Hooked:
How to Build Habit-Forming Products
By Nir Eyal
with Ryan Hoover
Copyright 2014 Nir Eyal
All rights reserved.
ISBN: 1494277530
ISBN-13: 978-1494277536
Library of Congress Control Number: 2014900549
v 1.2
For Julie
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Note: Some sections of this book have appeared in articles previously published by the author.
INTRODUCTION
79 percent of smartphone owners check their device within 15 minutes of waking up every morning.
A 2011 university study suggested people check their phones 34 times per day.
Face it, were hooked.
The technologies we use have turned into compulsions, if not full-fledged addictions. Its the impulse to check a message notification. Its the pull to visit YouTube, Facebook, or Twitter for just a few minutes, only to find yourself still tapping and scrolling an hour later. Its the urge you likely feel throughout your day but hardly notice.
Cognitive psychologists define habits as, automatic behaviors triggered by situational cues: things we do with little or no conscious thought. Our actions have been engineered.
How do companies, producing little more than bits of code displayed on a screen, seemingly control users minds? What makes some products so habit-forming?
For many products, forming habits is an imperative for survival. As infinite distractions compete for our attention, companies are learning to master novel tactics to stay relevant in users minds. Today, amassing millions of users is no longer good enough. Companies increasingly find that their economic value is a function of the strength of the habits they create. In order to win the loyalty of their users and create a product thats regularly used, companies must learn not only what compels users to click, but also what makes them tick.
Although some companies are just waking up to this new reality, others are already cashing in. By mastering habit-forming product design, the companies profiled in this book make their goods indispensable.
First-To-Mind Wins
Companies who form strong user habits enjoy several benefits to their bottom line. These companies attach their product to internal triggers. As a result, users show up without any external prompting.
Instead of relying on expensive marketing, habit-forming companies link their services to the users daily routines and emotions. A habit is at work when users feel a tad bored and instantly open Twitter. They feel a pang of loneliness and before rational thought occurs, they are scrolling through their Facebook feeds. A question comes to mind and before searching their brains, they query Google. The first-to-mind solution wins. In chapter one, this book explores the competitive advantages of habit-forming products.
How do products create habits? The answer: They manufacture them. While fans of the television show Mad Men are familiar with how the ad industry once created consumer desire during Madison Avenues golden era, those days are long gone. A multi-screen world of ad-wary consumers has rendered Don Drapers big budget brainwashing useless to all but the biggest brands.
Today, small startup teams can profoundly change behavior by guiding users through a series of experiences I call hooks. The more often users run through these hooks, the more likely they are to form habits.
How I Got Hooked
In 2008, I was among a team of Stanford MBAs starting a company backed by some of the brightest investors in Silicon Valley. Our mission was to build a platform for placing advertising into the booming world of online social games.
Notable companies were making billions of dollars selling virtual cows on digital farms while advertisers were spending huge sums of money to influence people to buy whatever they were peddling. I admit I didnt get it at first and found myself standing at the waters edge wondering, "How do they do it?"
At the intersection of these two industries dependent on mind manipulation, I embarked upon a journey to learn how products change our actions and, at times, create compulsions. How did these companies engineer user behavior? What were the moral implications of building potentially addictive products? Most importantly, could the same forces that made these experiences so compelling also be used to build products to improve peoples lives?
Where could I find the blueprints for forming habits? To my disappointment, I found no guide. Businesses skilled in behavior design guarded their secrets and although I uncovered books, white papers, and blog posts tangentially related to the topic, there was no how-to manual for building habit-forming products.
I began documenting my observations of hundreds of companies to uncover patterns in user experience designs and functionality. Although every business had its unique flavor, I sought to identify the commonalities behind the winners and understand what was missing among the losers.
I looked for insights from academia: drawing upon consumer psychology, human-computer interaction, and behavioral economics research. In 2011, I began sharing what I learned and started working as a consultant to a host of Silicon Valley companies, from small startups to Fortune 500 enterprises. Each client provided an opportunity to test my theories, draw new insights, and refine my thinking. I began blogging about what I learned at NirAndFar.com and my essays were syndicated to other sites. Soon, readers began writing in with their own observations and examples.
In the fall of 2012, Dr. Baba Shiv and I designed and taught a class at the Stanford Graduate School of Business on the science of influencing human behavior. The next year, I partnered with Dr. Steph Habif to teach a similar course at the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design.
These years of distilled research and real-world experience resulted in the creation of the Hook Model: a four-phase process companies use to forms habits. Through consecutive hook cycles, successful products reach their ultimate goal of unprompted user engagement, bringing users back repeatedly, without depending on costly advertising or aggressive messaging.
While I draw many examples from technology companies given my industry background, hooks are everywhere in apps, sports, movies, games, and even our jobs. Hooks can be found in virtually any experience that burrows into our minds (and often our wallets). The four steps of the Hook Model provide the framework for the chapters of this book.
The Hook Model
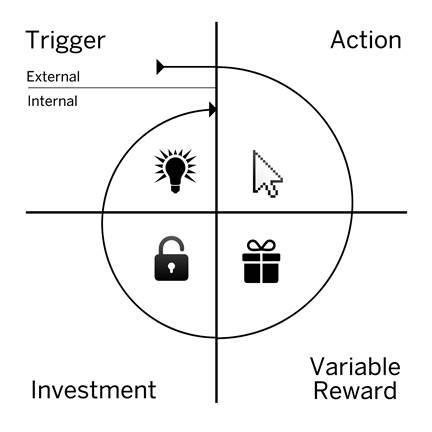
1. Trigger
A trigger is the actuator of behavior the spark plug in the engine. Triggers come in two types: external and internal. Habit-forming products start by alerting users with external triggers like an email, a website link, or the app icon on a phone.
For example, suppose Barbra, a young woman in Pennsylvania, happens to see a photo in her Facebook newsfeed taken by a family member from a rural part of the state. Its a lovely picture and since she is planning a trip there with her brother Johnny, the external triggers call-to-action intrigues her and she clicks. By cycling through successive hooks, users begin to form associations with internal triggers, which attach to existing behaviors and emotions.
When users start to automatically cue their next behavior, the new habit becomes part of their everyday routine. Over time, Barbra associates Facebook with her need for social connection. Chapter two explores external and internal triggers, answering the question of how product designers determine which triggers are most effective.
2. Action
Following the trigger comes the action: the behavior done in anticipation of a reward. The simple action of clicking on the interesting picture in her newsfeed takes Barbra to a website called Pinterest, a pinboard-style photo-sharing site.
Next page