- Basic information about modulations
- Waveforms used on VHF/UHF
- Tables for Radio Monitoring
- Abbreviations and Index
The part basic information is giving an overview about common modulation techniques with a short description and how they look like in the spectrum or phase plane display. This part also describes standard expressions from the field of coding, error correction and so on which are often used in the field of radio communication.
The following section describes most of the waveforms which can be heard on VHF and UHF.
The book is finished with some helpful tables taken from the HF edition, the abbreviation table and index.
4. Description of Waveforms
Analogue Waveforms
Analogue waveforms are mainly seperated in to different forms: the amplitude modulation in which the carrier frequency is fixed and the amplitude of the signal is modulated related to the information being sent.
The other modulation form is the frequency modulation in which the frequency is changed related to the information being sent. The carrier envelope remains on the same level.
Amplitude Modulation (AM)
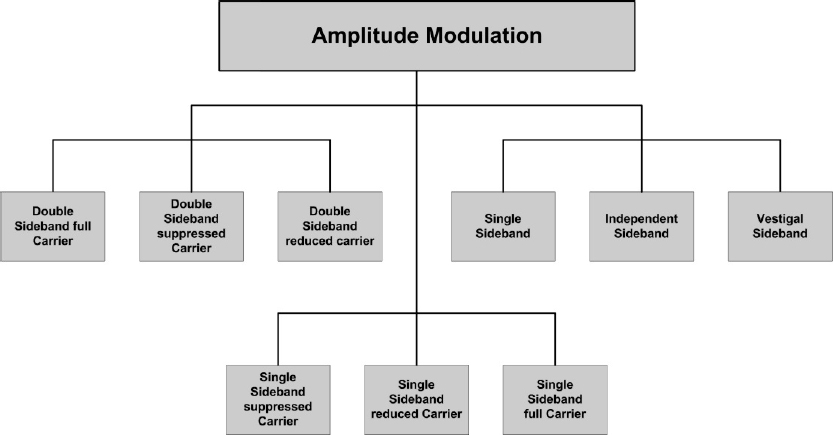
Picture 1: Different AM waveforms
The Ampitude modulation is mainly used for broadcast transmissions or in aeronautic mobile service on VHF. In a AM the strength of the carrier is varried in relation to the information which shall be send. In a pure AM both sidebands are modulated.
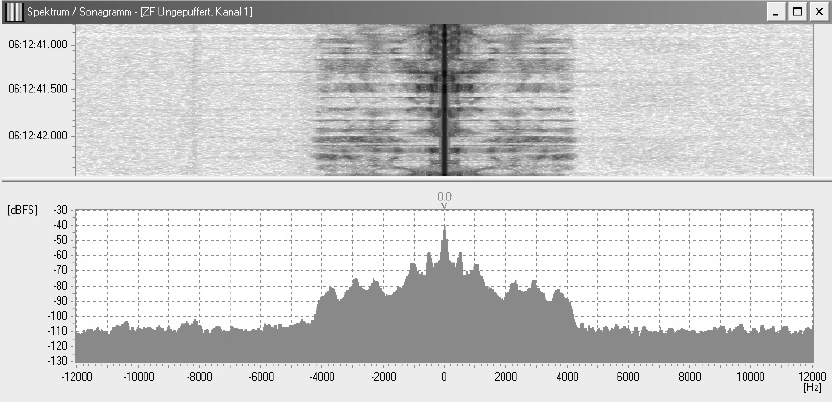
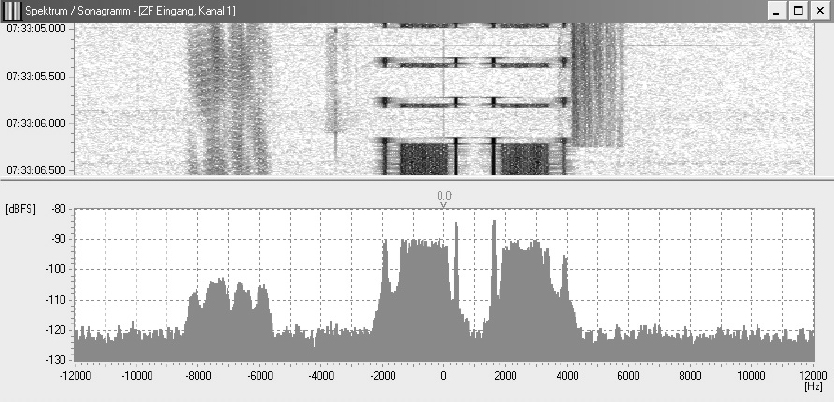
The following pictures shows the spectrum and sonagram of a typical amplitude modulation with bioth sidebands and the carrier:
Picture 2: Spectrum and sonagram of an amplitude modulation
The ITU designation is A3E.
Double Sideband reduced Carrier (DSB-RC)
In a double sideband reduced carrier (DSB-RC) transmission the carrier is reduced to a fixed level.
Double Sideband suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC)
In a double sideband suppressed carrier (DSB-SC) transmission only the sidebands are transmitted. The carrier is reduced to a lowest level as possible. Both sidebands contain the same information.
The following picture shows a LINK-11 signal in both sidebands with suppressed carrier:
Picture 3: Spectrum of a double sideband suppressed carrier signal
Single Sideband full Carrier
In this modulation form the carrier with full level and one side band is transmitted. This form is often used in the Russian aeronautical mobile sevice for the ground transmitter.
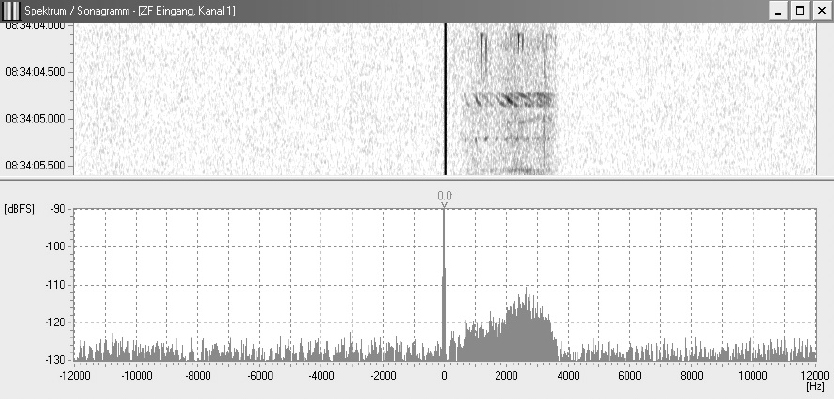
The following pictures shows the spectrum and sonagram of a single sideband modulation with full carrier:
Picture 4: Spectrum and sonagram of a single sidband modulation with full carrier
The ITU designation is H3E.
Single Sideband reduced Carrier (SSB-RC)
In a single sideband reduced carrier (SSB-RC) transmission the carrier is reduced to a fixed level.
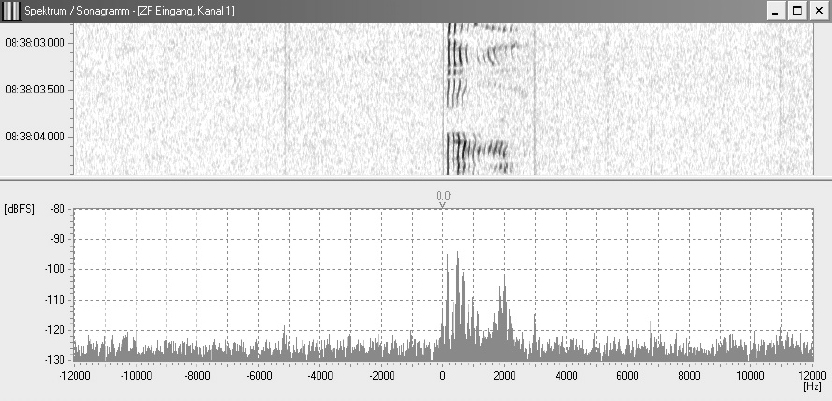
The following pictures shows the spectrum and sonagram of a single sideband modulation with reduced carrier:
Picture 5: Spectrum and sonagram of a single sidband modulation with reduced carrier
The ITU designation is R3E.
Single Sideband suppressed Carrier (SSB-SC)
In a single sideband suppressed carrier (SSB-SC) transmission the carrier is supressed. This form of modulation is used by ATSC which is a set of standards developed by the Advanced Television Systems Committee for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable, and satellite networks. It is the same waveform as the single sideband (SSB) below.
The ITU designation is J3E.
Single Sideband Modulation (SSB)
In a single sideband modulation as a form of the AM modulation the second sideband and the carrier are not transmitted. This type of modulation is much more efficient because all power can be used for transmitting the information in one sideband.
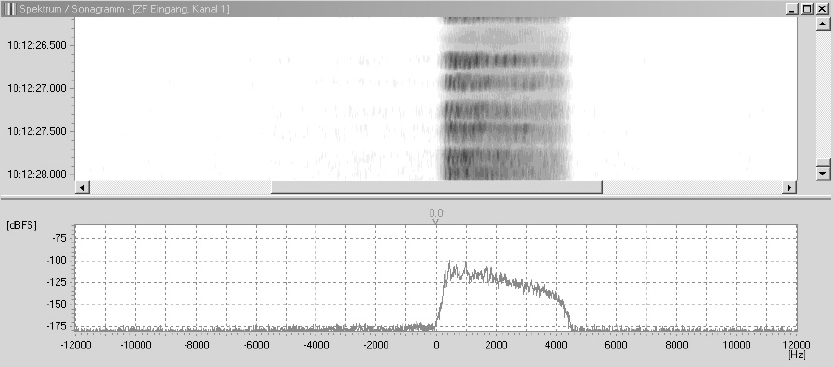
The following pictures shows the single sideband modulation:
Picture 6: Spectrum of a single sideband modulation